
How is the electrophile generated in the nitration of benzene?
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: The nitration of benzene takes place in the presence of nitric acid and sulphuric acid where the sulphuric acid is very strong and helps in producing nitronium ion from nitric acid which acts as a strong electrophile in the process.
Complete answer:
The nitration of benzene is an aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction in which an electrophile is attacked by a benzene ring and hydrogen from the ring gets substituted by a nitro group to produce nitrobenzene.
The mechanism involved is as follows:
Step (1) – Generation of electrophile.
Sulphuric acid is a strong acid and thus it donates a proton to nitric acid which results in the formation of water along with nitronium ion which is a stronger electrophile.
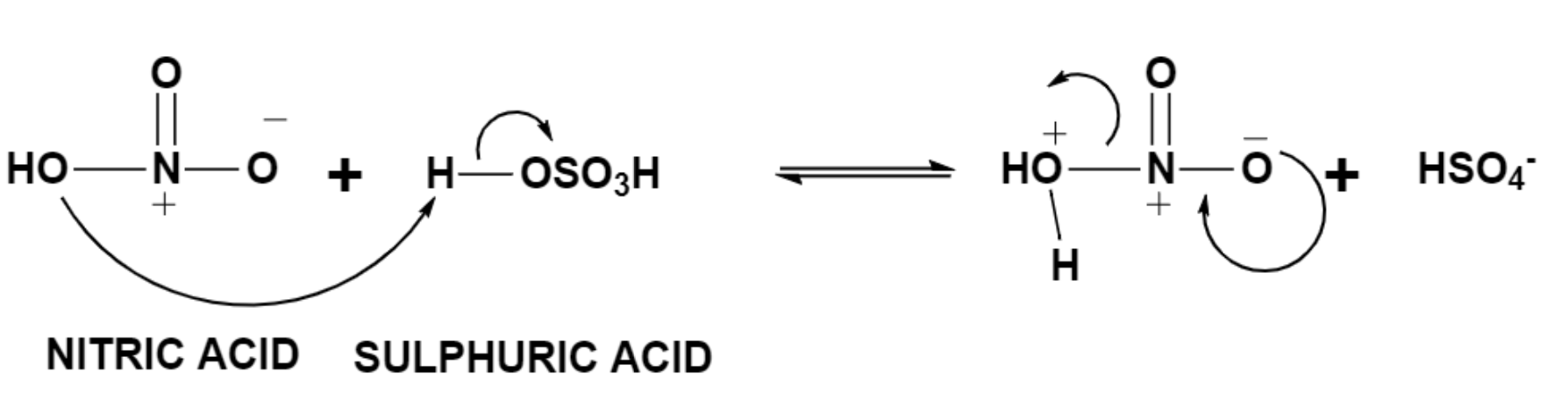
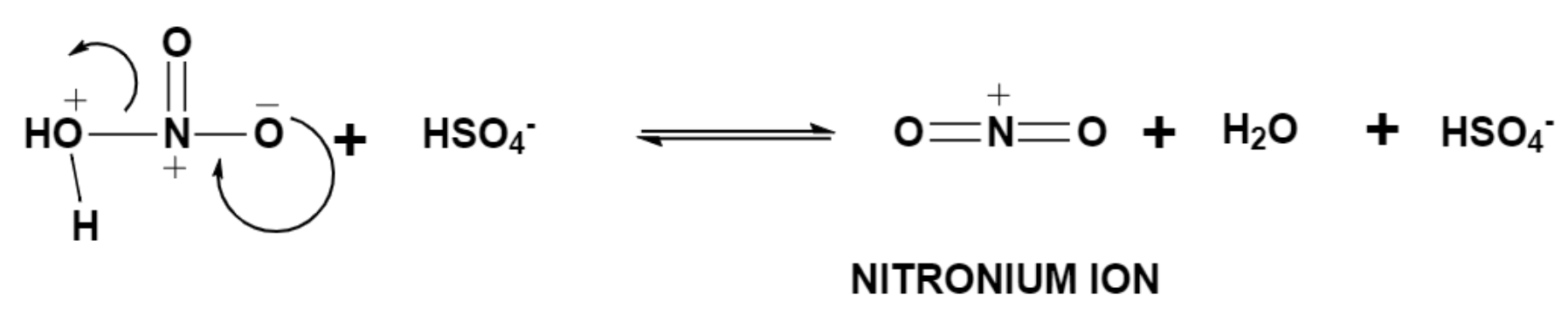
Step (2) – Attack by the benzene group.
The electrophile generated in the above step is then attacked by the benzene group and arenium ion forms which exhibit resonance.
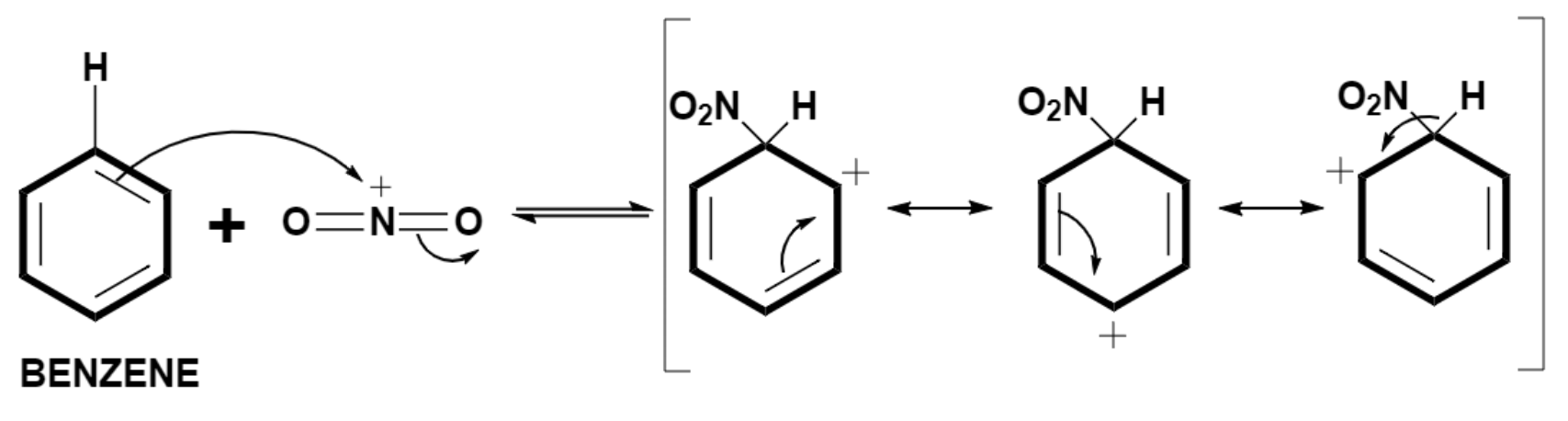
Step (3) – Formation of nitrobenzene.
The arenium ion loses a proton and forms nitrobenzene.
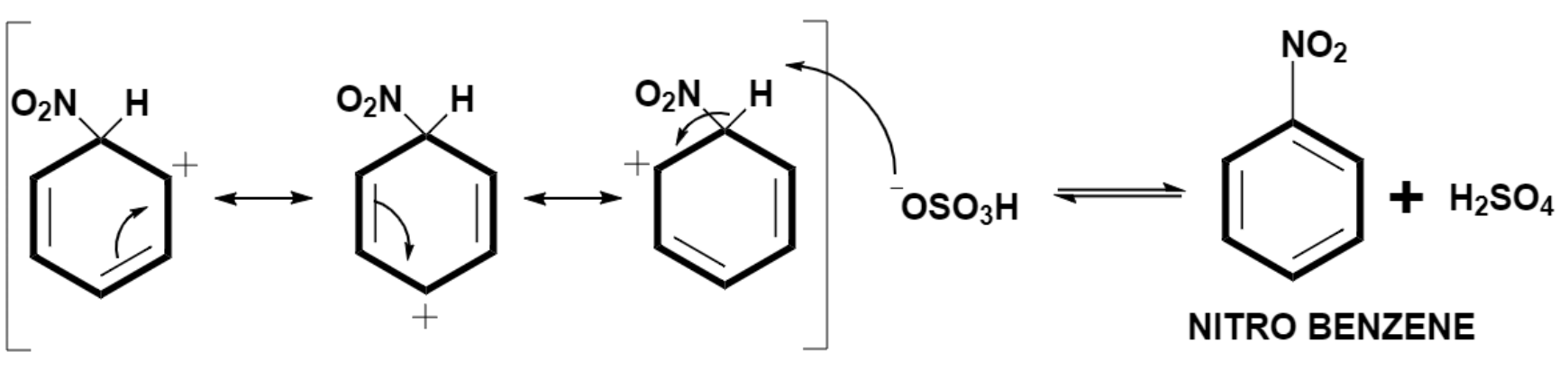
Hence, the generation of electrophile in nitration of benzene takes place by protonation of nitric acid with the help of sulphuric acid.
Additional information
The arenium ion is the resonance stabilized carbocation which forms during the electrophilic substitution in an aromatic ring.
Note:
In the last stage of nitration, hydrogen sulphate ion extracts proton from the arenium ring and regenerates sulphuric acid which can be further utilized in the formation of nitrobenzene. The sulphuric acid also acts as a catalyst for this reaction.
Complete answer:
The nitration of benzene is an aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction in which an electrophile is attacked by a benzene ring and hydrogen from the ring gets substituted by a nitro group to produce nitrobenzene.
The mechanism involved is as follows:
Step (1) – Generation of electrophile.
Sulphuric acid is a strong acid and thus it donates a proton to nitric acid which results in the formation of water along with nitronium ion which is a stronger electrophile.


Step (2) – Attack by the benzene group.
The electrophile generated in the above step is then attacked by the benzene group and arenium ion forms which exhibit resonance.

Step (3) – Formation of nitrobenzene.
The arenium ion loses a proton and forms nitrobenzene.

Hence, the generation of electrophile in nitration of benzene takes place by protonation of nitric acid with the help of sulphuric acid.
Additional information
The arenium ion is the resonance stabilized carbocation which forms during the electrophilic substitution in an aromatic ring.
Note:
In the last stage of nitration, hydrogen sulphate ion extracts proton from the arenium ring and regenerates sulphuric acid which can be further utilized in the formation of nitrobenzene. The sulphuric acid also acts as a catalyst for this reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




