
Element located in-center of the porphyrin ring of chlorophyll is.
(a) Potassium
(b) Manganese
(c) Magnesium
(d) Calcium
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Chlorophyll molecules embedded within the thylakoid membrane absorb light energy. These molecules are the foremost important pigments for absorbing the sunshine energy utilized in photosynthesis.
Complete answer:
Chlorophyll is found in all photosynthetic organisms, including green plants, cyanobacteria, and algae. It absorbs energy from light; this energy is then wont to convert carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
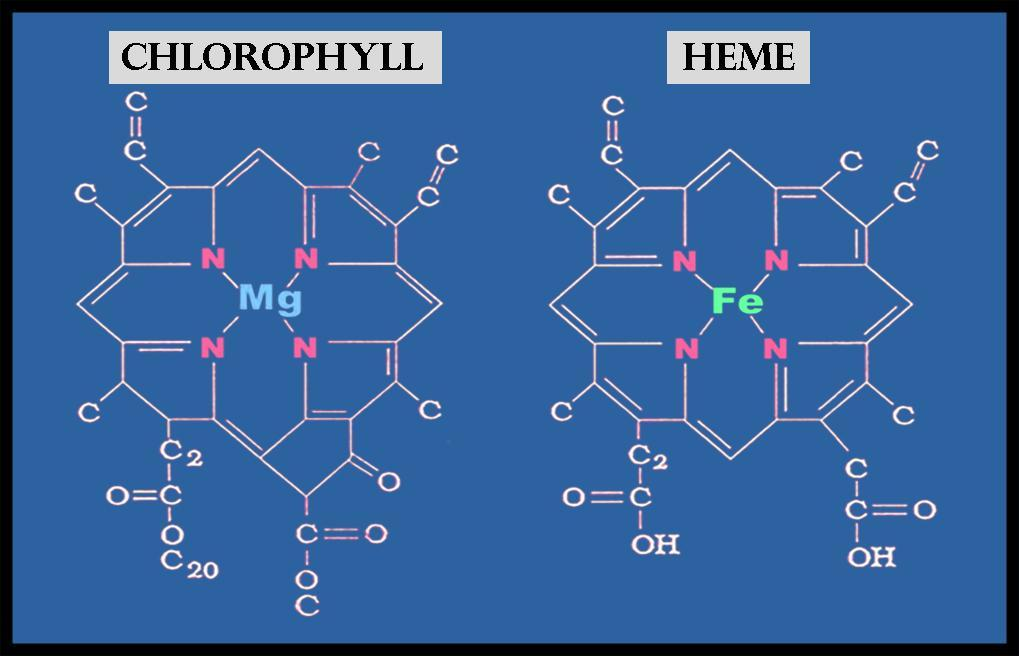
A chlorophyll molecule features a hydrophobic "tail" that embeds the molecule into the thylakoid membrane. The "head" of a chlorophyll molecule may be a ring called a porphyrin. The porphyrin ring of chlorophyll, which features a magnesium atom at its center, is a part of a chlorophyll molecule that absorbs light energy.
The chlorophyll molecule consists of a central magnesium atom surrounded by a nitrogen- containing structure called a porphyrin ring; attached to the ring may be a long carbon- hydrogen side chain, referred to as a phytol chain. Variations are thanks to minor modifications of certain side groups. Chlorophyll is remarkably similar in structure to hemoglobin, the oxygen- carrying pigment found within the red blood cells of mammals and other vertebrates.
So the correct answer is ‘(c) Magnesium’.
Additional Information:
- Like heme groups, chlorophylls are porphyrins found in plants. As such, they tetrapyrroles that contain a metal ion at their core. Unlike heme groups, which contain iron at their core, the metal ion found in chlorophyll is magnesium.
- Porphyrins are aromatic, highly conjugated heterocycles, with a score of 4 pyrrole rings coupled through four methylene units, that contain 11 conjugated double bonds, resulting in light absorption within the hellfire of the color spectrum.
- Beyond plants and animals, there are porphyrins almost everywhere within the world. Bacteria use porphyrins during a similar thanks to animal cells, although the ultimate molecules they use may look very different from the hemes in animals. Certain bacteria even have the power to photosynthesize, and like plants, they use porphyrins to capture the energy of the sun. There also are substances like vitamin B12, which are synthesized from porphyrin to start out, but hardly resemble one when complete.
Note:
- Tetrapyrroles are ubiquitous in nature. Their unique structure is important for a variety of critical biological processes including photosynthesis and respiration. Heme and chlorophyll are the most commonly known tetrapyrroles as mentioned as “The Colors of Life”.
- These pigments are liable for the red color of the blood and therefore the green color of leaves. In their cyclic form, four pyrrole subunits are linked together via methine bridges, with the exception of corrins, where two pyrroles are directly linked to each other.
- The macrocycle describes an aromatic system where the various families are often determined using the oxidation number or degree of saturation. Additionally to cyclic tetrapyrroles, linear tetrapyrroles (bilanes) function in cell metabolism, as regulators, and as photoreceptors.
Complete answer:
Chlorophyll is found in all photosynthetic organisms, including green plants, cyanobacteria, and algae. It absorbs energy from light; this energy is then wont to convert carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
A chlorophyll molecule features a hydrophobic "tail" that embeds the molecule into the thylakoid membrane. The "head" of a chlorophyll molecule may be a ring called a porphyrin. The porphyrin ring of chlorophyll, which features a magnesium atom at its center, is a part of a chlorophyll molecule that absorbs light energy.
The chlorophyll molecule consists of a central magnesium atom surrounded by a nitrogen- containing structure called a porphyrin ring; attached to the ring may be a long carbon- hydrogen side chain, referred to as a phytol chain. Variations are thanks to minor modifications of certain side groups. Chlorophyll is remarkably similar in structure to hemoglobin, the oxygen- carrying pigment found within the red blood cells of mammals and other vertebrates.

So the correct answer is ‘(c) Magnesium’.
Additional Information:
- Like heme groups, chlorophylls are porphyrins found in plants. As such, they tetrapyrroles that contain a metal ion at their core. Unlike heme groups, which contain iron at their core, the metal ion found in chlorophyll is magnesium.
- Porphyrins are aromatic, highly conjugated heterocycles, with a score of 4 pyrrole rings coupled through four methylene units, that contain 11 conjugated double bonds, resulting in light absorption within the hellfire of the color spectrum.
- Beyond plants and animals, there are porphyrins almost everywhere within the world. Bacteria use porphyrins during a similar thanks to animal cells, although the ultimate molecules they use may look very different from the hemes in animals. Certain bacteria even have the power to photosynthesize, and like plants, they use porphyrins to capture the energy of the sun. There also are substances like vitamin B12, which are synthesized from porphyrin to start out, but hardly resemble one when complete.
Note:
- Tetrapyrroles are ubiquitous in nature. Their unique structure is important for a variety of critical biological processes including photosynthesis and respiration. Heme and chlorophyll are the most commonly known tetrapyrroles as mentioned as “The Colors of Life”.
- These pigments are liable for the red color of the blood and therefore the green color of leaves. In their cyclic form, four pyrrole subunits are linked together via methine bridges, with the exception of corrins, where two pyrroles are directly linked to each other.
- The macrocycle describes an aromatic system where the various families are often determined using the oxidation number or degree of saturation. Additionally to cyclic tetrapyrroles, linear tetrapyrroles (bilanes) function in cell metabolism, as regulators, and as photoreceptors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




