
EMP is also known as
A. Glycolysis
B. Krebs cycle
C. ETS
D. Fermentation
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: EMP pathway is a metabolic process by which a single molecule of glucose is broken down into two pyruvate compounds. It breaks the six-carbon compounds into two molecules of three-carbon compounds.
Complete answer:
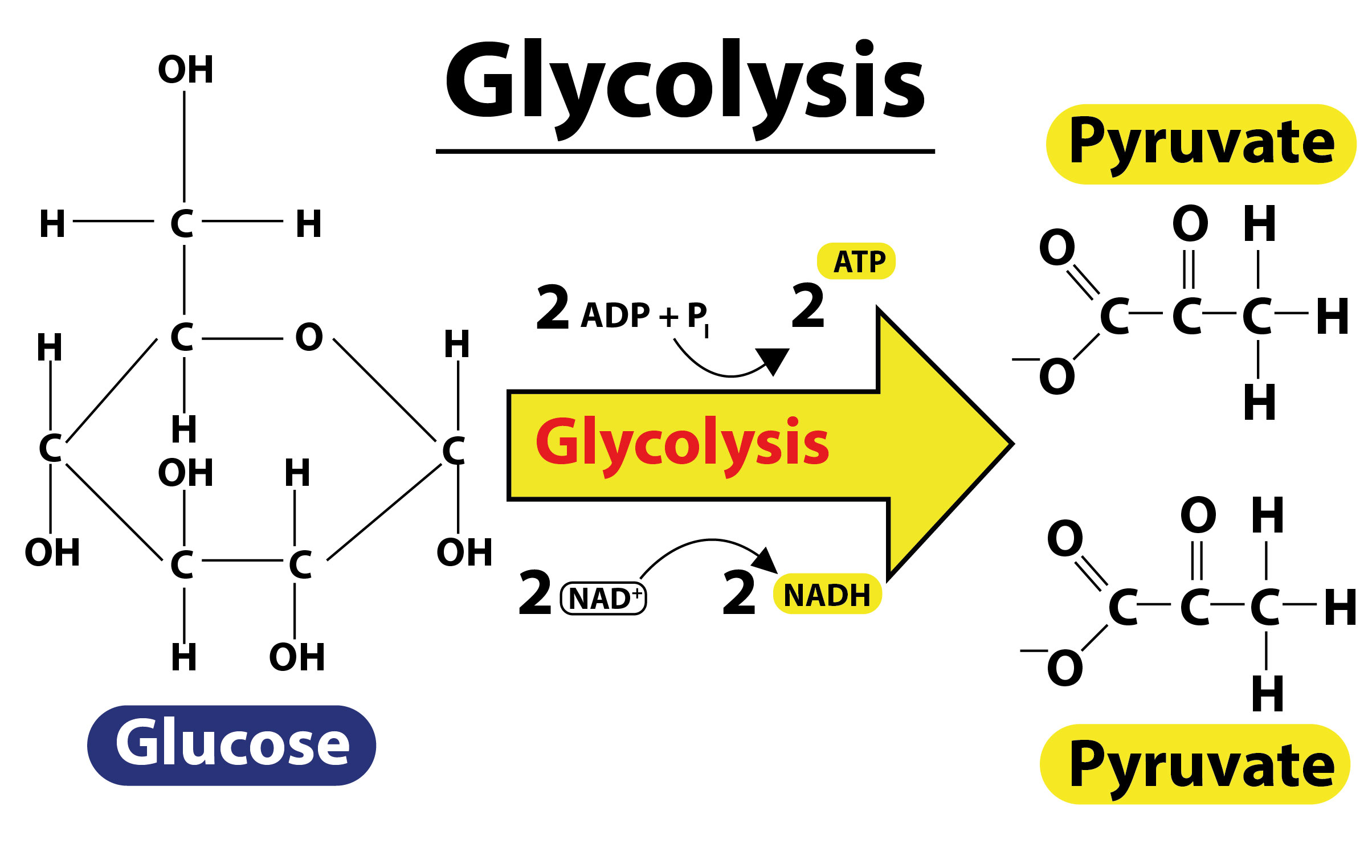
The process of glycolysis was first described in 1918 by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhoff, and Jakub Karol Parnas and therefore also referred to as the EMP pathway. It is the most common type of glycolysis.
Additional Information: -Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate and a hydrogen ion.
-It is a sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
-Glycolysis is an oxygen-independent metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytosol.
-The glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases:
(a)The preparatory phase – wherein ATP is consumed.
(b)The pay off phase – wherein ATP is produced.
-Glycolysis does not need or consume oxygen, it generally occurs during anaerobic respiration.
-In this case, 2 molecules of ATP are consumed to initiate the process.
-Four molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH are produced after the end of the process.
-The different Intermediary products formed in glycolysis can be used by plants in different metabolic functions of the body.
So, the correct answer is 'Glycolysis’.
Note: Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle which is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy. The electron transport chain is a series of complexes that transfers electrons through a membrane within mitochondria. Fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose is broken down anaerobically.
Complete answer:
The process of glycolysis was first described in 1918 by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhoff, and Jakub Karol Parnas and therefore also referred to as the EMP pathway. It is the most common type of glycolysis.
Additional Information: -Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate and a hydrogen ion.
-It is a sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
-Glycolysis is an oxygen-independent metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytosol.
-The glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases:
(a)The preparatory phase – wherein ATP is consumed.
(b)The pay off phase – wherein ATP is produced.
-Glycolysis does not need or consume oxygen, it generally occurs during anaerobic respiration.
-In this case, 2 molecules of ATP are consumed to initiate the process.
-Four molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH are produced after the end of the process.
-The different Intermediary products formed in glycolysis can be used by plants in different metabolic functions of the body.
So, the correct answer is 'Glycolysis’.

Note: Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle which is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy. The electron transport chain is a series of complexes that transfers electrons through a membrane within mitochondria. Fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose is broken down anaerobically.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




