
What is the empirical formula for magnesium oxide?
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: We need to know that empirical formula for any molecule is used to represent the number of atoms present and the type of atom in the molecule. There are generally two types of formula used to identify a molecule. One is Empirical Formula and one is Molecular Formula.
Complete answer:
We also remember that the empirical Formula is defined as the simplest form of representing a compound. It is calculated using weight percentages of elements present in the compound. It represents the simplest ratio for the atoms present in the molecule. Molecular formula is also calculated using empirical formula itself for a compound. Thus, molecular formula is a multiple of empirical formula.
Molecular formula is related to the total weight of the molecular entity.
An oxide is formed when an element reacts with oxygen. Oxide is the dianion of oxygen. They are called binary compounds of oxygen. Oxygen has a valency $ - 2$ hence the element present will get a subscript $2$ making it a binary compound.
Magnesium oxide is formed when Magnesium reacts with oxygen.
The word equation can be written as,
Magnesium +Oxygen → Magnesium oxide
By using the cross method of valency we can calculate the empirical formula
As we know Magnesium is a metal so it has a \[ + 2\] valency whereas oxygen has $ - 2$ valency.
Hence we have
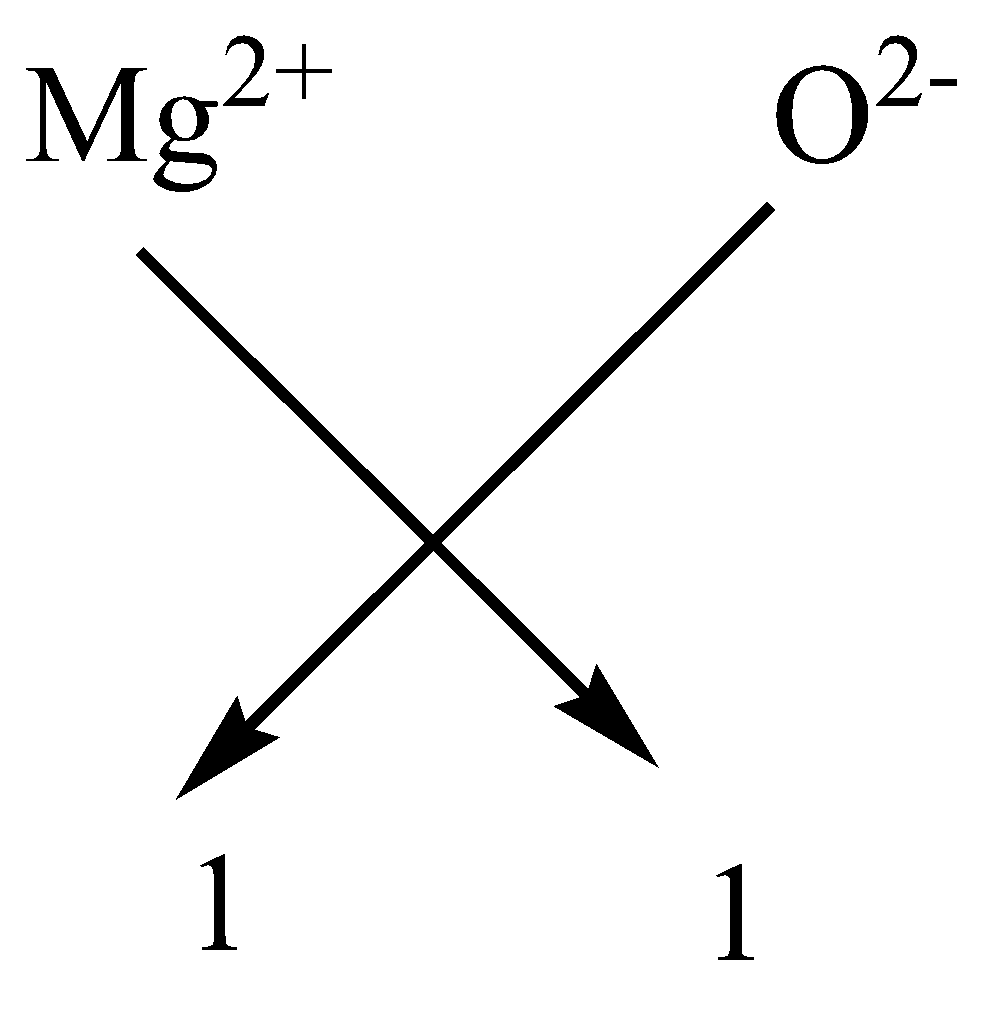
$M{g^{2 + }} + {O^{2 - }} \to MgO$
The subscript of oxygen and magnesium gets cancelled by each other and the formula becomes $MgO$.
Note:
We must have to know that the oxygen forms oxides with metals and non-metals. The oxides can be acidic, basic or amphoteric in nature. Generally metallic oxides are basic in nature whereas non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. Amphoteric oxides are those oxides which are basic as well acidic in nature.
Complete answer:
We also remember that the empirical Formula is defined as the simplest form of representing a compound. It is calculated using weight percentages of elements present in the compound. It represents the simplest ratio for the atoms present in the molecule. Molecular formula is also calculated using empirical formula itself for a compound. Thus, molecular formula is a multiple of empirical formula.
Molecular formula is related to the total weight of the molecular entity.
An oxide is formed when an element reacts with oxygen. Oxide is the dianion of oxygen. They are called binary compounds of oxygen. Oxygen has a valency $ - 2$ hence the element present will get a subscript $2$ making it a binary compound.
Magnesium oxide is formed when Magnesium reacts with oxygen.
The word equation can be written as,
Magnesium +Oxygen → Magnesium oxide
By using the cross method of valency we can calculate the empirical formula
As we know Magnesium is a metal so it has a \[ + 2\] valency whereas oxygen has $ - 2$ valency.
Hence we have

$M{g^{2 + }} + {O^{2 - }} \to MgO$
The subscript of oxygen and magnesium gets cancelled by each other and the formula becomes $MgO$.
Note:
We must have to know that the oxygen forms oxides with metals and non-metals. The oxides can be acidic, basic or amphoteric in nature. Generally metallic oxides are basic in nature whereas non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. Amphoteric oxides are those oxides which are basic as well acidic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




