
Endocrine gland responsible for immunity is
(a) Pineal
(b) Thymus
(c) Pituitary
(d) Adrenal
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: This is a soft, pinkish, bilobed mass of lymphoid tissue present just above the heart. This gland is large- sized and active in the young child and grows to the maximum size at puberty and then degrades gradually.
Complete Step by step answer:
A. Pineal gland is a small, rounded, and reddish- brown gland present at the dorsal side of the forebrain. This gland secretes melatonin and serotonin hormones.
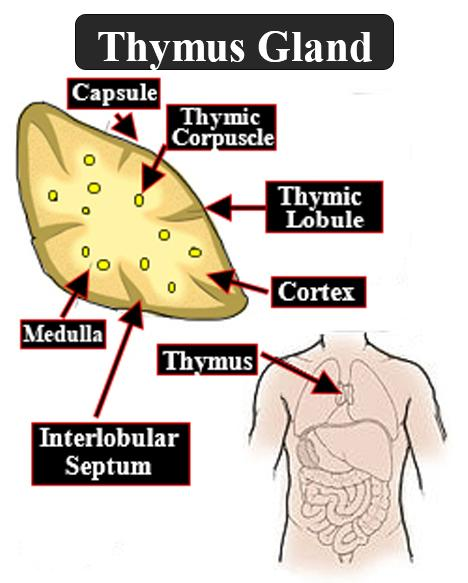
B. Thymus is related to the development of the immune system and presents on the dorsal side of the heart. It secretes the thymosin hormone which plays a vital role in the differentiation of T- lymphocytes.
C. pituitary is the master gland that regulates the activity of other endocrine glands and secretes many hormones like growth hormone, follicle- stimulating hormone, thyroid- stimulating hormone, etc.
D. adrenal is present on the top side of the kidneys and has two parts, the adrenal cortex which secretes glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex corticoids and the adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline and nor- adrenaline hormone.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Thymus gland.’
Additional information:
- Functions of the thymus gland:
1. It also has Hassall’s corpuscles which act as phagocytes.
2. It increases the rate of cell division so controls the rate of growth during early life.
3. It increases the production of the antibodies from B- lymphocytes so provides humoral immunity.
- The discovery of Thymosin took place in the mid- 1960s from investigations of the role of the thymus in the development of the vertebrate immune system.
- T- cells are very important in the case of the adaptive immune response, where the body adapts specifically to foreign invaders.
- Nowadays, the thymosin hormone is used in hair loss treatment.
- The thymus is made up of immature T- cells called thymocytes, and epithelial cell lining, which help the thymocytes develop.
- Any internal damage to the thymus gland can bring about a decrease in the number of T cells and lead to autoimmune diseases such as Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 and myasthenia gravis.
Note: The Thymus gland is also known as ‘Throne of immunity’ or ‘training schools of T- lymphocytes.’ The thymus is the site of differentiation of the t- lymphocytes of the immune system. Thymosin increases the activity of the T- lymphocytes which provide cell- mediated immunity.
Complete Step by step answer:
A. Pineal gland is a small, rounded, and reddish- brown gland present at the dorsal side of the forebrain. This gland secretes melatonin and serotonin hormones.
B. Thymus is related to the development of the immune system and presents on the dorsal side of the heart. It secretes the thymosin hormone which plays a vital role in the differentiation of T- lymphocytes.

C. pituitary is the master gland that regulates the activity of other endocrine glands and secretes many hormones like growth hormone, follicle- stimulating hormone, thyroid- stimulating hormone, etc.
D. adrenal is present on the top side of the kidneys and has two parts, the adrenal cortex which secretes glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex corticoids and the adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline and nor- adrenaline hormone.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Thymus gland.’
Additional information:
- Functions of the thymus gland:
1. It also has Hassall’s corpuscles which act as phagocytes.
2. It increases the rate of cell division so controls the rate of growth during early life.
3. It increases the production of the antibodies from B- lymphocytes so provides humoral immunity.
- The discovery of Thymosin took place in the mid- 1960s from investigations of the role of the thymus in the development of the vertebrate immune system.
- T- cells are very important in the case of the adaptive immune response, where the body adapts specifically to foreign invaders.
- Nowadays, the thymosin hormone is used in hair loss treatment.
- The thymus is made up of immature T- cells called thymocytes, and epithelial cell lining, which help the thymocytes develop.
- Any internal damage to the thymus gland can bring about a decrease in the number of T cells and lead to autoimmune diseases such as Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 and myasthenia gravis.
Note: The Thymus gland is also known as ‘Throne of immunity’ or ‘training schools of T- lymphocytes.’ The thymus is the site of differentiation of the t- lymphocytes of the immune system. Thymosin increases the activity of the T- lymphocytes which provide cell- mediated immunity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




