
Enzyme connected with opening and closing of stomata is -
(a)α-Amylase
(b)Pyruvic kinase
(c)PEP carboxylase
(d)RuBP carboxylase
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: Stomata (singular - stoma) are pores present on the surface of leaves, flowers, and green parts of a plant that are responsible for gas exchange. The enzyme belongs to the family of carboxy-lyases found in plants and helps in photosynthesis.
Complete answer:
The singular stoma is surrounded by two guard cells that regulate the rate of transpiration by opening and closing the stoma. These cells open and close the stomata due to various reasons.
- In transpiration, water from the parts of the plant moves towards the surface of the leaf and leaves the surface from stomata in the form of water vapor.
- Stomata in most plants remain open during the daytime, through which they gain carbon dioxide. However, as the air spaces in the leaf are saturated with water vapor, this water is lost by transpiration and evaporation.
- Carbon dioxide is generally fixed to RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate) by the enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase or RuBP carboxylase or RuBisCO. RuBisCO has a relatively low affinity for carbon and fixes oxygen to RuBP during photorespiration.
- So, in plants where water is limited but light supply is plenty, the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, or PEP carboxylase, fixes the carbon dioxide to RuBP. PEP carboxylase has a higher affinity for carbon, hence the leaves of the plants can have smaller stomatal openings with more acceptable carbon dioxide uptake.
Additional Information: - α-Amylase in plants breaks down the starch in plants by hydrolyzing the alpha bonds of large, alpha-linked polysaccharides to form glucose and simple sugars.
- Pyruvic/Pyruvate kinase catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP to yield ATP and pyruvate.
- RuBP carboxylase is an enzyme necessary for the first step of carbon fixation in plants where carbon dioxide from air is taken and converted into glucose.
So, the correct answer is ‘PEP Carboxylase’.
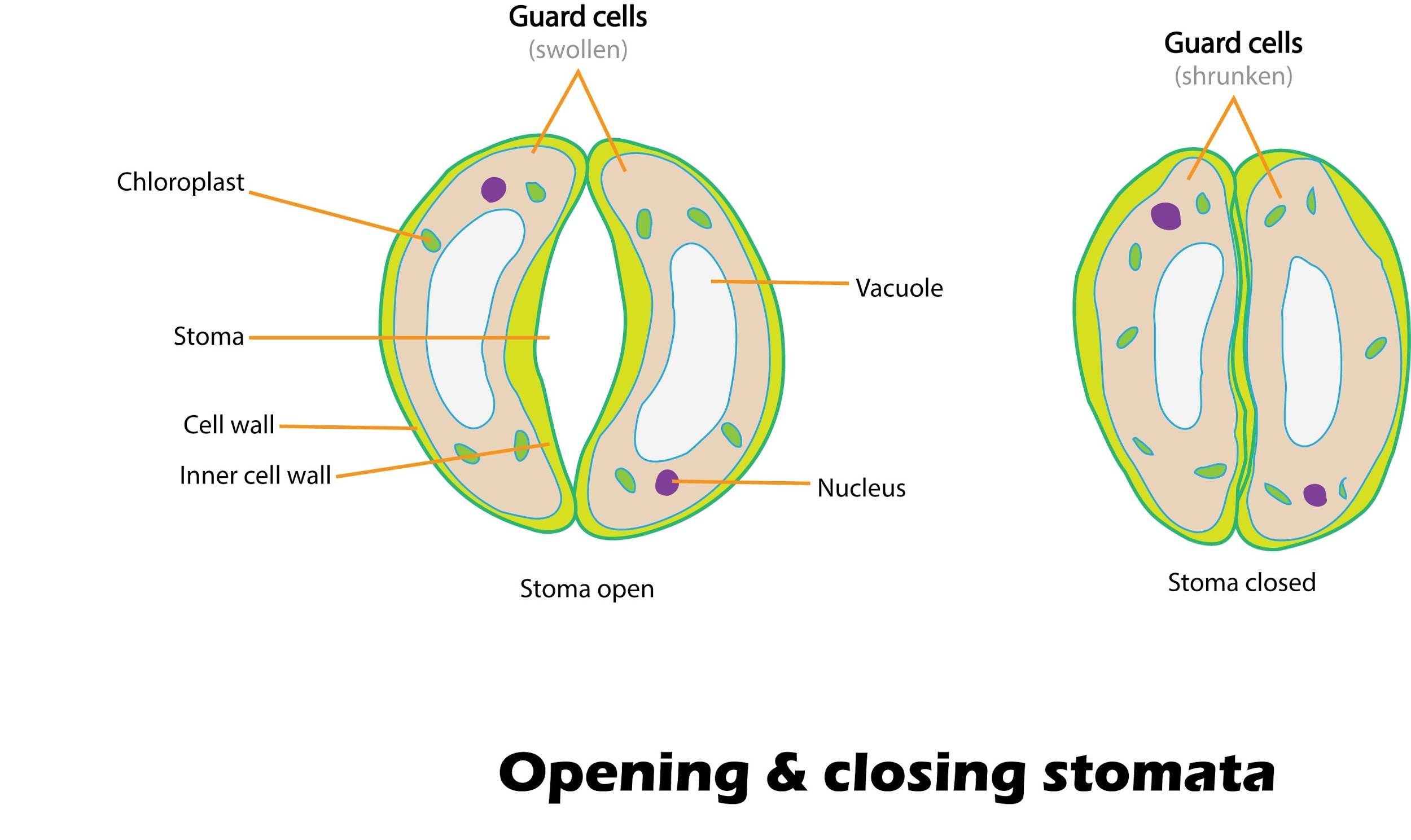
Note: - The guard cells are specialized parenchyma cells.
- RuBP carboxylase/RuBisCo is considered to be the most abundant enzyme on the planet.
- Stomata are present in all sporophyte generation of land plants except liverworts.
Complete answer:
The singular stoma is surrounded by two guard cells that regulate the rate of transpiration by opening and closing the stoma. These cells open and close the stomata due to various reasons.
- In transpiration, water from the parts of the plant moves towards the surface of the leaf and leaves the surface from stomata in the form of water vapor.
- Stomata in most plants remain open during the daytime, through which they gain carbon dioxide. However, as the air spaces in the leaf are saturated with water vapor, this water is lost by transpiration and evaporation.
- Carbon dioxide is generally fixed to RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate) by the enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase or RuBP carboxylase or RuBisCO. RuBisCO has a relatively low affinity for carbon and fixes oxygen to RuBP during photorespiration.
- So, in plants where water is limited but light supply is plenty, the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, or PEP carboxylase, fixes the carbon dioxide to RuBP. PEP carboxylase has a higher affinity for carbon, hence the leaves of the plants can have smaller stomatal openings with more acceptable carbon dioxide uptake.
Additional Information: - α-Amylase in plants breaks down the starch in plants by hydrolyzing the alpha bonds of large, alpha-linked polysaccharides to form glucose and simple sugars.
- Pyruvic/Pyruvate kinase catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP to yield ATP and pyruvate.
- RuBP carboxylase is an enzyme necessary for the first step of carbon fixation in plants where carbon dioxide from air is taken and converted into glucose.
So, the correct answer is ‘PEP Carboxylase’.

Note: - The guard cells are specialized parenchyma cells.
- RuBP carboxylase/RuBisCo is considered to be the most abundant enzyme on the planet.
- Stomata are present in all sporophyte generation of land plants except liverworts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




