
What is enzyme inhibition? How many types of enzyme inhibition are known? Explain how the effect of inhibitors be stopped?
Answer
501.6k+ views
Hint: Inhibition is to stop. So, enzyme inhibition refers to the stopping of the enzyme activity. The inhibition is carried out by inhibitors which do not lead to the formation of the product. The inhibitors can affect the substrate as well as the enzyme.
Complete answer:
The enzymes are the biomolecules which increases the rate of forward reaction. The enzymes act on the substrate and brings about the formation of the product. The enzyme is not used up in a bio-chemical reaction. There are certain molecules(inhibitors) which interfere with the enzyme activity and does not lead to the formation of the product. This is known as enzyme inhibition. These inhibitors can bind to the active sites and prevent/interfere with the further activity. This type of binding can be reversible as well as irreversible.
The inhibition is of four types-
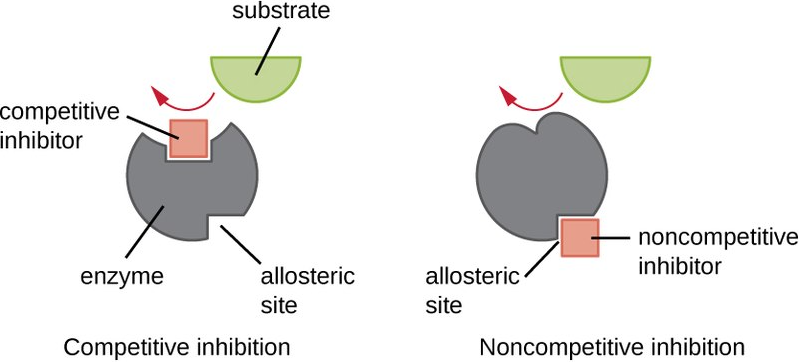
1) Competitive- In this type of inhibition, the inhibitor also has the affinity towards the enzyme active site. It competes with the substrate for the active site. If the inhibitor binds the active site, the enzyme activity is stopped.
2) Non-competitive- In this the inhibitor reduces the activity of the enzyme irrespective of whether the substrate bind to the enzyme or not.
3) Uncompetitive- It is also known as anti-competitive inhibition. The inhibitor binds to the enzyme substrate complex.
4) Allosteric- The inhibitors bind to the allosteric site and change the conformation of the enzymes.
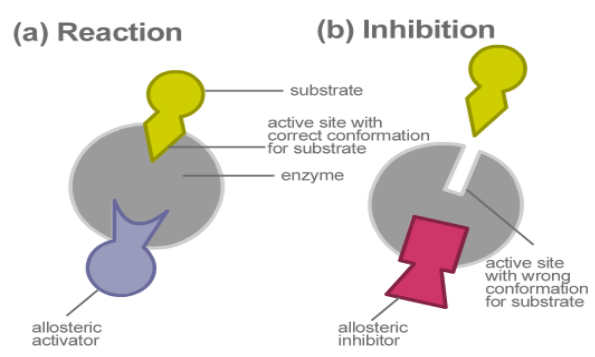
The inhibitors can be stopped by increasing the concentration of the substrate and also use of the molecules which out compete inhibitors.
Note: Inhibition is the mechanism which helps in stopping a biochemical reaction. They act as a cellular control mechanism. The formation of ATP is a mechanism which prevents the break down of too many glucose molecules. The enzyme inhibition mechanism is used for making several potential drugs.
Complete answer:
The enzymes are the biomolecules which increases the rate of forward reaction. The enzymes act on the substrate and brings about the formation of the product. The enzyme is not used up in a bio-chemical reaction. There are certain molecules(inhibitors) which interfere with the enzyme activity and does not lead to the formation of the product. This is known as enzyme inhibition. These inhibitors can bind to the active sites and prevent/interfere with the further activity. This type of binding can be reversible as well as irreversible.
The inhibition is of four types-
1) Competitive- In this type of inhibition, the inhibitor also has the affinity towards the enzyme active site. It competes with the substrate for the active site. If the inhibitor binds the active site, the enzyme activity is stopped.
2) Non-competitive- In this the inhibitor reduces the activity of the enzyme irrespective of whether the substrate bind to the enzyme or not.

3) Uncompetitive- It is also known as anti-competitive inhibition. The inhibitor binds to the enzyme substrate complex.
4) Allosteric- The inhibitors bind to the allosteric site and change the conformation of the enzymes.

The inhibitors can be stopped by increasing the concentration of the substrate and also use of the molecules which out compete inhibitors.
Note: Inhibition is the mechanism which helps in stopping a biochemical reaction. They act as a cellular control mechanism. The formation of ATP is a mechanism which prevents the break down of too many glucose molecules. The enzyme inhibition mechanism is used for making several potential drugs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




