
When is equilibrium reached in diffusion?
Answer
489.9k+ views
Hint: Chemical equilibrium is defined as the state where both the reactants and the products are present in equal concentration and thereby don’t have any tendency to change with time, and no observable change is found in the properties of the system. We will understand diffusion further in the question.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Molecular diffusion also known as diffusion is the motion of particles (liquids as well as gases) at a temperature above the absolute zero. The rate of diffusion depends on the temperature, viscosity of the fluids, size of the particles, etc. The diffusion results in the uniform distribution of molecules upon mixing of materials. Once the mixing is uniform, it achieves a state of dynamic equilibrium. In this phase molecules are still in motion, but the external net forces acting on the particles are absent. This gradually led to uniform mixing.
The simple example of diffusion is dispersion of dye in water. When one drop of dye is initially put in water contained in a beaker, it slowly spreads throughout the entire beaker, until no part of the water is left colorless. This is the stage where we say that the dye has been uniformly mixed in the container. The image below shows the process of diffusion of dye. Once the water is uniformly colored, we say that the state of equilibrium has been achieved.

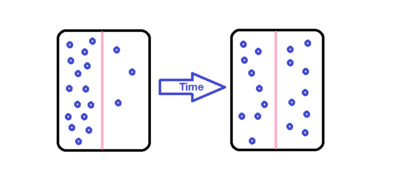
Diffusion also occurs across membranes. In the image shown below there are unequal concentrations of substance on either side of the semi permeable membrane given by the pink line. The concentration on either side of the pink line is different. If the molecules are small in size, the molecules tend to cross the membrane into a region with low concentration. The molecules can move in all directions, but major movement is found from the high concentrated region to low concentrated region. Eventually, the concentration on the lower side increases and a stage is reached where concentration is equal on both the sides. This state is known as the Diffusion Equilibrium. At this stage the molecules move back and forth at the same rate.
Note:
Osmosis is also a type of diffusion only but it is only limited to the liquid substances. Osmosis is the process of movement of solute particles from a higher concentration to a lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Water moves in and out of the cells by osmosis only.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Molecular diffusion also known as diffusion is the motion of particles (liquids as well as gases) at a temperature above the absolute zero. The rate of diffusion depends on the temperature, viscosity of the fluids, size of the particles, etc. The diffusion results in the uniform distribution of molecules upon mixing of materials. Once the mixing is uniform, it achieves a state of dynamic equilibrium. In this phase molecules are still in motion, but the external net forces acting on the particles are absent. This gradually led to uniform mixing.
The simple example of diffusion is dispersion of dye in water. When one drop of dye is initially put in water contained in a beaker, it slowly spreads throughout the entire beaker, until no part of the water is left colorless. This is the stage where we say that the dye has been uniformly mixed in the container. The image below shows the process of diffusion of dye. Once the water is uniformly colored, we say that the state of equilibrium has been achieved.

Diffusion also occurs across membranes. In the image shown below there are unequal concentrations of substance on either side of the semi permeable membrane given by the pink line. The concentration on either side of the pink line is different. If the molecules are small in size, the molecules tend to cross the membrane into a region with low concentration. The molecules can move in all directions, but major movement is found from the high concentrated region to low concentrated region. Eventually, the concentration on the lower side increases and a stage is reached where concentration is equal on both the sides. This state is known as the Diffusion Equilibrium. At this stage the molecules move back and forth at the same rate.

Note:
Osmosis is also a type of diffusion only but it is only limited to the liquid substances. Osmosis is the process of movement of solute particles from a higher concentration to a lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Water moves in and out of the cells by osmosis only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




