
Ethene on ozonolysis give,
A. Acetaldehyde
B. Formaldehyde
C. Acetone
D. Alcohol
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the process of ozonolysis and apply this concept to understand the ozonolysis of ethene. Ozone is also known as trioxygen and is a very active allotrope of carbon. The process of cleaving unsaturated bonds in an organic reaction with the help of ozone is known as ozonolysis. It is basically the reaction of alkenes and alkynes with ozone causing oxidative cleaving of the double and triple bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that ozonolysis is the process of cleaving of double and triple bonds of alkenes and alkynes, we now study the ozonolysis of alkenes only since the given organic compound (ethene) is an alkene.
The ozonolysis process of alkenes works by the oxidative cleavage of the double bond. It breaks both the pi and sigma bonds and also attacks the given alkene to produce an ozonide. Zinc dust is added to keep the oxygen away at intermediate stages since the zinc takes away the extra oxygen to form zinc oxide. The product of this reaction depends on the given type of alkene and the position of the double bond(s).
We can explain the process of ozonolysis by using the simplest compound containing a double bond which is ethene. The reaction is given below:
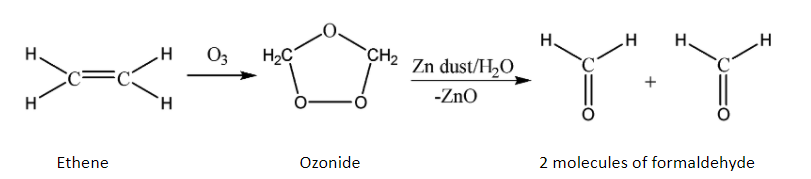
Hence, it can be concluded that ethene undergoes oxidative double bond cleavage when allowed to react with ozone and produces two molecules of formaldehyde.
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note: It must be noted that ozonolysis in organic chemistry is used for the detection of the position of carbon double bonds and triple bonds and hence we can determine the unknown alkene or alkyne. Alkenes on ozonolysis form alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids depending on the reactant. On ozonolysis, alkynes give acid anhydrides or diketones and on hydrolysis, the acid anhydride yields two carboxylic acids. Compounds with the functional diazinyl functional group known as azo compounds can also undergo ozonolysis to yield nitrosamines.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that ozonolysis is the process of cleaving of double and triple bonds of alkenes and alkynes, we now study the ozonolysis of alkenes only since the given organic compound (ethene) is an alkene.
The ozonolysis process of alkenes works by the oxidative cleavage of the double bond. It breaks both the pi and sigma bonds and also attacks the given alkene to produce an ozonide. Zinc dust is added to keep the oxygen away at intermediate stages since the zinc takes away the extra oxygen to form zinc oxide. The product of this reaction depends on the given type of alkene and the position of the double bond(s).
We can explain the process of ozonolysis by using the simplest compound containing a double bond which is ethene. The reaction is given below:

Hence, it can be concluded that ethene undergoes oxidative double bond cleavage when allowed to react with ozone and produces two molecules of formaldehyde.
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note: It must be noted that ozonolysis in organic chemistry is used for the detection of the position of carbon double bonds and triple bonds and hence we can determine the unknown alkene or alkyne. Alkenes on ozonolysis form alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids depending on the reactant. On ozonolysis, alkynes give acid anhydrides or diketones and on hydrolysis, the acid anhydride yields two carboxylic acids. Compounds with the functional diazinyl functional group known as azo compounds can also undergo ozonolysis to yield nitrosamines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




