
Ethylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent to give_
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint :Baeyer’s reagent is an alkaline potassium permanganate solution. Any alkene when subjected to reaction with any alkene will give a product of alcohol group in it.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When ethylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent, which is alkaline potassium permanganate solution, the product obtained is Ethylene glycol.
Ethylene is shown below
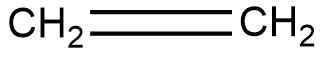
The reaction is shown below,
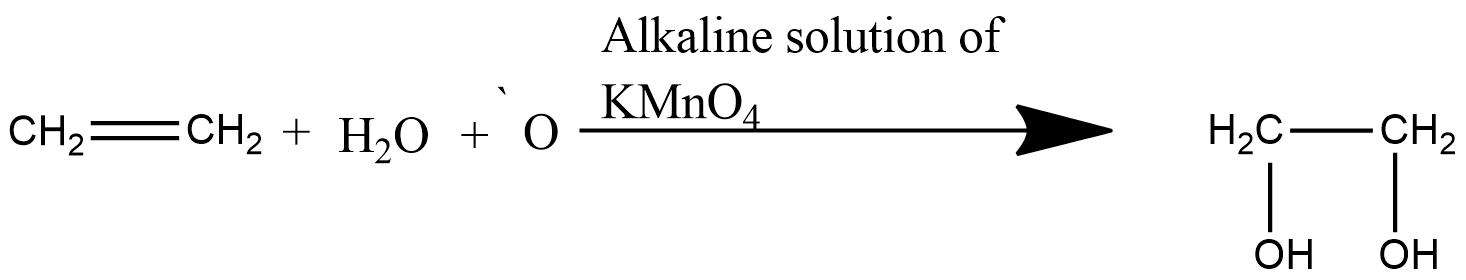
Here, alkene reacts with a cold dilute alkaline solution of \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] to produce ethylene glycol which is a diol.
Whenever an alkene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent, the primary and secondary carbon attached to the double bond gets reduced to single bond and alcohol group gets attached to it.
Here as the compound is ethylene, the product formed is ethylene glycol, in which the double bond of carbon gets reduced to single bond and alcohol groups are attached to them.
Thus, we can say that when any alkene is subjected to reaction with Baeyer’s reagent, the product obtained will be 1, 2 diol.
For another example, when propylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent, propylene 1, 2 glycol is formed. Similarly in any type of butene, the product formed will be diol and the alcohol group will be attached to the carbons with double bonds.
At first, due to presence of potassium permanganate, the solution is pinkish purple, due to reaction with Baeyer’s reagent it becomes brown. The by-products of the reaction are potassium manganate and manganese dioxide, as manganese dioxide is brown, the colour of the solution becomes brown.
Note :
Any alkene when reacted with Baeyer’s reagent, gives diol at the primary and secondary carbon with double bond in it. The carbons with double bonds can have any type of group attached to them.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When ethylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent, which is alkaline potassium permanganate solution, the product obtained is Ethylene glycol.
Ethylene is shown below
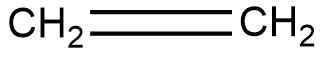
The reaction is shown below,
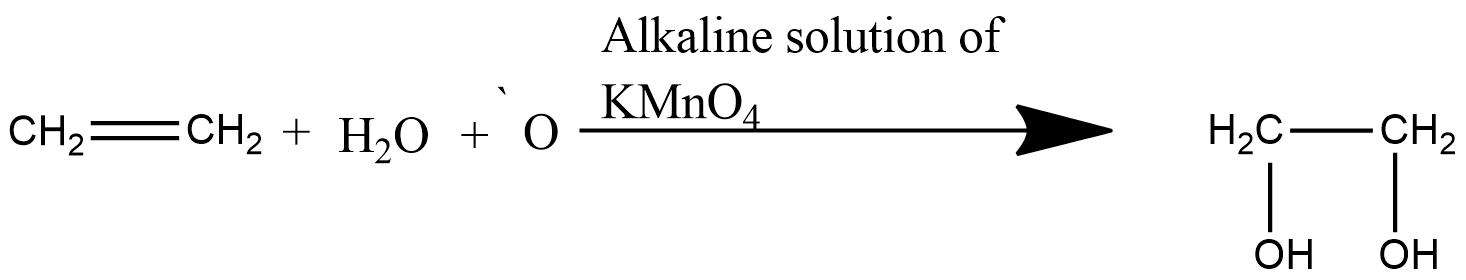
Here, alkene reacts with a cold dilute alkaline solution of \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] to produce ethylene glycol which is a diol.
Whenever an alkene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent, the primary and secondary carbon attached to the double bond gets reduced to single bond and alcohol group gets attached to it.
Here as the compound is ethylene, the product formed is ethylene glycol, in which the double bond of carbon gets reduced to single bond and alcohol groups are attached to them.
Thus, we can say that when any alkene is subjected to reaction with Baeyer’s reagent, the product obtained will be 1, 2 diol.
For another example, when propylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent, propylene 1, 2 glycol is formed. Similarly in any type of butene, the product formed will be diol and the alcohol group will be attached to the carbons with double bonds.
At first, due to presence of potassium permanganate, the solution is pinkish purple, due to reaction with Baeyer’s reagent it becomes brown. The by-products of the reaction are potassium manganate and manganese dioxide, as manganese dioxide is brown, the colour of the solution becomes brown.
Note :
Any alkene when reacted with Baeyer’s reagent, gives diol at the primary and secondary carbon with double bond in it. The carbons with double bonds can have any type of group attached to them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




