
Exarch xylem is found in
A. Root
B. Stem
C. Leaf
D. Rachis
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Exarch xylem is found in the plant organ that helps in the absorption of water from the soil. In some species of plants, this structure has fungal associations known as mycorrhiza. Nitrogen-fixing bacterias like Nostoc, Rhizobium, etc form symbiotic associations with this structure.
Complete answer:
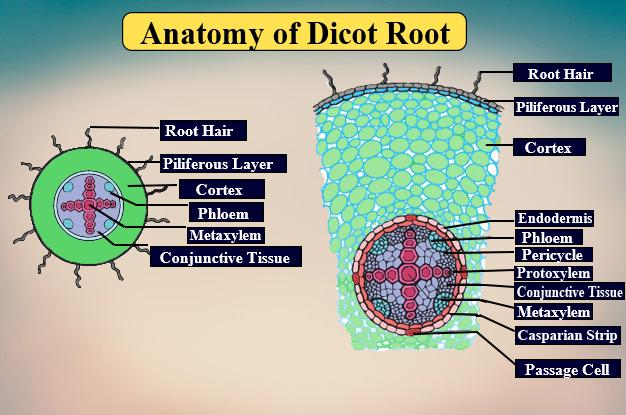
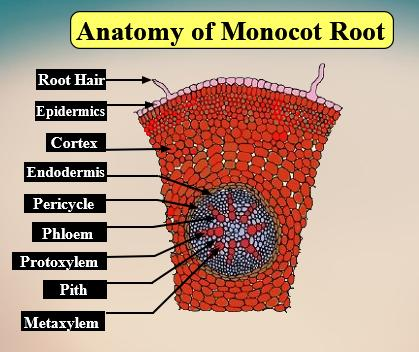
Exarch refers to a type of arrangement of vascular bundles where:
-The protoxylem or first formed xylem lies peripherally.
-The metaxylem or second formed xylem lies centrally.
-The development of vascular bundles in centripetal type.
Exarch xylem is found in both dicot and monocot root systems.
Additional Information: The anatomy of dicot and monocot root is as follows:
-Epiblema or Rhizodermis layer: It consists of living tubular components and is the outermost part. No cuticle and stomata are present. Root hairs arise from the maturation zone of epiblema. It helps in water absorption from the soil.
-Cortex: The cortex is made up of circular and polygonal parenchymatous cells, intercellular spaces are present.
-Endodermis: This layer is the innermost part and has Casparian strips. It is single-layered.
-Pericycle: It is composed of parenchymatous cells and consists of only one layer. The endogenous origin of roots occurs from the pericycle layer.
-Vascular Bundles: Contains xylem and phloem in radial and exarch fashion in dicots and monocots.
-Pith: it is present at the center and it is reduced or underdeveloped in dicot root but well developed in monocot root.
So, the correct answer is,” Exarch xylem is found in the root.”
Note: Even though xylem in both monocot and dicot root lies in exarch pattern, in monocots, xylem is present in polyarch(more than six in number) condition but the number of xylem bundles ranges from two to six in dicots, which means in dicot xylem is in diarch to hexarch condition. A parenchymatous layer is present between xylem and phloem, which is known as conjunctive tissue. The conjunctive tissue produces vascular cambium during secondary growth in dicots but not in monocots.
Complete answer:
Exarch refers to a type of arrangement of vascular bundles where:
-The protoxylem or first formed xylem lies peripherally.
-The metaxylem or second formed xylem lies centrally.
-The development of vascular bundles in centripetal type.
Exarch xylem is found in both dicot and monocot root systems.
Additional Information: The anatomy of dicot and monocot root is as follows:
-Epiblema or Rhizodermis layer: It consists of living tubular components and is the outermost part. No cuticle and stomata are present. Root hairs arise from the maturation zone of epiblema. It helps in water absorption from the soil.
-Cortex: The cortex is made up of circular and polygonal parenchymatous cells, intercellular spaces are present.
-Endodermis: This layer is the innermost part and has Casparian strips. It is single-layered.
-Pericycle: It is composed of parenchymatous cells and consists of only one layer. The endogenous origin of roots occurs from the pericycle layer.
-Vascular Bundles: Contains xylem and phloem in radial and exarch fashion in dicots and monocots.
-Pith: it is present at the center and it is reduced or underdeveloped in dicot root but well developed in monocot root.
So, the correct answer is,” Exarch xylem is found in the root.”
Note: Even though xylem in both monocot and dicot root lies in exarch pattern, in monocots, xylem is present in polyarch(more than six in number) condition but the number of xylem bundles ranges from two to six in dicots, which means in dicot xylem is in diarch to hexarch condition. A parenchymatous layer is present between xylem and phloem, which is known as conjunctive tissue. The conjunctive tissue produces vascular cambium during secondary growth in dicots but not in monocots.


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




