
Exchanging one part of a chromosome with a part of the same or other chromosome is
(a) Inversion
(b) Crossing over
(c) Translocation
(d) Linkage
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Exchanging one part of a chromosome with a part of the same or other chromosome is one of the causes of infertility or cancer. This can alter the total genetic material present in a particular chromosome.
Complete answer:
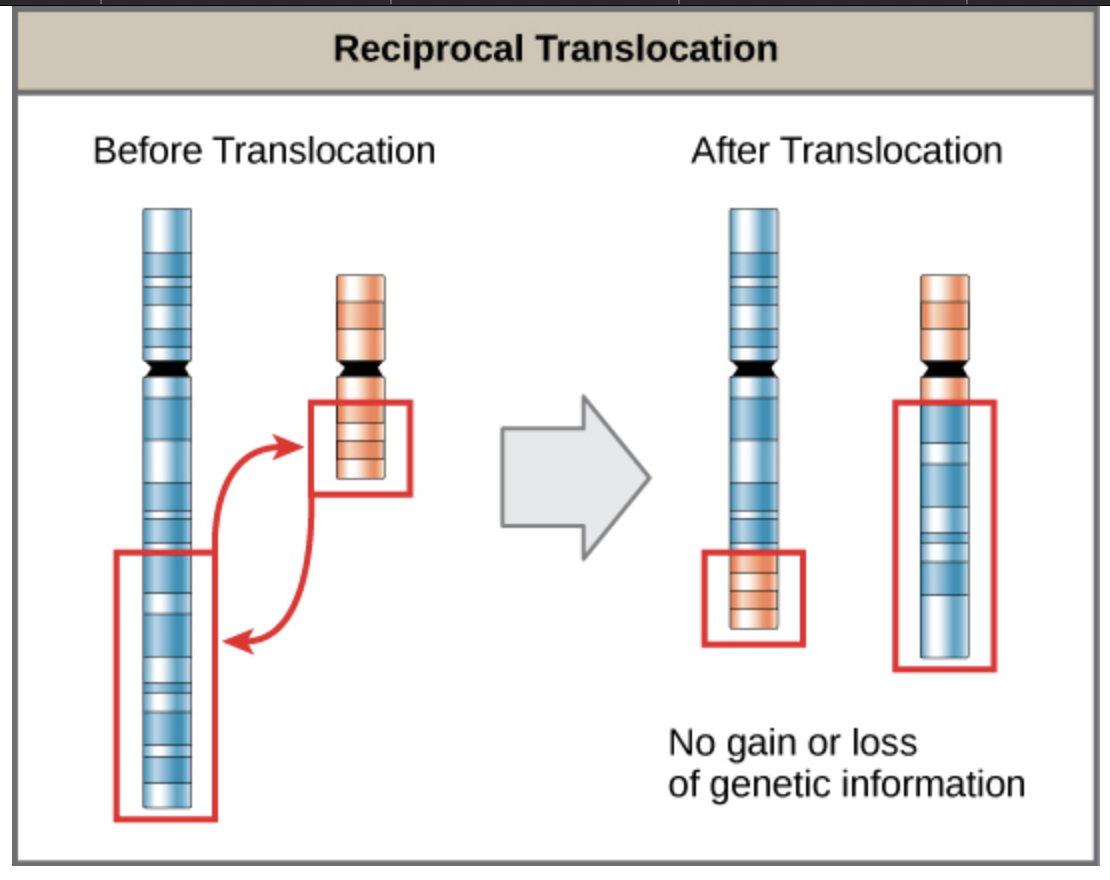
Translocation is a type of chromosomal rearrangement where a part of chromosome is exchanged with a part of the same or different chromosome. It may be reciprocal and non-reciprocal. In reciprocal translocation, only one-way transfer of a segment of chromosome occurs. This leads to an extended segment in the chromosome to which transfer occurs and a loss of segment in the chromosome from which transfer occurs. This is rarer than reciprocal translocation where a two-way transfer occurs and both the non-homologous chromosomes (different chromosomes) exchange their segments simultaneously without any extension or deletion of segments in either one.
- Crossing over is a process which is a characteristic feature of meiotic divisions. Here, the exchange of genetic material takes place between two homologous chromosomes and thus genetic recombination occurs.
- Linkage is the tendency for alleles of different genes to be passed together from one generation to next. It is inversely proportional to the distance between the genes on a chromosome. This means, the more the distance between the genes, the lesser is the tendency for linkage to occur between them and if they are closer, the more is the probability for them to be inherited together.
- An inversion is an event in the chromosome where a region breaks and rejoins it after rotating a 180°. Such a mutation does not change the overall amount of genetic material, so generally, no particular abnormalities at the phenotypic level are observed.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Translocation.’
Note:
- Crossing over provides new gene combinations and therefore it is a source of genetic diversity in a population.
- In an inversion, If the breaks are within a gene of essential function, then this breakpoint could act as a lethal gene mutation.
- T.H Morgan is the first scientist to study the phenomenon of linkage in Drosophila.
Complete answer:
Translocation is a type of chromosomal rearrangement where a part of chromosome is exchanged with a part of the same or different chromosome. It may be reciprocal and non-reciprocal. In reciprocal translocation, only one-way transfer of a segment of chromosome occurs. This leads to an extended segment in the chromosome to which transfer occurs and a loss of segment in the chromosome from which transfer occurs. This is rarer than reciprocal translocation where a two-way transfer occurs and both the non-homologous chromosomes (different chromosomes) exchange their segments simultaneously without any extension or deletion of segments in either one.
- Crossing over is a process which is a characteristic feature of meiotic divisions. Here, the exchange of genetic material takes place between two homologous chromosomes and thus genetic recombination occurs.
- Linkage is the tendency for alleles of different genes to be passed together from one generation to next. It is inversely proportional to the distance between the genes on a chromosome. This means, the more the distance between the genes, the lesser is the tendency for linkage to occur between them and if they are closer, the more is the probability for them to be inherited together.
- An inversion is an event in the chromosome where a region breaks and rejoins it after rotating a 180°. Such a mutation does not change the overall amount of genetic material, so generally, no particular abnormalities at the phenotypic level are observed.

So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Translocation.’
Note:
- Crossing over provides new gene combinations and therefore it is a source of genetic diversity in a population.
- In an inversion, If the breaks are within a gene of essential function, then this breakpoint could act as a lethal gene mutation.
- T.H Morgan is the first scientist to study the phenomenon of linkage in Drosophila.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




