
Excretory organs of Earthworm are:
(a) Coelum
(b) Flame cells
(c) Nephridia
(d) Gizzard
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Excretory organs are the organs that help in the disposal of metabolic nitrogenous wastes from the body. Earthworm belongs to phylum Annelida which are known for their metameric segmentation i.e body is divided into segments or ‘metameres’ both internally and externally.
Complete answer:
Nephridia are the primary excretory organs of earthworm that carry out the duties of excretion and osmoregulation. Based on where they remove the metabolic wastes, they are of two types – enteronephric nephridia and enteronephric nephridia. Exonephric nephridia or ectonephric nephridia are the types of nephridia that directly remove the nitrogenous wastes outside the body of earthworm by nephridiopores( external opening of nephridia). Enteronephric nephridia eject their wastes into the alimentary canal.
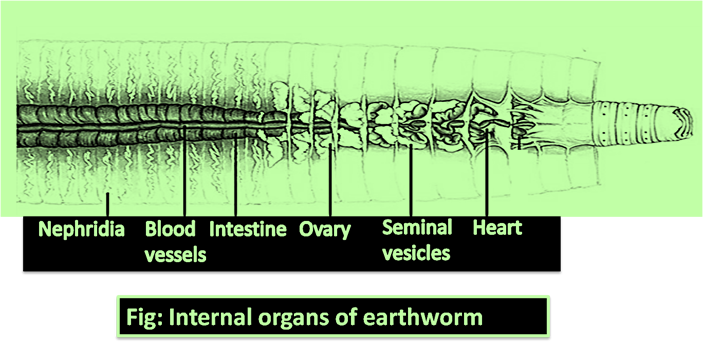
So, the correct answer is ‘Nephridia.’
Additional Information: Based on location, 3 types of nephridia can be found in an earthworm -Septal nephridia, Pharyngeal nephridia, and integumentary nephridia.
Coelum is the main body cavity which is lined by embryonic mesodermal cells. The true coelom is present in annelids. Flame cells are the organs of excretion and osmoregulation of Platyhelminthes which are flatworms. The gizzard is an additional chamber located in the alimentary canal of birds. It helps in the churning and crushing of food.
Note:
- The habitat of earthworms is cosmopolitan except the frigid zones of the arctic and Antarctica.
- They are found in moist soil rich in organic matter.
- They feed on decaying organic matter of plants and animals buried in the soil.
- They are regarded as ‘friends of farmers’ because they make the soil porous with their burrowing. Also, their nitrogenous wastes increase the fertility of the soil.
Complete answer:
Nephridia are the primary excretory organs of earthworm that carry out the duties of excretion and osmoregulation. Based on where they remove the metabolic wastes, they are of two types – enteronephric nephridia and enteronephric nephridia. Exonephric nephridia or ectonephric nephridia are the types of nephridia that directly remove the nitrogenous wastes outside the body of earthworm by nephridiopores( external opening of nephridia). Enteronephric nephridia eject their wastes into the alimentary canal.

So, the correct answer is ‘Nephridia.’
Additional Information: Based on location, 3 types of nephridia can be found in an earthworm -Septal nephridia, Pharyngeal nephridia, and integumentary nephridia.
| Properties | Septal Nephridia | Pharyngeal Nephridia | Integumentary Nephridia |
| Location | Attached to the septa. | Lie on the sides of the gut. | Attached to the inner lining of the body wall. |
| Opening of nephridia | In the intestine | Ducts of the 6th segment open into the buccal cavity while those of 4th and 5th open into the pharynx. | Directly to the outside. |
| Type | Enteronephric | Enteronephric | Ecto Nephric |
| Waste removal | Remove metabolic wastes from the blood and coelomic fluid | Remove metabolic wastes from the blood only. | Remove metabolic wastes from the blood only. |
Coelum is the main body cavity which is lined by embryonic mesodermal cells. The true coelom is present in annelids. Flame cells are the organs of excretion and osmoregulation of Platyhelminthes which are flatworms. The gizzard is an additional chamber located in the alimentary canal of birds. It helps in the churning and crushing of food.
Note:
- The habitat of earthworms is cosmopolitan except the frigid zones of the arctic and Antarctica.
- They are found in moist soil rich in organic matter.
- They feed on decaying organic matter of plants and animals buried in the soil.
- They are regarded as ‘friends of farmers’ because they make the soil porous with their burrowing. Also, their nitrogenous wastes increase the fertility of the soil.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




