
Exodermis occurs in
(a)Monocot root
(b)Dicot root
(c)Leaf
(d)stem
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The exodermis acts as a physiological barrier and has a role in root function and protection. The exodermis is a membrane, which is variable and can adjust according to the soil. It is responsible for the radial flow of water, ions, and nutrients.
Complete answer:
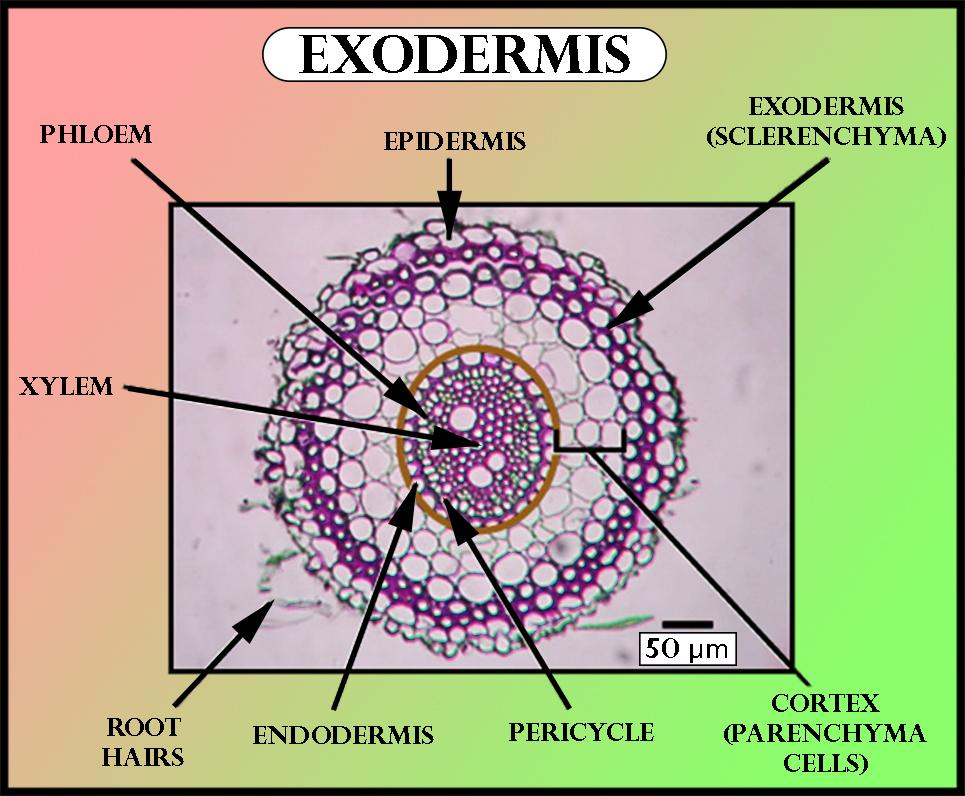
The exodermis occurs in the roots of the monocot plant. After the loss of the epidermis, the external cells of the overall cortex are suberized (with a material called suberin) and become a thick-walled layer called exodermis. The exodermis is the external layer of a plant's cortex, serves a twofold capacity by shielding the root from the intrusion by unfamiliar microbes, and guarantees that the plant doesn’t lose water. The plants can lose water through diffusion, through the root framework and can appropriately renew their stores at a good rate.
Additional Information: -The exodermis is a special type of hypodermis and has Casparian strips in its cell wall, as well as further wall modifications. The strips function to prevent solution backflow into the cortex and to maintain root pressure.
-The Casparian strip is also involved in ensuring that soil is not pulled directly into the root system during the uptake of nutrients.
-The exodermis can modify its permeability in response to a different external stimulus, it can change to better suit the root's requirements.
So, the correct answer is, ’Monocot root.’
Note: Many angiosperms including onion, maize, and sunflower plants have an exodermis layer on the outermost layer of the cortex and the outermost layer of almost all seeded vascular plants. It is not present in seedless vascular plants.
Complete answer:
The exodermis occurs in the roots of the monocot plant. After the loss of the epidermis, the external cells of the overall cortex are suberized (with a material called suberin) and become a thick-walled layer called exodermis. The exodermis is the external layer of a plant's cortex, serves a twofold capacity by shielding the root from the intrusion by unfamiliar microbes, and guarantees that the plant doesn’t lose water. The plants can lose water through diffusion, through the root framework and can appropriately renew their stores at a good rate.
Additional Information: -The exodermis is a special type of hypodermis and has Casparian strips in its cell wall, as well as further wall modifications. The strips function to prevent solution backflow into the cortex and to maintain root pressure.
-The Casparian strip is also involved in ensuring that soil is not pulled directly into the root system during the uptake of nutrients.
-The exodermis can modify its permeability in response to a different external stimulus, it can change to better suit the root's requirements.
So, the correct answer is, ’Monocot root.’
Note: Many angiosperms including onion, maize, and sunflower plants have an exodermis layer on the outermost layer of the cortex and the outermost layer of almost all seeded vascular plants. It is not present in seedless vascular plants.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




