
Explain about Transverse Waves?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Waves can be described as disturbances that propagate from one spot to another through a medium. Waves can be found in a variety of shapes and sizes. While all waves have the same standard qualities and behavior, some waves can be separated from others by specific observable characteristics. One method of classification is based on the direction of movement of individual particles in the medium about the direction of wave propagation. On this basis, waves are classified into two types: transverse waves and longitudinal waves. A transverse wave is one in which the particles move perpendicular to the wave's propagation direction.
Complete answer:
Transverse Waves:
A transverse wave is a moving wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the wave's direction. By securing one end of the thread and moving the other up and down, a rudimentary demonstration of the wave can be constructed on a horizontal length of a string. Light is another example of a transverse wave, with oscillations that are at right angles to the ideal light rays that describe the propagation route.
Transverse waves are prevalent in elastic solids, and oscillations are the displacement of solid particles from their relaxed state in the direction perpendicular to the wave's propagation. Because these displacements correlate to local shear deformation of the material, transverse waves of this type are referred to as shear waves. Shear waves are sometimes known as secondary waves or S-waves in seismology.
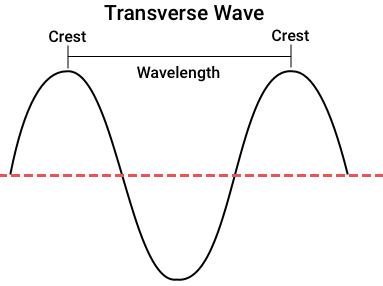
Note: The vibrations of transverse waves are perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
Examples of transverse waves:
Ripples on the water surface,
vibrations in a guitar string,
Mexican wave at a sports stadium.
Examples of electromagnetic waves include light waves, microwaves, and radio waves.
S-waves in the seismic field.
Complete answer:
Transverse Waves:
A transverse wave is a moving wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the wave's direction. By securing one end of the thread and moving the other up and down, a rudimentary demonstration of the wave can be constructed on a horizontal length of a string. Light is another example of a transverse wave, with oscillations that are at right angles to the ideal light rays that describe the propagation route.
Transverse waves are prevalent in elastic solids, and oscillations are the displacement of solid particles from their relaxed state in the direction perpendicular to the wave's propagation. Because these displacements correlate to local shear deformation of the material, transverse waves of this type are referred to as shear waves. Shear waves are sometimes known as secondary waves or S-waves in seismology.

Note: The vibrations of transverse waves are perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
Examples of transverse waves:
Ripples on the water surface,
vibrations in a guitar string,
Mexican wave at a sports stadium.
Examples of electromagnetic waves include light waves, microwaves, and radio waves.
S-waves in the seismic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




