
Explain Dixon-Jolly of the ascent of sap with a diagram.
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: The 'Dixon-Jolly' hypothesis was introduced in 1894 by Dixon and Jolly. According to this theory, water molecules are in constant motion and are strongly attracted to one another, forming a continuous column of water xylem elements, with water being drawn upwards by transpiration.
Complete answer:
The ascent of sap is the upward movement of water and minerals through the xylem vessels. This theory was put forward by Dixon and Jolly. The following are the key characteristics of this theory:
Water's tensile strength has a strong cohesion force: The theory is founded on the following facts: I. Water molecules have a deep mutual attraction (cohesion) with one another and are difficult to separate. (ii) Water molecules and xylem element walls are attracted to each other (cohesion). Together, the cohesive and adhesive attractions keep the water column in the xylem. In xylem tracheids, the cohesive and adhesive attractions work together to keep the water column stable.
Water column continuity in the plant: Evidence for the presence of air bubbles in the water column of xylem elements has been a strong objection to the theory. They disrupt the water column's continuity.
Stress on the unbroken water column due to transpiration: Water is lost from the mesophyll cells to the intercellular spaces as a result of transpiration. Stomata are the openings in the plant that enable water vapour to escape. As a result, the DPD of mesophyll rises. These cells consume water from neighbouring cells as their DPD rises.
Water is eventually drained from the xylem components of the leaf's vascular bundles. Since the xylem elements are filled with a continuous water column, this stress is conveyed down from the roots, causing water to rise.
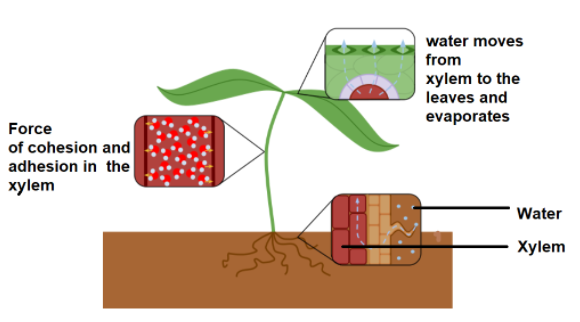
Note: From the theory it is clear that water ascends in plants due to transpiration pull, and the water column stays continuous due to the unified force of water molecules. This is the most widely known hypothesis at the moment. The force of cohesion between the water molecules and the adhesion between the water and the xylem column is very much essential for the upward movement of water.
Complete answer:
The ascent of sap is the upward movement of water and minerals through the xylem vessels. This theory was put forward by Dixon and Jolly. The following are the key characteristics of this theory:
Water's tensile strength has a strong cohesion force: The theory is founded on the following facts: I. Water molecules have a deep mutual attraction (cohesion) with one another and are difficult to separate. (ii) Water molecules and xylem element walls are attracted to each other (cohesion). Together, the cohesive and adhesive attractions keep the water column in the xylem. In xylem tracheids, the cohesive and adhesive attractions work together to keep the water column stable.
Water column continuity in the plant: Evidence for the presence of air bubbles in the water column of xylem elements has been a strong objection to the theory. They disrupt the water column's continuity.
Stress on the unbroken water column due to transpiration: Water is lost from the mesophyll cells to the intercellular spaces as a result of transpiration. Stomata are the openings in the plant that enable water vapour to escape. As a result, the DPD of mesophyll rises. These cells consume water from neighbouring cells as their DPD rises.
Water is eventually drained from the xylem components of the leaf's vascular bundles. Since the xylem elements are filled with a continuous water column, this stress is conveyed down from the roots, causing water to rise.

Note: From the theory it is clear that water ascends in plants due to transpiration pull, and the water column stays continuous due to the unified force of water molecules. This is the most widely known hypothesis at the moment. The force of cohesion between the water molecules and the adhesion between the water and the xylem column is very much essential for the upward movement of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




