
Explain electron spin and intrinsic properties of electrons
Answer
474.6k+ views
Hint: The intrinsic spin of an electron is fundamentally a classical mechanical phenomenon and is associated with the angular momentum of the electron wavefield.
An electron has three intrinsic properties they are charge, spin, and orbital angular momentum.
The electron is then not spinning. It does have characteristics of a spinning object containing an electrical charge.
Complete answer:
A spin of an electron is a degree of freedom, just like the position and momentum of a particle. If the particle force is zero, then its momentum is conserved and in the same way, as long as there is no torque on the system, the spin is also conserved.
But No torque on the system sounds like Angular momentum should be conserved, and yes it is, but spin in Quantum mechanics follows the same algebra that angular momentum does and to a large extent has a similar behavior(actually the total angular momentum is the sum of spin + orbital angular momentum).
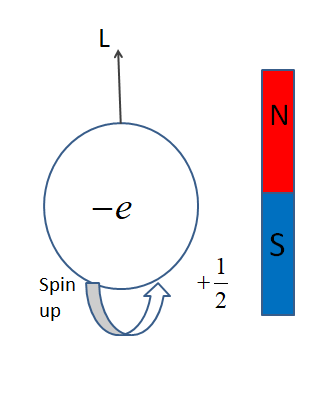
Each elementary particle is characterized by its quantum numbers like charge, baryon or lepton numbers, spin, isospin, parity, and of course its mass.
All particle characteristics can be visualized from the compilation updated each year by the Particle Data Group.
Note:
Electrons have the intrinsic angular momentum they were like rotating tiny spheres but attempts to calculate their angular momenta from hypothetical rotation have failed.
Spin is a term that has stuck based on them as if the idea.
The intrinsic angular momentum of an electron creates a corresponding magnetic moment so the electrons are effectively really tiny magnets.
An electron has three intrinsic properties they are charge, spin, and orbital angular momentum.
The electron is then not spinning. It does have characteristics of a spinning object containing an electrical charge.
Complete answer:
A spin of an electron is a degree of freedom, just like the position and momentum of a particle. If the particle force is zero, then its momentum is conserved and in the same way, as long as there is no torque on the system, the spin is also conserved.
But No torque on the system sounds like Angular momentum should be conserved, and yes it is, but spin in Quantum mechanics follows the same algebra that angular momentum does and to a large extent has a similar behavior(actually the total angular momentum is the sum of spin + orbital angular momentum).

Each elementary particle is characterized by its quantum numbers like charge, baryon or lepton numbers, spin, isospin, parity, and of course its mass.
All particle characteristics can be visualized from the compilation updated each year by the Particle Data Group.
Note:
Electrons have the intrinsic angular momentum they were like rotating tiny spheres but attempts to calculate their angular momenta from hypothetical rotation have failed.
Spin is a term that has stuck based on them as if the idea.
The intrinsic angular momentum of an electron creates a corresponding magnetic moment so the electrons are effectively really tiny magnets.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




