
Explain esterification reaction with the help of a chemical equation. Describe an activity to show esterification.
Answer
564k+ views
Hint: Esters are a class of organic compounds which are also called as derivatives of carboxylic acids. They are obtained by the substitution of hydrogen atoms of acid by an alkyl group.
Complete step by step answer: Esterification reaction is a named reaction in organic chemistry discovered by Hermann Emil Louis Fischer. The reaction is achieved by heating a mixture of carboxylic acid and alcohol in presence of acid catalyst.
The role of the catalyst is to protonate the carbonyl oxygen atom which increases the electrophilicity of the carbon. Thus this makes the attack of the hydroxyl group of alcohol facile and smooth. Generally sulfuric acid or Lewis acid are employed for this purpose.
The first step is a reversible reaction which involves protonation of the carbonyl oxygen atom. The second step involves attack of the alcohol hydroxyl group to the carbonyl carbon. The last step involves the release of a water molecule thereby producing the desired ester compound.
Let us consider the esterification reaction of acetic acid and ethanol. The step by step sequence is shown as follows:
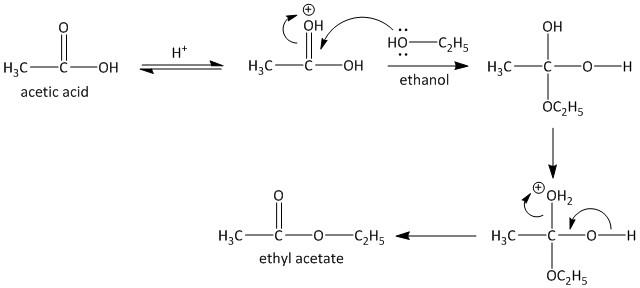
The activity performed to observe the esterification reaction is as follows:
Take a mixture of acetic acid in ethanol solvent in a conical flask. To this solution added a few drops of sulfuric acid. The reaction mixture is boiled over a hot water bath for five to ten minutes. The contents of the mixture are poured into water taken in a beaker. A sweet odour is observed which indicates the formation of ester compounds. Thus reaction is referred as esterification reaction in which ethyl acetate is formed.
Note:
The inverse of esterification reaction is a saponification reaction where water are converted into carboxylic acid and alcohol. The use of esters is mainly due to the characteristic odour as synthetic flavors.
Complete step by step answer: Esterification reaction is a named reaction in organic chemistry discovered by Hermann Emil Louis Fischer. The reaction is achieved by heating a mixture of carboxylic acid and alcohol in presence of acid catalyst.
The role of the catalyst is to protonate the carbonyl oxygen atom which increases the electrophilicity of the carbon. Thus this makes the attack of the hydroxyl group of alcohol facile and smooth. Generally sulfuric acid or Lewis acid are employed for this purpose.
The first step is a reversible reaction which involves protonation of the carbonyl oxygen atom. The second step involves attack of the alcohol hydroxyl group to the carbonyl carbon. The last step involves the release of a water molecule thereby producing the desired ester compound.
Let us consider the esterification reaction of acetic acid and ethanol. The step by step sequence is shown as follows:

The activity performed to observe the esterification reaction is as follows:
Take a mixture of acetic acid in ethanol solvent in a conical flask. To this solution added a few drops of sulfuric acid. The reaction mixture is boiled over a hot water bath for five to ten minutes. The contents of the mixture are poured into water taken in a beaker. A sweet odour is observed which indicates the formation of ester compounds. Thus reaction is referred as esterification reaction in which ethyl acetate is formed.
Note:
The inverse of esterification reaction is a saponification reaction where water are converted into carboxylic acid and alcohol. The use of esters is mainly due to the characteristic odour as synthetic flavors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




