
Explain Hoffmann's exhaustive alkylation with examples.
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: To explain Hoffmann's exhaustive alkylation, we first need to know what is Hoffmann's rule. According to Hoffmann's rule, during elimination reactions, the alkene which is the least substituted will be formed as a major product.
Complete answer:
Hoffmann's rule stated that in eliminating reactions of an amine, the outcome of the product is heavily dependent on the steric effects. Since the least substituted position in an alkane is the least hindered, the loss of $\beta $-hydrogen occurs from this position.
\[-C{{H}_{3}}>-C{{H}_{2}}R>-CH{{R}_{2}}\]
This is why the olefin or the alkene which is the least substituted will be formed as a major product. The product formed is known as Hoffman Product.
Now, when an amine is treated with an excess of an alkyl iodide to form an alkene, the process is known as Hoffman exhaustive alkylation.
The alkyl iodide used in Hoffman exhaustive alkylation is methyl iodide $C{{H}_{3}}I$ because it does not contain any $\beta $-hydrogens and hence cannot take part in the elimination reaction itself. So, the process is also known as Hoffman exhaustive methylation.
Let us understand the mechanism of Hoffman exhaustive methylation by taking dimethylcyclooctanamine as the amine which is used to synthesize cyclooctene.
- First, the excess methyl iodide attacks the $\beta $-hydrogens of the dimethylcyclooctanamine to form an ammonium iodide salt.
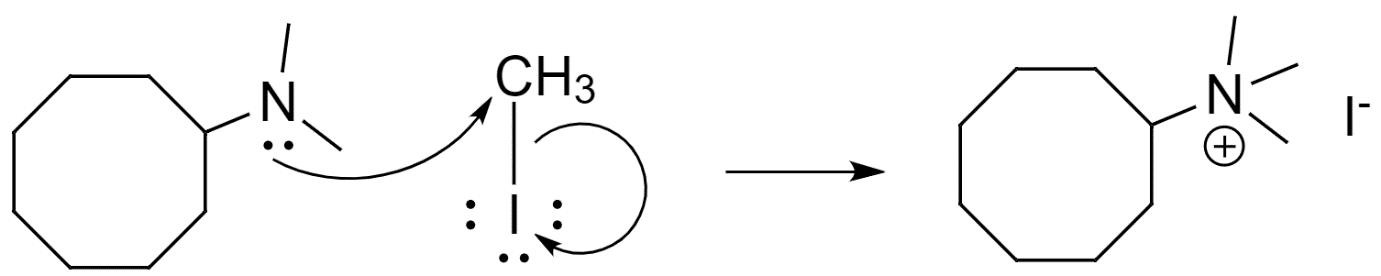
- The iodide ion formed is substituted with the hydroxide ion. This is done by reacting silver oxide and iodide and water being deprotonated successively by the ion of silver oxide.
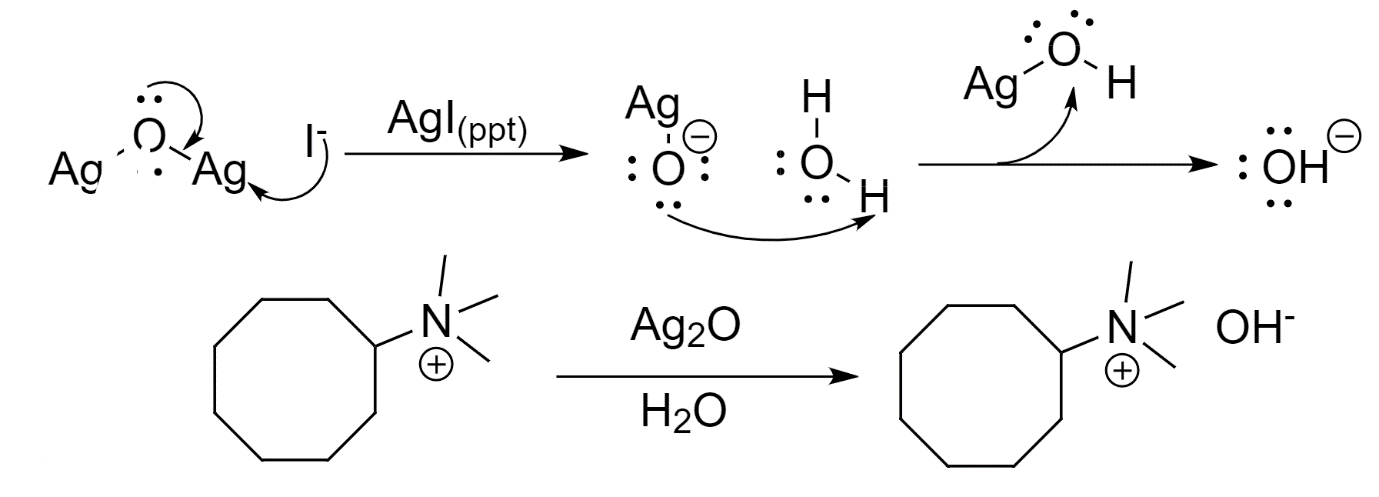
- Finally, to facilitate the elimination reaction, the reaction mixture is heated to obtain cyclooctene.
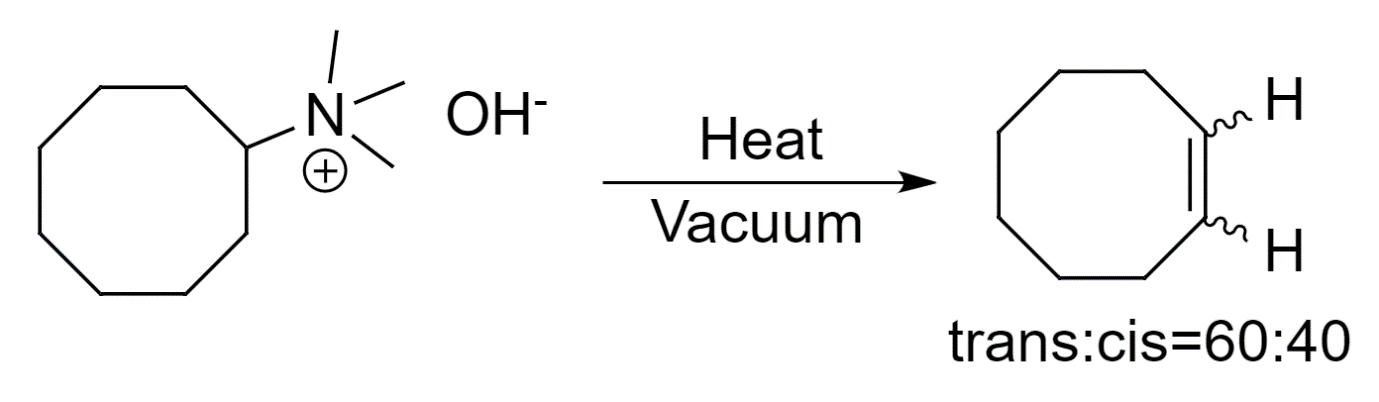
- Further, trans-cyclooctene can be isolated from the cis-trans mixture of products as follows
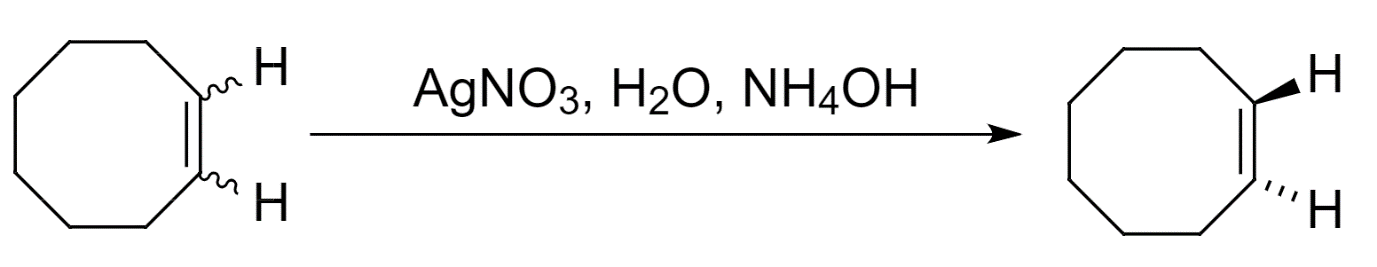
Note:
It should be noted that among neutral $-N{{H}_{3}}$ groups, anionic $-N{{H}_{2}}$ and $-N{{R}_{2}}$ groups, the better leaving group is neutral $-N{{H}_{3}}$. Large leaving groups also affect the products formed in the reaction due to steric effects.
Complete answer:
Hoffmann's rule stated that in eliminating reactions of an amine, the outcome of the product is heavily dependent on the steric effects. Since the least substituted position in an alkane is the least hindered, the loss of $\beta $-hydrogen occurs from this position.
\[-C{{H}_{3}}>-C{{H}_{2}}R>-CH{{R}_{2}}\]
This is why the olefin or the alkene which is the least substituted will be formed as a major product. The product formed is known as Hoffman Product.
Now, when an amine is treated with an excess of an alkyl iodide to form an alkene, the process is known as Hoffman exhaustive alkylation.
The alkyl iodide used in Hoffman exhaustive alkylation is methyl iodide $C{{H}_{3}}I$ because it does not contain any $\beta $-hydrogens and hence cannot take part in the elimination reaction itself. So, the process is also known as Hoffman exhaustive methylation.
Let us understand the mechanism of Hoffman exhaustive methylation by taking dimethylcyclooctanamine as the amine which is used to synthesize cyclooctene.
- First, the excess methyl iodide attacks the $\beta $-hydrogens of the dimethylcyclooctanamine to form an ammonium iodide salt.
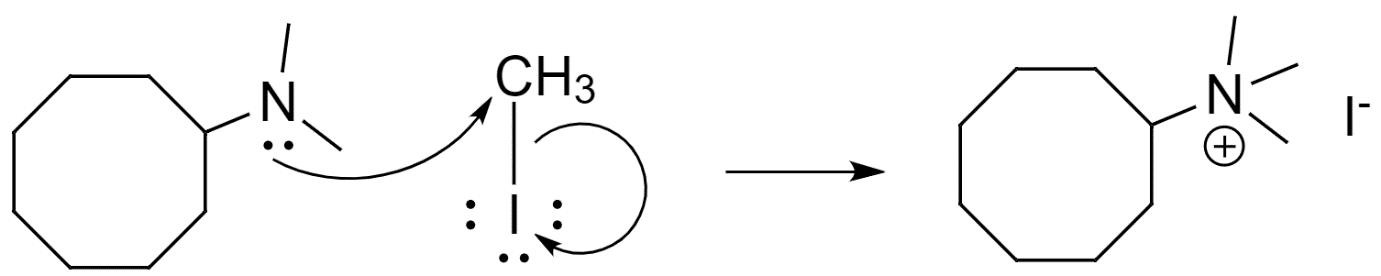
- The iodide ion formed is substituted with the hydroxide ion. This is done by reacting silver oxide and iodide and water being deprotonated successively by the ion of silver oxide.

- Finally, to facilitate the elimination reaction, the reaction mixture is heated to obtain cyclooctene.

- Further, trans-cyclooctene can be isolated from the cis-trans mixture of products as follows
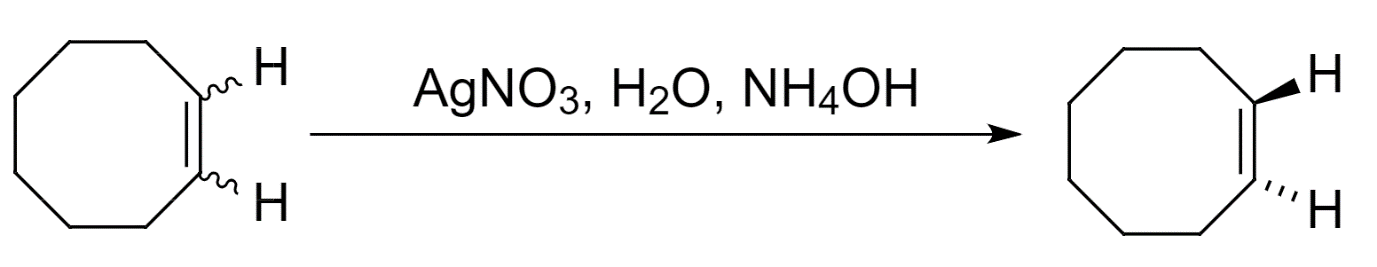
Note:
It should be noted that among neutral $-N{{H}_{3}}$ groups, anionic $-N{{H}_{2}}$ and $-N{{R}_{2}}$ groups, the better leaving group is neutral $-N{{H}_{3}}$. Large leaving groups also affect the products formed in the reaction due to steric effects.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




