
Explain hybridization of central atom in: $Br{{F}_{5}}$
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: The Coordination number of the bromine atom is 5 with one lone pair present on the bromine atom. The geometry of the compound $Br{{F}_{5}}$ is Square pyramidal with a bond angle of ${{90}^{{}^\circ }}$ each. Concept of hybridization is explained by the VSEPR theory.
Complete step by step answer:
Redistribution of the energy of orbitals of individual atoms to give orbitals of equivalent energy happens when two atomic orbitals combine together to form hybrid orbital in a molecule. This process is called Hybridisation. The new orbitals thus formed are called hybrid orbitals.
Bromine Pentafluoride is a chemical compound with strong odour , high toxicity and is corrosive in nature. It is a colourless liquid.
The electronic configuration of bromine atom is $1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}},2{{p}^{6}},3{{s}^{2}},3{{p}^{6}},3{{d}^{10}},4{{s}^{2}},4{{p}^{5}}$.
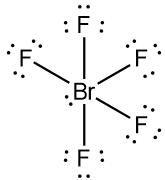
In order to obtain pentavalency, some of the electrons in the p-orbitals are shifted to the 4d-orbitals. Two of the electrons of the p-orbitals become unpaired. Bromine will come in an excited state and hybridization occurs. During the hybridization one 4s, and three 4p and two 4d orbitals take part in the process giving rise to $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals. Five valence electrons of bromine will be used to form sigma bonds with 5 fluorine atoms. The molecule will consist of one lone pair.
Note: During the process of hybridization, the atomic orbitals of similar energy are mixed together such as the mixing of two ‘s’ orbitals or two ‘p’ orbitals or mixing of an ‘s’ orbital with a ‘p’ orbital or ‘s’ with a ‘d’ orbital.
Complete step by step answer:
Redistribution of the energy of orbitals of individual atoms to give orbitals of equivalent energy happens when two atomic orbitals combine together to form hybrid orbital in a molecule. This process is called Hybridisation. The new orbitals thus formed are called hybrid orbitals.
Bromine Pentafluoride is a chemical compound with strong odour , high toxicity and is corrosive in nature. It is a colourless liquid.
The electronic configuration of bromine atom is $1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}},2{{p}^{6}},3{{s}^{2}},3{{p}^{6}},3{{d}^{10}},4{{s}^{2}},4{{p}^{5}}$.

In order to obtain pentavalency, some of the electrons in the p-orbitals are shifted to the 4d-orbitals. Two of the electrons of the p-orbitals become unpaired. Bromine will come in an excited state and hybridization occurs. During the hybridization one 4s, and three 4p and two 4d orbitals take part in the process giving rise to $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals. Five valence electrons of bromine will be used to form sigma bonds with 5 fluorine atoms. The molecule will consist of one lone pair.
Note: During the process of hybridization, the atomic orbitals of similar energy are mixed together such as the mixing of two ‘s’ orbitals or two ‘p’ orbitals or mixing of an ‘s’ orbital with a ‘p’ orbital or ‘s’ with a ‘d’ orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




