
Explain hybridization of central atom in: ${H_2}O$
Answer
609k+ views
Hint- In order to deal with this question first we will come to know what are the proper steps to determine the hybridization of any compound on the basis of the VSEPR model then according to it we will explain the hybridization of ${H_2}O$.
Complete answer:
These are some steps that will help us to determine hybridization of any compound:
1) Look at the atom.
2) Count the number of other atoms which are connected to that atom (atoms – not bonds!)
3) Then Count for the number of the lone pairs which are attached to it.
4) Add these two numbers together.
- If it’s 4, your atom is $s{p^3}$ .
- If it’s 3, your atom is $s{p^2}$.
- If it’s 2, your atom is $sp$.
(If it’s 1, it’s probably hydrogen!)
Structure of ${H_2}O$ is:
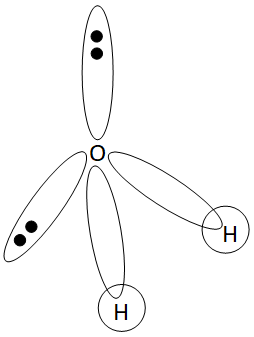
Given compound is ${H_2}O$.
- In ${H_2}O$ , O is the central atom and its one 2s of three 2p orbitals hybridized to give four $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals.
- Two $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals having unpaired electrons overlap with the s-orbital of H to form two $H - O$ $s{p^3} = s$ bonds.
- Geometry is tetrahedral.
- Bond angles reduced to ${104.5^0}$ from ${109.5^0}$ due to more lone pair repulsion and hence the molecule requires a V−shape.
Note- The abbreviated Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory as VSEPR theory is based on the premise that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a way that minimizes this repulsion by the electron pair. That atom structure determines the geometry of the resulting molecule. Students must remember some important points of this theory in order to solve such questions.
Complete answer:
These are some steps that will help us to determine hybridization of any compound:
1) Look at the atom.
2) Count the number of other atoms which are connected to that atom (atoms – not bonds!)
3) Then Count for the number of the lone pairs which are attached to it.
4) Add these two numbers together.
- If it’s 4, your atom is $s{p^3}$ .
- If it’s 3, your atom is $s{p^2}$.
- If it’s 2, your atom is $sp$.
(If it’s 1, it’s probably hydrogen!)
Structure of ${H_2}O$ is:

Given compound is ${H_2}O$.
- In ${H_2}O$ , O is the central atom and its one 2s of three 2p orbitals hybridized to give four $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals.
- Two $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals having unpaired electrons overlap with the s-orbital of H to form two $H - O$ $s{p^3} = s$ bonds.
- Geometry is tetrahedral.
- Bond angles reduced to ${104.5^0}$ from ${109.5^0}$ due to more lone pair repulsion and hence the molecule requires a V−shape.
Note- The abbreviated Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory as VSEPR theory is based on the premise that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a way that minimizes this repulsion by the electron pair. That atom structure determines the geometry of the resulting molecule. Students must remember some important points of this theory in order to solve such questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




