
Explain Kolbe Schmitt reaction and Fries rearrangement reaction
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Kolbe Schmitt reaction is also known as Kolbe’s reaction which is named after Herman Kolbe and Rudolf Schmitt which is basically a carboxylation reaction that takes place by heating sodium salt of phenol in presence of carbon dioxide at a pressure of hundred atm. Fries rearrangement reaction: It is a reaction in which a rearrangement reaction of a phenolic ester to a hydroxyl aryl ketone in the presence of Lewis acid such as aluminium chloride.
Complete step by step solution:
We consider Kolbe’s reaction first. The Kolbe reaction is aimed towards formation of an aromatic hydroxy acid known as salicylic acid by the carboxylation of sodium salt of phenol. It is an addition reaction which proceeds via the nucleophilic addition of a phenoxide to give salicylate .Then it reacts with sulfuric acid to form salicylic acid. The mechanism is shown below as follows
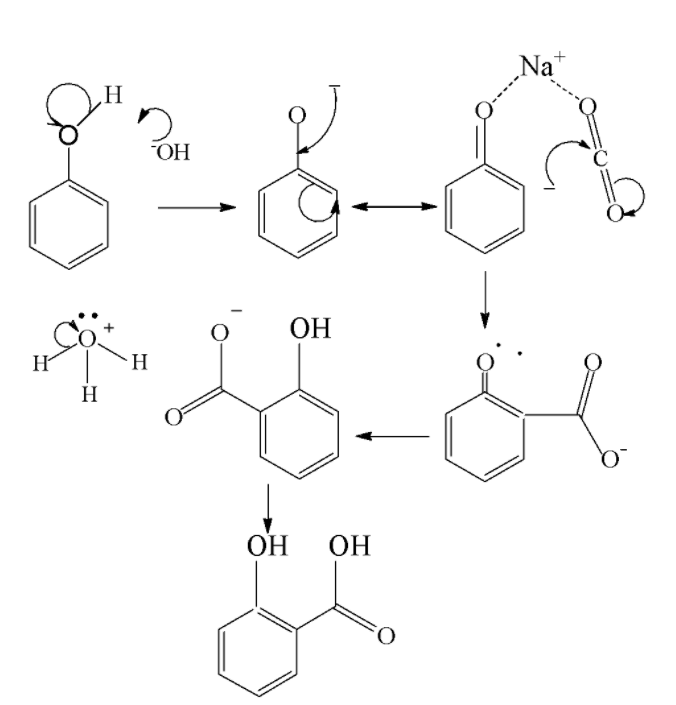
The electrophile here is carbon dioxide. After addition of phenoxide it reacts with sulfuric acid it forms salicylic acid as the end product.
Fries rearrangement reaction: It is a rearrangement reaction in which an aryl ester is transformed into a hydroxyl aryl ketone with the help of a Lewis acid catalyst and an aqueous acid. In this very reaction the acyl group belonging to the phenolic ester migrates to the aryl ring. The mechanism is given as follows
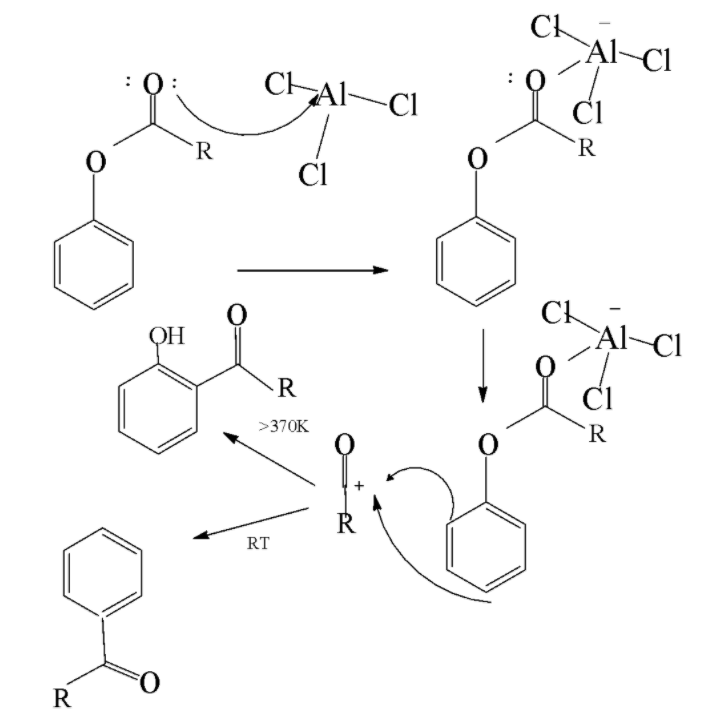
In the above mechanism the oxygen attached with the acyl group forms a complex with Lewis acid catalyst .Now the bond between phenolic oxygen and complex becomes polar leading to the rearrangement of the aluminium chloride bond to the phenolic oxygen. This results in the generation of acylium carbocation .Now the acylium carbocation attacks the aromatic ring and forms product via the electrophilic aromatic substitution route to form hydroxyl aryl ketone product.
Note: The Kolbe reaction is used for preparation of salicylic acid derivatives as well. Fries rearrangement is an ortho-para selective which is dependent on conditions like temperature and the solvent used in the reaction. The use of non - polar solvent favors formation of ortho products and polar solvents favor para products.
Complete step by step solution:
We consider Kolbe’s reaction first. The Kolbe reaction is aimed towards formation of an aromatic hydroxy acid known as salicylic acid by the carboxylation of sodium salt of phenol. It is an addition reaction which proceeds via the nucleophilic addition of a phenoxide to give salicylate .Then it reacts with sulfuric acid to form salicylic acid. The mechanism is shown below as follows

The electrophile here is carbon dioxide. After addition of phenoxide it reacts with sulfuric acid it forms salicylic acid as the end product.
Fries rearrangement reaction: It is a rearrangement reaction in which an aryl ester is transformed into a hydroxyl aryl ketone with the help of a Lewis acid catalyst and an aqueous acid. In this very reaction the acyl group belonging to the phenolic ester migrates to the aryl ring. The mechanism is given as follows

In the above mechanism the oxygen attached with the acyl group forms a complex with Lewis acid catalyst .Now the bond between phenolic oxygen and complex becomes polar leading to the rearrangement of the aluminium chloride bond to the phenolic oxygen. This results in the generation of acylium carbocation .Now the acylium carbocation attacks the aromatic ring and forms product via the electrophilic aromatic substitution route to form hydroxyl aryl ketone product.
Note: The Kolbe reaction is used for preparation of salicylic acid derivatives as well. Fries rearrangement is an ortho-para selective which is dependent on conditions like temperature and the solvent used in the reaction. The use of non - polar solvent favors formation of ortho products and polar solvents favor para products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




