
Explain myopia with the help of a ray diagram?
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Myopia is a vision disorder in which we can have a clear look of closer objects but the far objects appear blurry. It is also known as near-sightedness.
Complete step by step answer:
For normal eye functioning, the cornea, and lens bend light so it focuses on the retina. The retina behaves like a screen where the picture is formed by the bending of light rays. It sends the picture to the brain through the optic nerve, which is actually part of the brain.
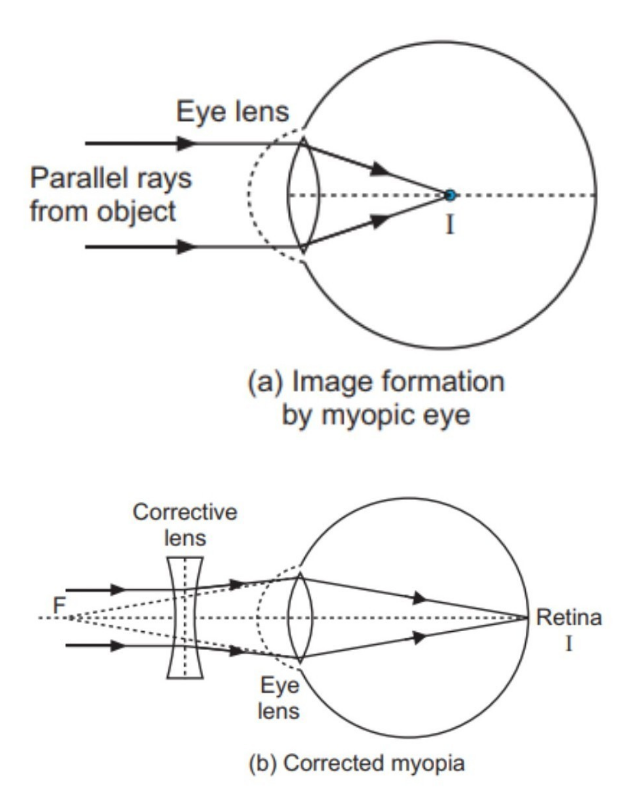
In a myopic disorder, the eye is longer than normal or has a cornea that is too steep. As a result, light rays focus in front of the retina instead of on it. Therefore, you can see near objects clearly, but distant objects will appear blurred. That’s the reason, this disorder is also called near-sightedness.
To correct the myopic defect of vision, we require a lens that can diverge the incoming rays. Out of both the lenses, the concave lens has the ability to diverge incoming rays. Therefore, it is used to correct this defect of vision. The image is allowed to form at the retina by using a concave lens of suitable power.
The myopic defect of vision as well as its correction is depicted below in the diagram.
Additional Information:
Myopia is a kind of refractive error. By refractive error, we mean that an error in the vision when the eye does not bend the light properly.
Note:
This question requires you to know the exact difference between different types of vision problems.
Myopia can be caused by
1. increase in curvature of the lens.
2. increase in the length of the eyeball
Complete step by step answer:
For normal eye functioning, the cornea, and lens bend light so it focuses on the retina. The retina behaves like a screen where the picture is formed by the bending of light rays. It sends the picture to the brain through the optic nerve, which is actually part of the brain.
In a myopic disorder, the eye is longer than normal or has a cornea that is too steep. As a result, light rays focus in front of the retina instead of on it. Therefore, you can see near objects clearly, but distant objects will appear blurred. That’s the reason, this disorder is also called near-sightedness.
To correct the myopic defect of vision, we require a lens that can diverge the incoming rays. Out of both the lenses, the concave lens has the ability to diverge incoming rays. Therefore, it is used to correct this defect of vision. The image is allowed to form at the retina by using a concave lens of suitable power.
The myopic defect of vision as well as its correction is depicted below in the diagram.

Additional Information:
Myopia is a kind of refractive error. By refractive error, we mean that an error in the vision when the eye does not bend the light properly.
Note:
This question requires you to know the exact difference between different types of vision problems.
Myopia can be caused by
1. increase in curvature of the lens.
2. increase in the length of the eyeball
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




