
Explain Rutherford’s \[\alpha \] ray scattering experiment with a neat diagram.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Rutherford’s experiment was regarding the proposal of the structure of atoms. He used a metal sheet in his experiment which was bombarded with particles. These particles are a form of radiation.
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram of Rutherford’s \[\alpha \] rays scattering experiment.
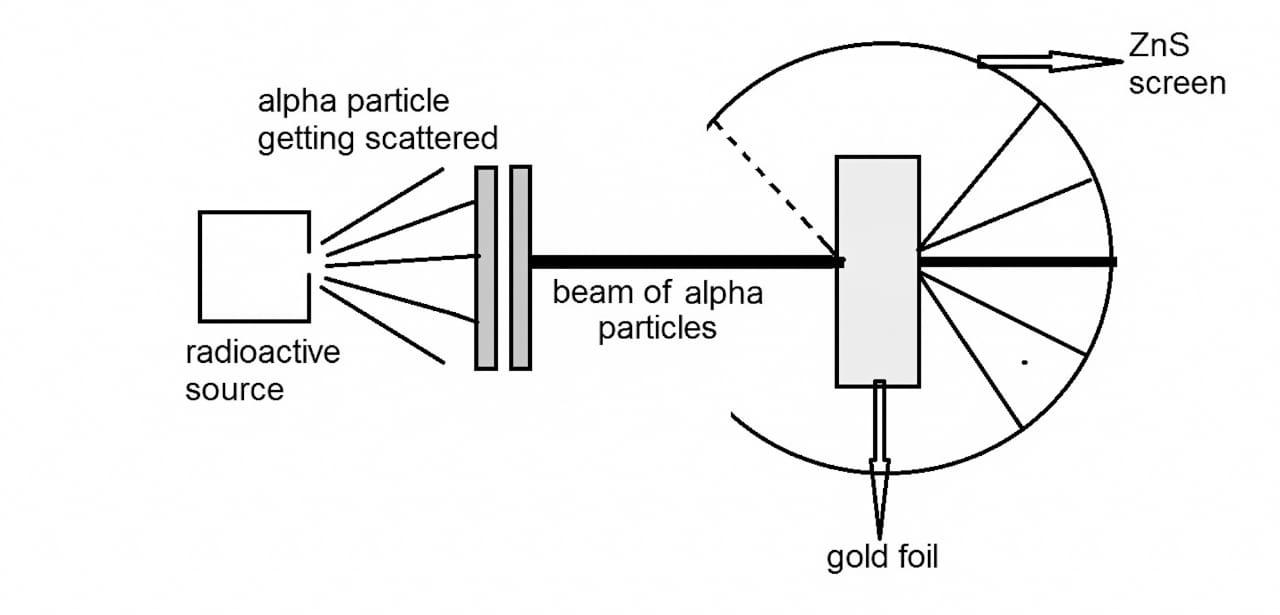
Rutherford used the observations of Thomson’s experiment to propose the atomic structure. Rutherford conducted the experiment using radioactivity phenomenon. He used radium bromide, ${\text{RaBr}}$ which is a radioactive material. This substance emits \[\alpha \] particle which is a form of radiation. These particles were bombarded on a thin gold metal sheet of thickness of a few nanometers. In order to observe the deflection of the particles he used a screen of zinc sulphide, ${\text{ZnS}}$ which was placed behind the gold foil. Rutherford then developed a detector which counts the number of radioactive particles. He initially recorded the count rate of ${\text{RaBr}}$ as if he made a note of $\alpha$ particles emitted per minute.
Rutherford made some observations in this experiment and gave the conclusions accordingly which are as follows:
1) Most of the \[\alpha \] particles passed through the thin sheet. This observation depicts that the maximum of the space in an atom is empty.
2) He then observed that some of the \[\alpha \] particles were deflected to some direction. This proved that the positive charge was not distributed uniformly throughout the atom.
3) He also observed that very few \[\alpha \] particles were deflected back. This was because of charges like repulsion. He then concluded that the positive charge in an atom is concentrated at a very small volume.
4) He also concluded that along with the positively charged particles most of the mass is concentrated in a very small volume. He called this region a nucleus.
5) He proposed that electrons are present in particular orbits around the nucleus of the atom. These electrons which are negatively charged species revolve around the nucleus.
5) Both the electrons which are negatively charged particles and the nucleus which is positively charged are held by electrostatic force of attraction.
Additional Information:
The size of the nucleus was found to be less than ${10^{ - 14}}$.
\[\alpha \] particles cause an explosive collision.
Note: Rutherford gave the basic structure of an atom which was further referred for experiments. He could not explain about the arrangement of the electrons in the orbits. Also, Rutherford could not explain the stability of the atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram of Rutherford’s \[\alpha \] rays scattering experiment.

Rutherford used the observations of Thomson’s experiment to propose the atomic structure. Rutherford conducted the experiment using radioactivity phenomenon. He used radium bromide, ${\text{RaBr}}$ which is a radioactive material. This substance emits \[\alpha \] particle which is a form of radiation. These particles were bombarded on a thin gold metal sheet of thickness of a few nanometers. In order to observe the deflection of the particles he used a screen of zinc sulphide, ${\text{ZnS}}$ which was placed behind the gold foil. Rutherford then developed a detector which counts the number of radioactive particles. He initially recorded the count rate of ${\text{RaBr}}$ as if he made a note of $\alpha$ particles emitted per minute.
Rutherford made some observations in this experiment and gave the conclusions accordingly which are as follows:
1) Most of the \[\alpha \] particles passed through the thin sheet. This observation depicts that the maximum of the space in an atom is empty.
2) He then observed that some of the \[\alpha \] particles were deflected to some direction. This proved that the positive charge was not distributed uniformly throughout the atom.
3) He also observed that very few \[\alpha \] particles were deflected back. This was because of charges like repulsion. He then concluded that the positive charge in an atom is concentrated at a very small volume.
4) He also concluded that along with the positively charged particles most of the mass is concentrated in a very small volume. He called this region a nucleus.
5) He proposed that electrons are present in particular orbits around the nucleus of the atom. These electrons which are negatively charged species revolve around the nucleus.
5) Both the electrons which are negatively charged particles and the nucleus which is positively charged are held by electrostatic force of attraction.
Additional Information:
The size of the nucleus was found to be less than ${10^{ - 14}}$.
\[\alpha \] particles cause an explosive collision.
Note: Rutherford gave the basic structure of an atom which was further referred for experiments. He could not explain about the arrangement of the electrons in the orbits. Also, Rutherford could not explain the stability of the atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




