
Explain sky wave propagation by making a diagram.
Answer
603.3k+ views
- Hint: To solve this question, we need to focus more on the topic Skywave propagation. understanding the meaning of radio wave propagation defining is important. High frequency wave propagation is the features of these waves as they travel from one section to the other or into various parts of the earth atmosphere.
Complete step-by-step solution -
To understand the significations of sky wave propagation.
Following is the classification of these waves:
Ground waves propagation
Skywave propagation
Free space propagation
Radio waves propagation is refracted (or reflected) back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere in Skywave propagation. thus, it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, and it can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is very widely used in the shortwave frequency bands.
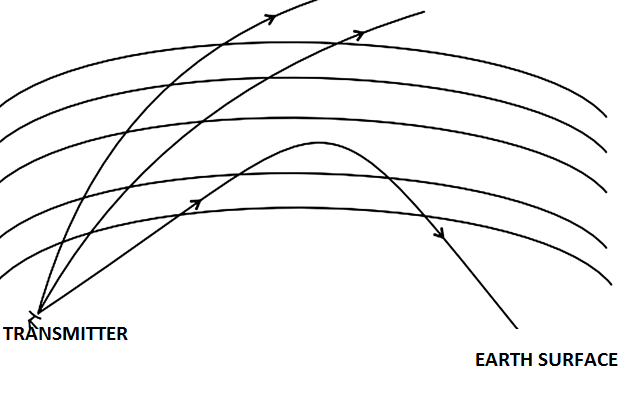
Upper region of the atmosphere is called the ionosphere, nearly about 80 km to 1000 km in altitude, where neutral air is ionized by solar photons and cosmic rays. High frequency signals enter the upper region of the ionosphere obliquely and they are back-scattered from this layer as scatter waves. When ionization is strong in the middle of this layer enough compared to the signal frequency, a scatter wave can exit the bottom of the layer earthwards as if reflected from a mirror. Surface near the earth (ground or water) then diffusely reflects the incoming wave back towards the lower region of the ionosphere. Consequently, the signal may effectively bounce between the earth and ionosphere two or more times (multihop propagation).
Hence, signals of only a few watts may sometimes be received many thousands of miles away as a result of this. This is what enables shortwave broadcasts to travel all over the world. ionization is not great enough in this region, then it will scatter waves deflected downwards, and subsequently upwards (above the layer peak) such that it exits the top of the layer slightly displaced. This wave propagation exhibits in the waveguide formed by the ground and ionosphere and each serving as reflectors.
Note-Shortwave frequencies (and also Medium wave) can be refracted back to the surface of earth which is beyond the horizon of earth which makes them very beneficial in the transcontinental transmission of the waves.
Complete step-by-step solution -
To understand the significations of sky wave propagation.
Following is the classification of these waves:
Ground waves propagation
Skywave propagation
Free space propagation
Radio waves propagation is refracted (or reflected) back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere in Skywave propagation. thus, it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, and it can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is very widely used in the shortwave frequency bands.

Upper region of the atmosphere is called the ionosphere, nearly about 80 km to 1000 km in altitude, where neutral air is ionized by solar photons and cosmic rays. High frequency signals enter the upper region of the ionosphere obliquely and they are back-scattered from this layer as scatter waves. When ionization is strong in the middle of this layer enough compared to the signal frequency, a scatter wave can exit the bottom of the layer earthwards as if reflected from a mirror. Surface near the earth (ground or water) then diffusely reflects the incoming wave back towards the lower region of the ionosphere. Consequently, the signal may effectively bounce between the earth and ionosphere two or more times (multihop propagation).
Hence, signals of only a few watts may sometimes be received many thousands of miles away as a result of this. This is what enables shortwave broadcasts to travel all over the world. ionization is not great enough in this region, then it will scatter waves deflected downwards, and subsequently upwards (above the layer peak) such that it exits the top of the layer slightly displaced. This wave propagation exhibits in the waveguide formed by the ground and ionosphere and each serving as reflectors.
Note-Shortwave frequencies (and also Medium wave) can be refracted back to the surface of earth which is beyond the horizon of earth which makes them very beneficial in the transcontinental transmission of the waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




