
Explain symbiotic nitrogen fixation.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Some prokaryotes help the plants in converting the inert nitrogen in the atmosphere into usable forms. They do so by forming a type of association which will be useful for both the partners involved in it.
Complete step by step answer:
The reduction of nitrogen to ammonia by living organisms living in a mutualistic relationship in the roots of plants is known as symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Examples of symbiotic nitrogen fixation include that of Rhizobia and Frankia.
Species of rod- shaped bacteria Rhizobium form an endosymbiotic nitrogen- fixing association with roots of the leguminous plants such as sweet pea, and lentils. The microbe Frankia also produces such nitrogen- fixing nodules on the roots of non- leguminous plants like Alnus.
Rhizobium is a symbiotic genus of Gram- negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen with the aid of the nitrogenase enzymes that are exclusively present in prokaryotes.
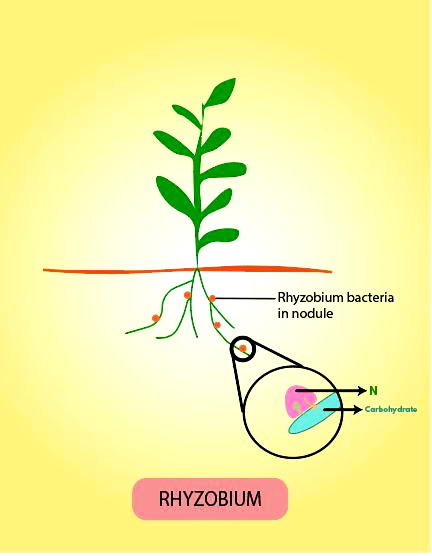
The process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation proceed this way:
- Rhizobia multiply and colonize the root hair cells of legumes. The bacteria invade the root hair and enter the cortex via an infection thread.
- In the cortex region of the plant, nodule formation begins. The nodule, thus formed, establishes a direct vascular connection with the host for the exchange of nutrients.
- The enzyme nitrogenase complex performs the important task of catalyzing the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia.
- The ammonia is protonated to form ammonium ion, which is used by the plants to synthesize amino acids.
Note:
- The nitrogenase enzyme is highly sensitive to oxygen and thus requires an anaerobic condition for it to properly function.
- This requirement is ensured by an oxygen scavenger called leghaemoglobin. Its presence makes the nodules pink in color.
Complete step by step answer:
The reduction of nitrogen to ammonia by living organisms living in a mutualistic relationship in the roots of plants is known as symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Examples of symbiotic nitrogen fixation include that of Rhizobia and Frankia.
Species of rod- shaped bacteria Rhizobium form an endosymbiotic nitrogen- fixing association with roots of the leguminous plants such as sweet pea, and lentils. The microbe Frankia also produces such nitrogen- fixing nodules on the roots of non- leguminous plants like Alnus.
Rhizobium is a symbiotic genus of Gram- negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen with the aid of the nitrogenase enzymes that are exclusively present in prokaryotes.

The process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation proceed this way:
- Rhizobia multiply and colonize the root hair cells of legumes. The bacteria invade the root hair and enter the cortex via an infection thread.
- In the cortex region of the plant, nodule formation begins. The nodule, thus formed, establishes a direct vascular connection with the host for the exchange of nutrients.
- The enzyme nitrogenase complex performs the important task of catalyzing the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia.
- The ammonia is protonated to form ammonium ion, which is used by the plants to synthesize amino acids.
Note:
- The nitrogenase enzyme is highly sensitive to oxygen and thus requires an anaerobic condition for it to properly function.
- This requirement is ensured by an oxygen scavenger called leghaemoglobin. Its presence makes the nodules pink in color.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




