
Explain the carbon cycle in nature.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The element is a major contributor to greenhouse effect with atmosphere and hydrosphere as its main reservoir.
Complete answer:
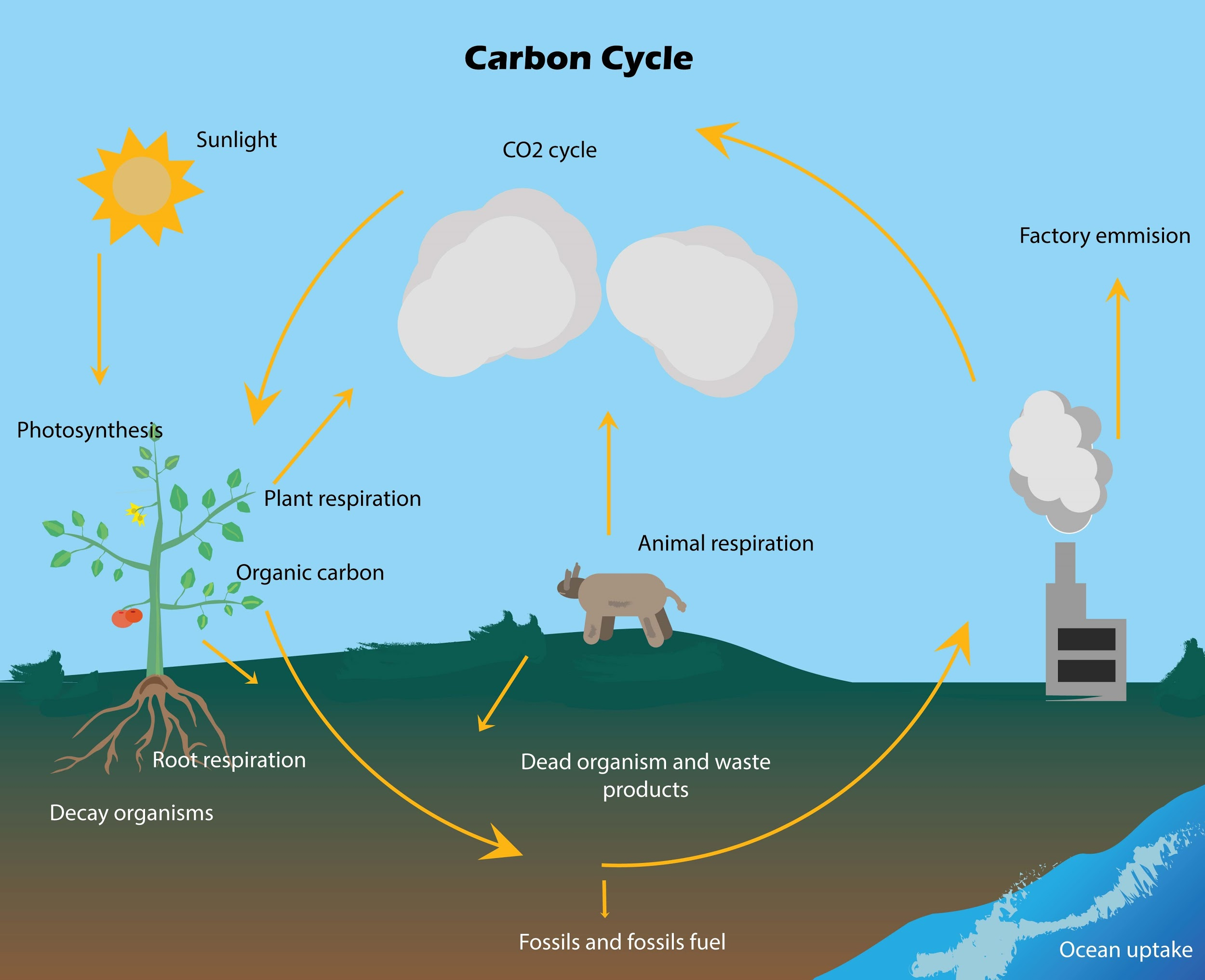
Carbon cycle is a gaseous cycle in which the nutrient ‘carbon’ recycles through the atmosphere, oceans and living and dead organisms predominantly in the form of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and bicarbonates. Terrestrial plants use atmospheric ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ as their carbon supply for photosynthesis. The carbon fixed in plants in the form of carbohydrates is consumed by consumers, directly or indirectly. Plants and animals that are buried may turn into fossil fuels like coal and oil by the action of decomposers.
In the aquatic system, close to the air-water barrier, ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ dissolves in water to form carbonic acid(${ H }_{ 2 }{ CO }_{ 3 }$). Carbonic acid further dissociates to release carbonate ions which when combined with calcium forms calcium carbonate, a key constituent of shells present in corals, molluscs etc. When animals die and sink to the seafloor, their sediments and shells accumulate over a timespan of million years, to form calcium-rich rocks such as limestone.
The cycle is incomplete without the release of fixed carbon back into the atmosphere. Respiration by all plants, animals and microorganisms releases the carbon locked in photosynthetic products back to the atmospheric and hydrospheric reservoir. Weathering of limestone and dolomite, accompanied by combustion of fossil fuels, wood, organic matter as well as volcanic eruptions also fill the reservoir.
Note: Gaseous cycle is a nutrient cycle where the atmosphere constitutes a major reservoir(pool) of the element that predominantly exists in the gaseous phase. Human activities over the years have immensely influenced the carbon cycle. This involves rapid and excessive deforestation, unchecked industrial emissions, burning of fossil fuels(coal) and vehicular emissions (from petrol or diesel). Disruption in the carbon cycle has contributed to global warming.
Complete answer:
Carbon cycle is a gaseous cycle in which the nutrient ‘carbon’ recycles through the atmosphere, oceans and living and dead organisms predominantly in the form of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and bicarbonates. Terrestrial plants use atmospheric ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ as their carbon supply for photosynthesis. The carbon fixed in plants in the form of carbohydrates is consumed by consumers, directly or indirectly. Plants and animals that are buried may turn into fossil fuels like coal and oil by the action of decomposers.
In the aquatic system, close to the air-water barrier, ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ dissolves in water to form carbonic acid(${ H }_{ 2 }{ CO }_{ 3 }$). Carbonic acid further dissociates to release carbonate ions which when combined with calcium forms calcium carbonate, a key constituent of shells present in corals, molluscs etc. When animals die and sink to the seafloor, their sediments and shells accumulate over a timespan of million years, to form calcium-rich rocks such as limestone.
The cycle is incomplete without the release of fixed carbon back into the atmosphere. Respiration by all plants, animals and microorganisms releases the carbon locked in photosynthetic products back to the atmospheric and hydrospheric reservoir. Weathering of limestone and dolomite, accompanied by combustion of fossil fuels, wood, organic matter as well as volcanic eruptions also fill the reservoir.
Note: Gaseous cycle is a nutrient cycle where the atmosphere constitutes a major reservoir(pool) of the element that predominantly exists in the gaseous phase. Human activities over the years have immensely influenced the carbon cycle. This involves rapid and excessive deforestation, unchecked industrial emissions, burning of fossil fuels(coal) and vehicular emissions (from petrol or diesel). Disruption in the carbon cycle has contributed to global warming.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




