
Explain the cleansing action of soap. Why does soap not work in hard water?
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: Soaps are salts of naturally occurring fatty acids. They are formed by treating animal fats with sodium hydroxide, known as caustic lye.
Complete step-by-step answer:
> The cleansing action of soap:
The soap works with the mechanism of micelle formation. Actually the Soap is a sodium(Na) or potassium(K) salt of a long-chain fatty acid in which the fatty acid ion is made of a polar head group, also called hydrophilic (water-loving) group, and a long zig-zag non-polar hydrocarbon chain which is insoluble in water called as a hydrophobic end.
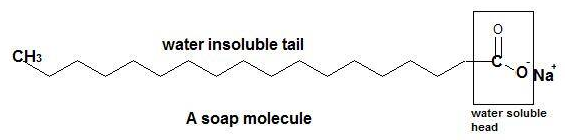
Figure: Structure of a common soap
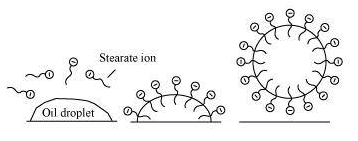
> When soap molecules are available in the water, the molecules organize themselves in the form of a cluster in such a way that their hydrophobic ends are away from the water particles and their hydrophilic or ionic ends are towards the water particles. This process is called micelle formation and the cluster that is formed is called a micelle.
At the point, when a piece of cloth is put in this soap solution, the hydrophobic ends of the soap particles adhere to the dirt whereas the hydrophilic end remains suspended in water. Thus when the cloth is rinsed and taken out of the water, it is free from dirt.
> Soap doesn't work properly in hard water (it forms scum with the calcium and magnesium impurities) Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. These ions form insoluble magnesium and calcium soaps respectively when potassium or sodium soaps are dissolved in hard water. That is why soaps do not work in water.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may confuse between soap and detergent. Detergent works properly in hard water but soap doesn’t work properly in hard water.
Complete step-by-step answer:
> The cleansing action of soap:
The soap works with the mechanism of micelle formation. Actually the Soap is a sodium(Na) or potassium(K) salt of a long-chain fatty acid in which the fatty acid ion is made of a polar head group, also called hydrophilic (water-loving) group, and a long zig-zag non-polar hydrocarbon chain which is insoluble in water called as a hydrophobic end.

Figure: Structure of a common soap
> When soap molecules are available in the water, the molecules organize themselves in the form of a cluster in such a way that their hydrophobic ends are away from the water particles and their hydrophilic or ionic ends are towards the water particles. This process is called micelle formation and the cluster that is formed is called a micelle.
At the point, when a piece of cloth is put in this soap solution, the hydrophobic ends of the soap particles adhere to the dirt whereas the hydrophilic end remains suspended in water. Thus when the cloth is rinsed and taken out of the water, it is free from dirt.

> Soap doesn't work properly in hard water (it forms scum with the calcium and magnesium impurities) Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. These ions form insoluble magnesium and calcium soaps respectively when potassium or sodium soaps are dissolved in hard water. That is why soaps do not work in water.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may confuse between soap and detergent. Detergent works properly in hard water but soap doesn’t work properly in hard water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




