
Explain the construction and working of a radio telescope.
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: We are asked to state the construction and working of a radio telescope. We can start to answer this question by mentioning what a radio telescope is and why is it being used. We can then move onto the construction, working and the advantages and disadvantages of using one.
Complete answer:
Radio telescopes, as the name suggests are telescopes that help us to view the radio waves coming from space. Telescopes have been an important invention to mankind. They helped us understand the universe better and the earth is not the center of the universe. Radio telescopes are used to study the naturally occurring radio waves from the stars and other astronomical bodies.
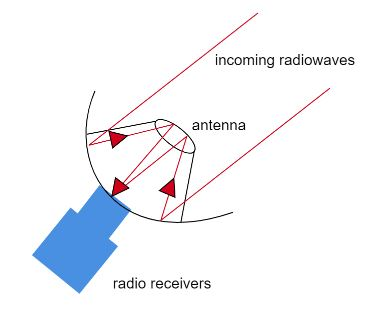
There are four parts in a radio telescope. Namely the reflector, antenna, amplifier, and receiver. The large dish you see in the telescope is the reflector that is used to focus the radio waves. The antenna is placed in the middle of the dish. The waves focused by the dish are forwarded to the antenna. After the antenna absorbs the radio waves, they are forwarded to the amplifier so that the strength of the signal increases.
After the amplification process, the amplified signal is forwarded to the receiver. The receiver also amplifies the signal and it is integrated. This data or signal is then sent to a computer that records and processes the data. Often, the data is converted into a map which helps us by showing the area of dense and less dense waves.
Note: Radio astronomy began when an engineer randomly came across the radio waves that come from naturally occurring objects in space and not just from our creations. Radio telescopes provide very important information about the astronomical bodies that are alternate to that seen with the optical telescope. They help us learn about the parts of the universe that are not yet discovered by the optical telescope.
Complete answer:
Radio telescopes, as the name suggests are telescopes that help us to view the radio waves coming from space. Telescopes have been an important invention to mankind. They helped us understand the universe better and the earth is not the center of the universe. Radio telescopes are used to study the naturally occurring radio waves from the stars and other astronomical bodies.
There are four parts in a radio telescope. Namely the reflector, antenna, amplifier, and receiver. The large dish you see in the telescope is the reflector that is used to focus the radio waves. The antenna is placed in the middle of the dish. The waves focused by the dish are forwarded to the antenna. After the antenna absorbs the radio waves, they are forwarded to the amplifier so that the strength of the signal increases.
After the amplification process, the amplified signal is forwarded to the receiver. The receiver also amplifies the signal and it is integrated. This data or signal is then sent to a computer that records and processes the data. Often, the data is converted into a map which helps us by showing the area of dense and less dense waves.

Note: Radio astronomy began when an engineer randomly came across the radio waves that come from naturally occurring objects in space and not just from our creations. Radio telescopes provide very important information about the astronomical bodies that are alternate to that seen with the optical telescope. They help us learn about the parts of the universe that are not yet discovered by the optical telescope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




