
Explain the construction of the transformer. Mention its principle
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: When charge is at rest it produces only electric fields but when charge is under motion it produces both electric and magnetic fields. The current carrying produces a magnetic field. Due to this, magnetic flux will be created and when that flux varies emf will be generated across the conductor.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{{N_P}}} = \dfrac{{{V_S}}}{{{N_S}}}$
Complete answer:
Transformer is a device which converts magnetic energy into electrical energy. Coming to the construction of the transformer, it has two coils called primary coil and secondary coil. Assume there are ${N_P}$ number of windings in primary coil and ${N_S}$ number of windings in secondary coil. There will be a soft iron core which connects these two coils. All these are shown in the diagram below.
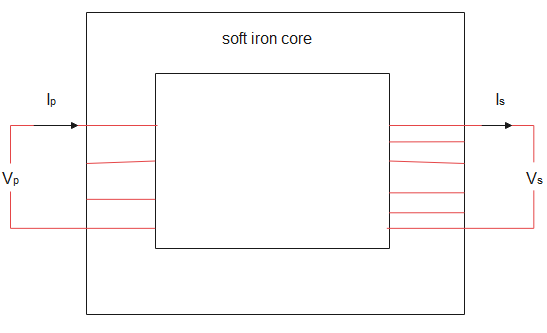
${I_P}$ amount of current is passed through the input alternating source. Since the current is alternating the current will be varying with time. That means the magnetic flux that is linked to the secondary coil also varies with time. When flux is varied, voltage will be induced and due to that voltage current ${I_S}$ will be induced in the secondary coil.
The soft iron core will offer the path for the flow of magnetic field to induce voltage.
The rate of change of flux per unit turn will be the same in both primary and secondary coils assuming 100 percent efficiency. So we have
$\dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{{N_P}}} = \dfrac{{{V_S}}}{{{N_S}}}$
So if the number of turns in secondary coils is less than primary coil number then voltage will reduce and it is called step down transformer.
If the number of turns in secondary coils is more than primary coil number then voltage will increase and it is called step up transformer.
Note:
The reason why we had chosen soft iron is because it has low coercivity and low retentivity. These properties are must for electromagnets. The coils are electrically isolated but are magnetically linked. Even though voltage will vary in two coils, power in the two coils will be constant for an ideal transformer.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{{N_P}}} = \dfrac{{{V_S}}}{{{N_S}}}$
Complete answer:
Transformer is a device which converts magnetic energy into electrical energy. Coming to the construction of the transformer, it has two coils called primary coil and secondary coil. Assume there are ${N_P}$ number of windings in primary coil and ${N_S}$ number of windings in secondary coil. There will be a soft iron core which connects these two coils. All these are shown in the diagram below.

${I_P}$ amount of current is passed through the input alternating source. Since the current is alternating the current will be varying with time. That means the magnetic flux that is linked to the secondary coil also varies with time. When flux is varied, voltage will be induced and due to that voltage current ${I_S}$ will be induced in the secondary coil.
The soft iron core will offer the path for the flow of magnetic field to induce voltage.
The rate of change of flux per unit turn will be the same in both primary and secondary coils assuming 100 percent efficiency. So we have
$\dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{{N_P}}} = \dfrac{{{V_S}}}{{{N_S}}}$
So if the number of turns in secondary coils is less than primary coil number then voltage will reduce and it is called step down transformer.
If the number of turns in secondary coils is more than primary coil number then voltage will increase and it is called step up transformer.
Note:
The reason why we had chosen soft iron is because it has low coercivity and low retentivity. These properties are must for electromagnets. The coils are electrically isolated but are magnetically linked. Even though voltage will vary in two coils, power in the two coils will be constant for an ideal transformer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




