
Explain the endocrine and exocrine functions of the pancreas.
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: An organ found in the abdomen is the pancreas. In transforming the food we eat into fuel for the cells of the body, it plays an important role. There are two key functions of the pancreas: an exocrine function that assists in digestion and an endocrine function that manages blood sugar.
Complete answer:
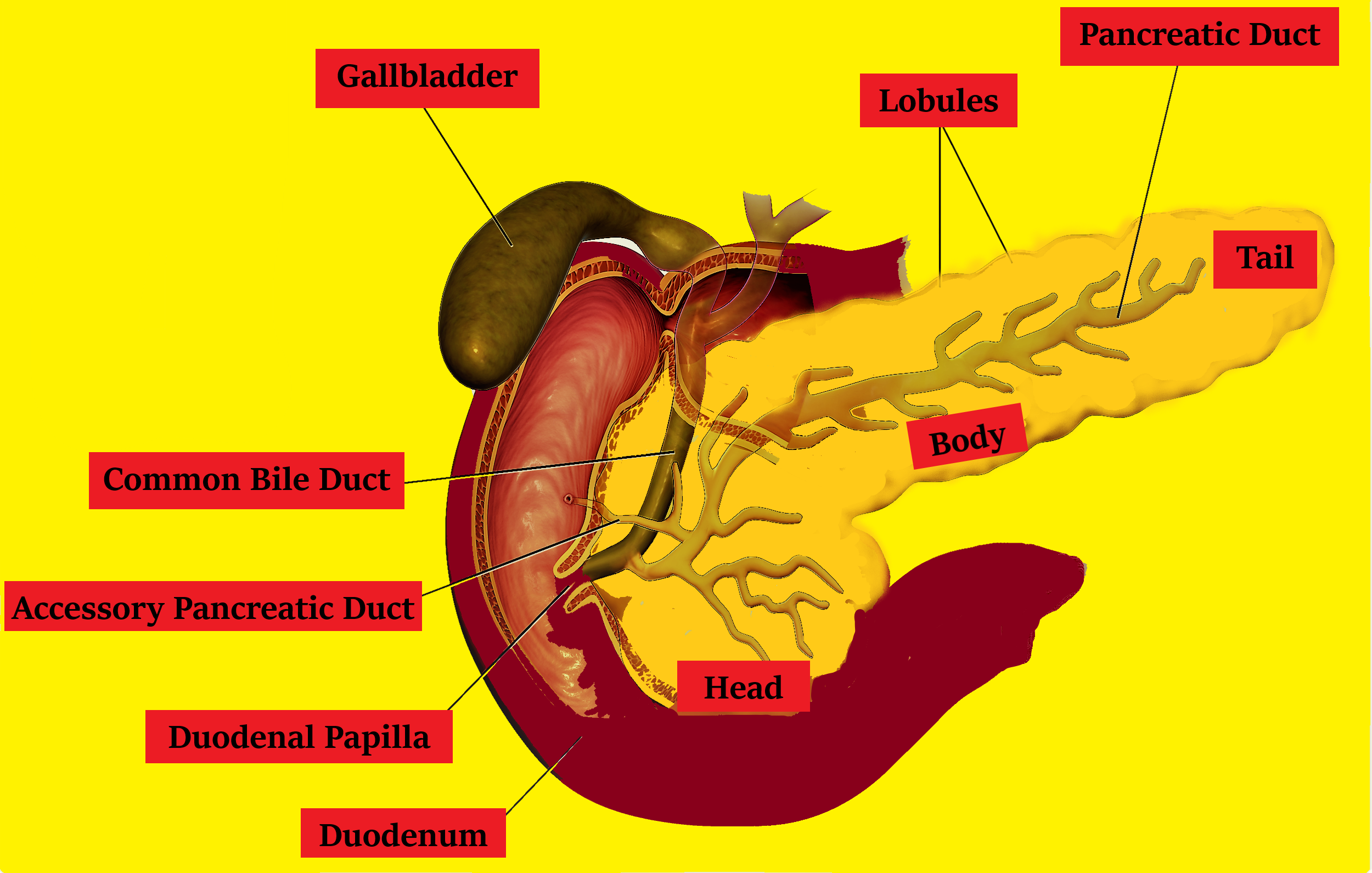
Function Exocrine: There are exocrine glands in the pancreas that produce enzymes essential for digestion. To digest proteins, these enzymes include trypsin and chymotrypsin; amylase for carbohydrate digestion; and lipase to break down fats. These pancreatic juices are released into a series of ducts when food reaches the stomach, resulting in the main pancreatic duct. The pancreatic duct joins the typical bile duct to form Vater's ampulla, which is situated in the duodenum, the first portion of the small intestine. In the liver and the gallbladder, the common bile duct originates and produces another significant digestive juice called bile. The pancreatic juices and bile released into the duodenum assist the body to digest fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Feature Endocrine: The pancreas's endocrine portion consists of islet cells (Langerhans islets) that directly produce and release essential hormones into the bloodstream. Insulin, which acts to lower blood sugar, and glucagon, which acts to increase blood sugar, are two of the major pancreatic hormones. It is essential for the functioning of key organs, including the brain, liver, and kidneys, to maintain proper blood sugar levels.
Additional Information:
Pancreatic inflammation is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic use of alcohol and bile ducts. The pancreas is also a central organ in diabetes mellitus, due to its role in the control of blood sugar. After chronic pancreatitis or for other causes, pancreatic cancer may develop and has a rather poor prognosis, since it is only diagnosed when it has spread to other areas of the body.
Note: Pancreatitis is a pancreas inflammation that occurs when secretions of pancreatic enzymes build up and begin to digest the organ itself. It can occur as sudden, debilitating attacks that last a few days, or it can be a chronic illness that progresses for years to come.
Complete answer:
Function Exocrine: There are exocrine glands in the pancreas that produce enzymes essential for digestion. To digest proteins, these enzymes include trypsin and chymotrypsin; amylase for carbohydrate digestion; and lipase to break down fats. These pancreatic juices are released into a series of ducts when food reaches the stomach, resulting in the main pancreatic duct. The pancreatic duct joins the typical bile duct to form Vater's ampulla, which is situated in the duodenum, the first portion of the small intestine. In the liver and the gallbladder, the common bile duct originates and produces another significant digestive juice called bile. The pancreatic juices and bile released into the duodenum assist the body to digest fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Feature Endocrine: The pancreas's endocrine portion consists of islet cells (Langerhans islets) that directly produce and release essential hormones into the bloodstream. Insulin, which acts to lower blood sugar, and glucagon, which acts to increase blood sugar, are two of the major pancreatic hormones. It is essential for the functioning of key organs, including the brain, liver, and kidneys, to maintain proper blood sugar levels.
Additional Information:
Pancreatic inflammation is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic use of alcohol and bile ducts. The pancreas is also a central organ in diabetes mellitus, due to its role in the control of blood sugar. After chronic pancreatitis or for other causes, pancreatic cancer may develop and has a rather poor prognosis, since it is only diagnosed when it has spread to other areas of the body.
Note: Pancreatitis is a pancreas inflammation that occurs when secretions of pancreatic enzymes build up and begin to digest the organ itself. It can occur as sudden, debilitating attacks that last a few days, or it can be a chronic illness that progresses for years to come.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




