
Explain the following terms with suitable examples.
(a) Cationic detergents
(b) Anionic detergents
(c) Non-ionic detergents
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Detergents are surfactants. Like soap, they also have hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. They are classified as cationic, anionic and non-ionic detergents based on the charge carried by the bigger portion of the detergent molecule which is also responsible for cleansing action of the detergent.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First let us understand about detergents. Detergents are similar to soaps but their chemical structures are different. Detergents are generally ammonium, sulfate or sulphate salts of long chain hydrocarbons (containing 12-18 carbon atoms). A detergent has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. If we are using hard water for cleaning purposes, it is better to use detergents than using soap. Hard water is composed of calcium and magnesium ions. So if we use soap with hard water, it will lead in the formation of ‘scum’ but the calcium and magnesium salts of detergents are soluble in water and hence no scum is formed.
Based on the electrical charge, detergents are classified as:
(a) Anionic detergents: Detergents in which a large portion of the molecule carries a negative charge i.e. it is an anion and is responsible for the cleansing action, such detergents are called anionic detergents. They are of two types:
-Sodium Alkyl Sulphates: They are prepared from long straight chain alcohols (containing 12-18 carbon atoms) which are treated with concentrated sulphuric acid followed by an alkali such as NaOH. Example: sodium lauryl sulphate. Its preparation is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }OH \\ Lauryl\quad alcohol \end{matrix}\xrightarrow { Conc.\quad { H }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 } } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }O{ SO }_{ 3 }H \\ Lauryl\quad hydrogen\quad sulphate\quad \end{matrix}$
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }O{ SO }_{ 3 }H \\ Lauryl\quad hydrogen\quad sulphate \end{matrix}\xrightarrow { NaOH } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }{ OSO }_{ 3 }^{ - }{ Na }^{ + } \\ Sodium\quad lauryl\quad sulphate \end{matrix}$
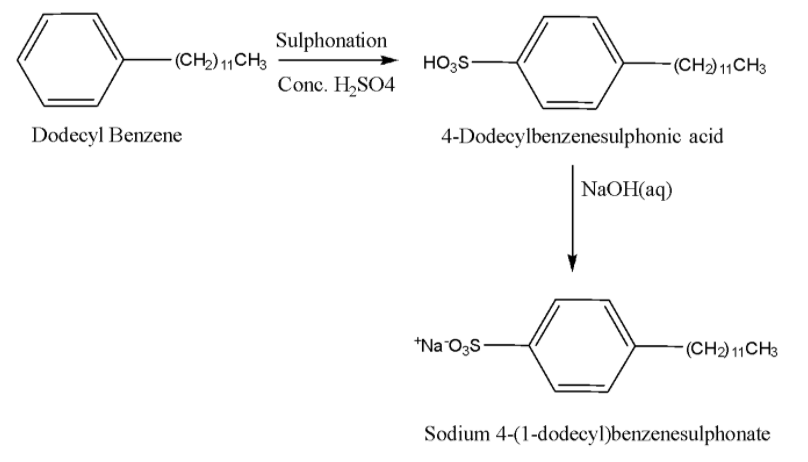
-Sodium alkylbenzene sulphonates: They are sodium salts of long chain alkyl benzene sulphonic acids. They are prepared by Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene using long chain alkyl halide/alkene/alcohol followed by sulphonation and neutralization using an alkali such as NaOH. Example: 4-(1-dodecyl)benzenesulfonate (SDS). Its preparation is given below:
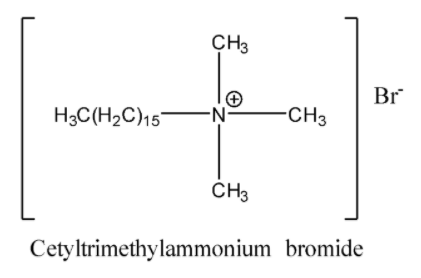
(b) Cationic Detergents: Detergents in which a large portion of the molecule carries a positive charge i.e. it is a cation and is responsible for the cleansing action, such detergents are called cationic detergents. They consist of quaternary ammonium salts containing one or more long chain alkyl groups. They are used as germicides and as ingredients in shampoos and conditioners. Example: cetyltrimethylammonium bromide.
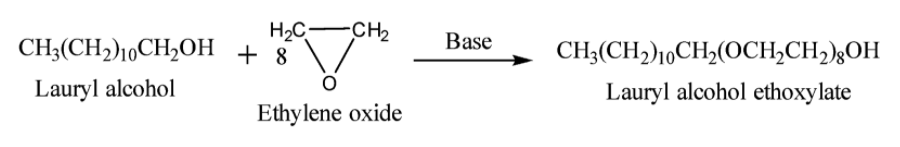
(c) Non-ionic detergents: They do not consist of any ion. They are esters of high molecular weight alcohols. They can be prepared by treating long chain alcohols with excess of ethylene oxide in the presence of a base. Example: Lauryl alcohol ethoxylate. The reaction is given below:
Hence cationic, anionic and non-ionic detergents are explained.
Note: Detergents have many advantages over soaps. However they are not completely biodegradable while soaps are completely biodegradable. This is due to the presence of highly branched hydrocarbon chains in detergents due to which bacteria are not able to decompose them.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First let us understand about detergents. Detergents are similar to soaps but their chemical structures are different. Detergents are generally ammonium, sulfate or sulphate salts of long chain hydrocarbons (containing 12-18 carbon atoms). A detergent has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. If we are using hard water for cleaning purposes, it is better to use detergents than using soap. Hard water is composed of calcium and magnesium ions. So if we use soap with hard water, it will lead in the formation of ‘scum’ but the calcium and magnesium salts of detergents are soluble in water and hence no scum is formed.
Based on the electrical charge, detergents are classified as:
(a) Anionic detergents: Detergents in which a large portion of the molecule carries a negative charge i.e. it is an anion and is responsible for the cleansing action, such detergents are called anionic detergents. They are of two types:
-Sodium Alkyl Sulphates: They are prepared from long straight chain alcohols (containing 12-18 carbon atoms) which are treated with concentrated sulphuric acid followed by an alkali such as NaOH. Example: sodium lauryl sulphate. Its preparation is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }OH \\ Lauryl\quad alcohol \end{matrix}\xrightarrow { Conc.\quad { H }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 } } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }O{ SO }_{ 3 }H \\ Lauryl\quad hydrogen\quad sulphate\quad \end{matrix}$
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }O{ SO }_{ 3 }H \\ Lauryl\quad hydrogen\quad sulphate \end{matrix}\xrightarrow { NaOH } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 11 }{ H }_{ 23 }{ CH }_{ 2 }{ OSO }_{ 3 }^{ - }{ Na }^{ + } \\ Sodium\quad lauryl\quad sulphate \end{matrix}$
-Sodium alkylbenzene sulphonates: They are sodium salts of long chain alkyl benzene sulphonic acids. They are prepared by Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene using long chain alkyl halide/alkene/alcohol followed by sulphonation and neutralization using an alkali such as NaOH. Example: 4-(1-dodecyl)benzenesulfonate (SDS). Its preparation is given below:

(b) Cationic Detergents: Detergents in which a large portion of the molecule carries a positive charge i.e. it is a cation and is responsible for the cleansing action, such detergents are called cationic detergents. They consist of quaternary ammonium salts containing one or more long chain alkyl groups. They are used as germicides and as ingredients in shampoos and conditioners. Example: cetyltrimethylammonium bromide.

(c) Non-ionic detergents: They do not consist of any ion. They are esters of high molecular weight alcohols. They can be prepared by treating long chain alcohols with excess of ethylene oxide in the presence of a base. Example: Lauryl alcohol ethoxylate. The reaction is given below:

Hence cationic, anionic and non-ionic detergents are explained.
Note: Detergents have many advantages over soaps. However they are not completely biodegradable while soaps are completely biodegradable. This is due to the presence of highly branched hydrocarbon chains in detergents due to which bacteria are not able to decompose them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




