
Explain the formation of $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule using hybridisation
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: The hybridisation of any compound uses the valence bond theory according to which the hybridisation or the mixing of the orbitals takes place and all the hybrid orbitals have equal energy.
It takes in account the electronic configuration of the central atom in the compound and the unpaired electrons in the central atom vouches for the incoming electrons from the other atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The electronic configuration of boron is $2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$, so we can see that it has one unpaired electron. So, this electron from the ‘s’ orbital gets excited to the higher energy level and forms $2{{s}^{1}}2{{p}^{2}}$ where all the electrons are unpaired.
The structure of boron trifluoride consists of an atom of boron along with the three fluorine atoms which are in $120{}^\circ $ angle with one another. So, the geometry of this structure is trigonal planar. The structure can be represented as,
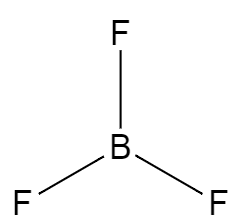
The boron has only three electrons in its outermost orbital and the fluorine atoms have seven electrons in its outermost shell. So, during the formation of the compound the $2s$ orbital and the two $2p$ orbitals combine with each other and form a hybridised orbital which is $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Hence the boron trifluoride molecule is formed and with the use of hybridisation, which is the required answer.
Note:The formation of the boron trifluoride takes place when one ‘s’ orbital and two ‘p’ orbitals in order to become three $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbitals which have equal energy.
This process is based on the valence bond theory and it takes in account the orbitals of individual atoms.
It takes in account the electronic configuration of the central atom in the compound and the unpaired electrons in the central atom vouches for the incoming electrons from the other atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The electronic configuration of boron is $2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$, so we can see that it has one unpaired electron. So, this electron from the ‘s’ orbital gets excited to the higher energy level and forms $2{{s}^{1}}2{{p}^{2}}$ where all the electrons are unpaired.
The structure of boron trifluoride consists of an atom of boron along with the three fluorine atoms which are in $120{}^\circ $ angle with one another. So, the geometry of this structure is trigonal planar. The structure can be represented as,

The boron has only three electrons in its outermost orbital and the fluorine atoms have seven electrons in its outermost shell. So, during the formation of the compound the $2s$ orbital and the two $2p$ orbitals combine with each other and form a hybridised orbital which is $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Hence the boron trifluoride molecule is formed and with the use of hybridisation, which is the required answer.
Note:The formation of the boron trifluoride takes place when one ‘s’ orbital and two ‘p’ orbitals in order to become three $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbitals which have equal energy.
This process is based on the valence bond theory and it takes in account the orbitals of individual atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




