
Explain the formation of \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}\] molecule with Valence bond theory.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: VBT is also known as Valence bond theory. The covalent bond will form between the orbital of hydrogen and nitrogen. Only the vacant or half filled orbital will form a bond and not the fully filled orbital.
Complete step by step answer:
The valence shell electronic configuration of nitrogen is \[2{{\text{s}}^2}2{{\text{p}}^3}\]. It has 5 electrons in its valence shell.
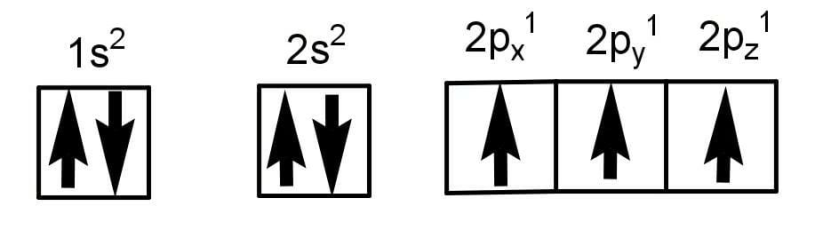
An orbital can have a maximum of 2 electrons. There is 1 s orbital and 3 p orbital in nitrogen. The s orbital is fully filled and hence will not take part in hybridization. 3 electrons are present in 3 p orbital, one orbital contains one electron each according to Hund’s rule which says the electrons won’t get paired unless each orbital is singly occupied.
Hydrogen has only one electron in its atom. The electronic configuration of Hydrogen is \[{\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^1}\].
Hence the 3 p orbital of nitrogen will hybridize with three s orbital of three hydrogen atoms. Three \[{\text{N}} - {\text{H}}\] sigma bonds will form. The shape formed is trigonal pyramidal and the geometry is tetrahedral.
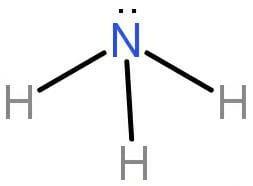
The bond is formed by the overlapping of the orbital. VBT considers the bond to be a polar covalent bond. The hybridisation of ammonia that is \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}\] is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\]. 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair are present in ammonia.
Note:
Valence bond theory introduced the concept of hybridization in which the orbital with different energy mix together to form the orbital of nearly the same energy during bond formation. The valence bond theory gave various results but has still very limitations. The more acceptable theory is the Molecular orbital theory which is based on the principle that the orbital with nearly the same energy mixes to form the molecular orbital of different energies.
Complete step by step answer:
The valence shell electronic configuration of nitrogen is \[2{{\text{s}}^2}2{{\text{p}}^3}\]. It has 5 electrons in its valence shell.

An orbital can have a maximum of 2 electrons. There is 1 s orbital and 3 p orbital in nitrogen. The s orbital is fully filled and hence will not take part in hybridization. 3 electrons are present in 3 p orbital, one orbital contains one electron each according to Hund’s rule which says the electrons won’t get paired unless each orbital is singly occupied.
Hydrogen has only one electron in its atom. The electronic configuration of Hydrogen is \[{\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^1}\].
Hence the 3 p orbital of nitrogen will hybridize with three s orbital of three hydrogen atoms. Three \[{\text{N}} - {\text{H}}\] sigma bonds will form. The shape formed is trigonal pyramidal and the geometry is tetrahedral.

The bond is formed by the overlapping of the orbital. VBT considers the bond to be a polar covalent bond. The hybridisation of ammonia that is \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}\] is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\]. 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair are present in ammonia.
Note:
Valence bond theory introduced the concept of hybridization in which the orbital with different energy mix together to form the orbital of nearly the same energy during bond formation. The valence bond theory gave various results but has still very limitations. The more acceptable theory is the Molecular orbital theory which is based on the principle that the orbital with nearly the same energy mixes to form the molecular orbital of different energies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




