
Explain the formation of nitrogen molecules.
Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint – Here we will proceed by explaining the electronic configuration of nitrogen that is ‘N’ atoms. By explaining the structural formula of a nitrogen molecule.
Nitrogen is a non-metal and it has 5 electrons in its outer shell. Nitrogen is in a group 5 of the periodic table.
Complete answer:
Both the nitrogen atoms will each share three electrons and thus, form three covalent bonds and make a nitrogen molecule $\left( {{N_2}} \right)$.
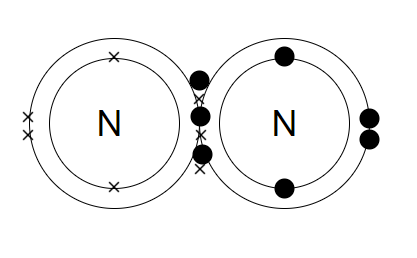
By sharing 6 electrons where the shells touch each nitrogen atom can count 8 electrons in its outer shell. The full outer shells with their shared electrons are stable as shown in the diagram.
Further the ${N_2}$ molecule will not react with other nitrogen atoms.
Now the 3 pairs i.e. (6 electrons) shared between the N-atoms. Each electron pair is one bond. Nitrogen has three bonds between its atoms. This is called a triple bond. This triple bond is very strong and thus makes the nitrogen so unreactive (i.e. stable).
The structural formula of a nitrogen molecule is written
$N \equiv N$
In this no ions are present (no + or – charges) in nitrogen gas because here the electrons are shared, not transferred from one atom to another.
Note – Whenever we come up with this type of question, one must know that molecular nitrogen $\left( {{N_2}} \right)$is a very common chemical compound in which two nitrogen atoms are tightly bound together. Molecular nitrogen is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, and inert gas at normal temperatures and pressures. About 78% of Earth’s atmosphere is nitrogen. One can easily solve this question by using these basics.
Nitrogen is a non-metal and it has 5 electrons in its outer shell. Nitrogen is in a group 5 of the periodic table.
Complete answer:
Both the nitrogen atoms will each share three electrons and thus, form three covalent bonds and make a nitrogen molecule $\left( {{N_2}} \right)$.

By sharing 6 electrons where the shells touch each nitrogen atom can count 8 electrons in its outer shell. The full outer shells with their shared electrons are stable as shown in the diagram.
Further the ${N_2}$ molecule will not react with other nitrogen atoms.
Now the 3 pairs i.e. (6 electrons) shared between the N-atoms. Each electron pair is one bond. Nitrogen has three bonds between its atoms. This is called a triple bond. This triple bond is very strong and thus makes the nitrogen so unreactive (i.e. stable).
The structural formula of a nitrogen molecule is written
$N \equiv N$
In this no ions are present (no + or – charges) in nitrogen gas because here the electrons are shared, not transferred from one atom to another.
Note – Whenever we come up with this type of question, one must know that molecular nitrogen $\left( {{N_2}} \right)$is a very common chemical compound in which two nitrogen atoms are tightly bound together. Molecular nitrogen is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, and inert gas at normal temperatures and pressures. About 78% of Earth’s atmosphere is nitrogen. One can easily solve this question by using these basics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




