
Explain the function of the following part of an electric motor.
Armature
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Think about the different parts of a motor. Recall what an armature does. Think about the moving or rotating part in an electric motor. When a current carrying conductor is kept in a magnetic field it experiences force in the direction perpendicular to both motion of electrons and magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
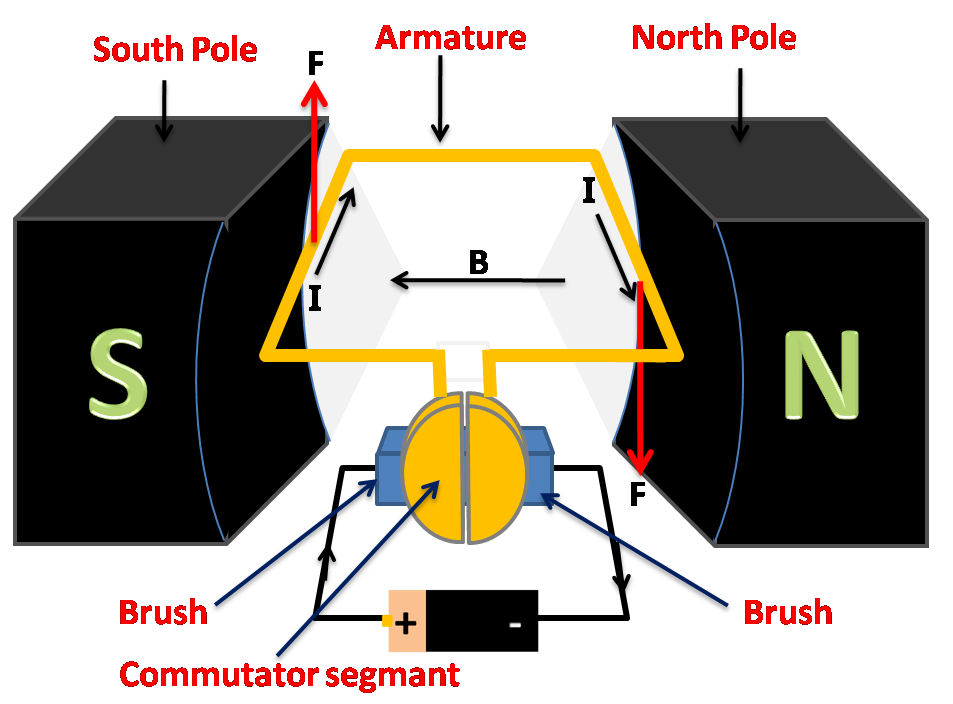
An armature is a rectangular coil inside the electric motor. Current passes through the armature. Being in an external magnetic field, it experiences a force, more specifically a torque, and hence rotates. This is responsible for the mechanical motion of the electric motor and due to this the shaft of the motor rotates.
The schematic diagram of an electric motor is:
Additional Information:
Other than the armature, there are different parts of an electric motor. They are:
1) Power Source: A simple motor usually has a DC power source. It supplies power to the motor armature or field coils.
2) Commutator: It is the rotating interface of the armature coil with a stationary circuit.
3) Field Magnet: The magnetic field helps to produce a torque on the rotating armature coil by virtue of Fleming’s left-hand rule.
4) Armature Core: Holds the armature coil in place and provides mechanical support.
5) Armature Coil: It helps the motor to run.
6) Brushes: It is a device that conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, most commonly the rotating shaft.
An electric motor is used for different purposes Drills, Water Pumps, Hard Disc Drives, Washing Machine and Industrial Equipment.
Note: Do keep a note of the other parts of an electric motor and their functions. You may be asked about them as well. When the current flows through the coil, the coil experiences a force in the perpendicular direction (tangential direction). Since this force is a cross product of magnetic field and direction of current, the magnetic field should never be parallel or antiparallel to the direction of current.
Complete step by step answer:
An armature is a rectangular coil inside the electric motor. Current passes through the armature. Being in an external magnetic field, it experiences a force, more specifically a torque, and hence rotates. This is responsible for the mechanical motion of the electric motor and due to this the shaft of the motor rotates.
The schematic diagram of an electric motor is:

Additional Information:
Other than the armature, there are different parts of an electric motor. They are:
1) Power Source: A simple motor usually has a DC power source. It supplies power to the motor armature or field coils.
2) Commutator: It is the rotating interface of the armature coil with a stationary circuit.
3) Field Magnet: The magnetic field helps to produce a torque on the rotating armature coil by virtue of Fleming’s left-hand rule.
4) Armature Core: Holds the armature coil in place and provides mechanical support.
5) Armature Coil: It helps the motor to run.
6) Brushes: It is a device that conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, most commonly the rotating shaft.
An electric motor is used for different purposes Drills, Water Pumps, Hard Disc Drives, Washing Machine and Industrial Equipment.
Note: Do keep a note of the other parts of an electric motor and their functions. You may be asked about them as well. When the current flows through the coil, the coil experiences a force in the perpendicular direction (tangential direction). Since this force is a cross product of magnetic field and direction of current, the magnetic field should never be parallel or antiparallel to the direction of current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




