
Explain the Hatch-Slack pathway.
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: We know that in most of the plants, Oxaloacetic acid which is a 3-carbon containing compound is the first ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ fixation product. But some plants also make use of Phospho-enol pyruvate (PEP) as the first product of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ fixation which is a 4-carbon containing compound.
Complete answer:
The plants which make use of phospho-enol pyruvate (PEP) as the first product of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ fixation is called as ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants as PEP is a 4-carbon containing compound. The ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathway is also called the Hatch-Slack pathway.
Let us take a look at this pathway step by step:
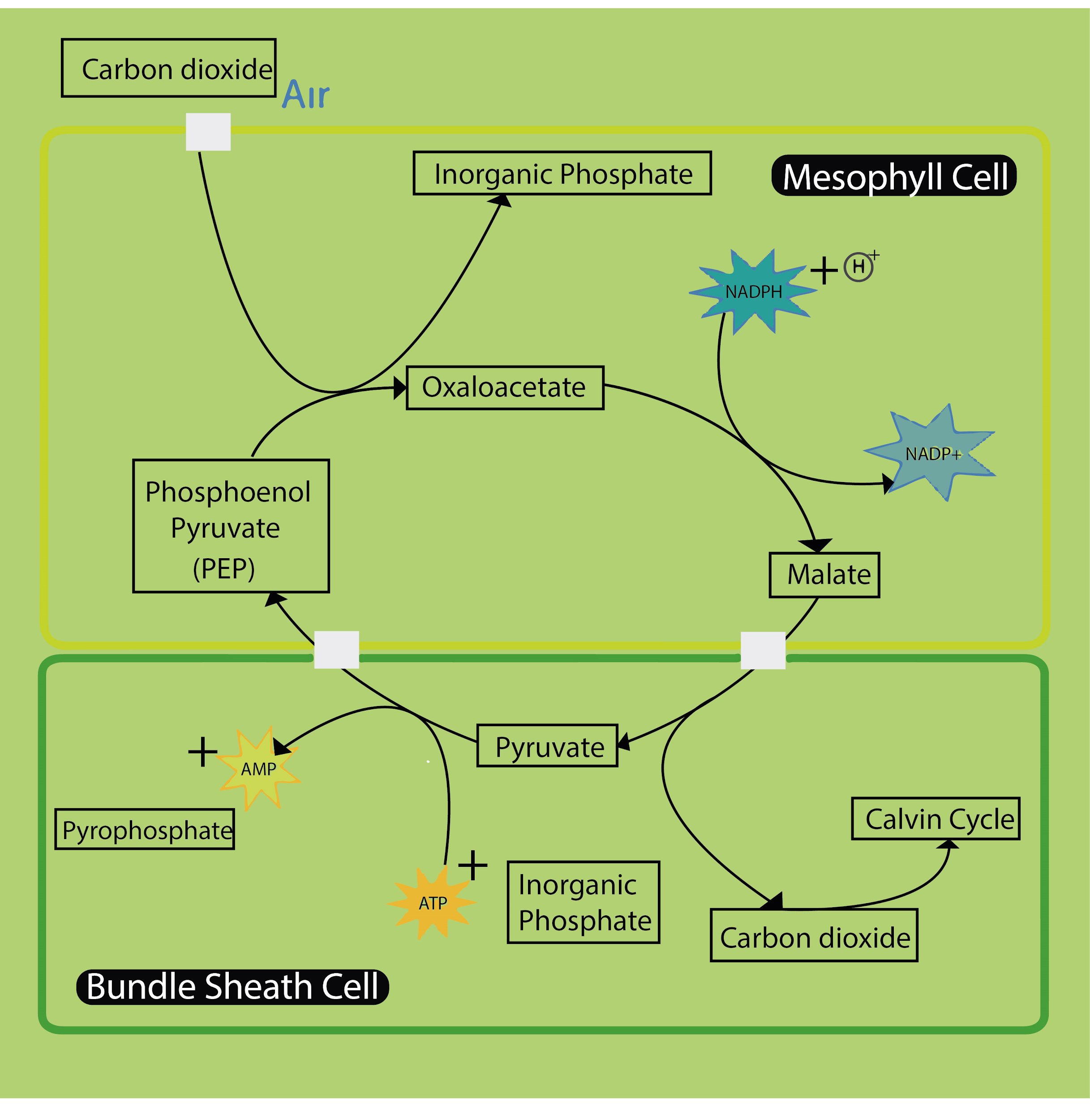
- First, phospho-enol pyruvate (PEP) which is present in the mesophyll cells accepts ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ under the influence of the enzyme PEP carboxylase. (Mesophyll cells of ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants lack RuBisCO enzyme and hence the normal pathway with OAA is not used).
- After accepting ${ CO }_{ 2 }$, Malic acid or aspartic acid form in the mesophyll cell itself which are then transported to bundle sheath cells. In bundle sheath cells these acids are broken down in order to release ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and a 3-carbon molecule.
- This 3-carbon containing molecule is then transported back to mesophyll cells where it again forms PEP and hence one turn of the cycle is completed.
- The ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ which was released in bundle sheath cells participates in the regular ${ C }_{ 3 }$ pathway since these cells are rich in RuBisCO enzyme but they lack PEPcarboxylase.
For better understanding, let us take a look at the diagram below –
Note:
Plants that show ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathways are called as ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants are showing a specific type of anatomy in the leaf called Kranz anatomy. They also respond to high light intensities and lack photorespiration.
Complete answer:
The plants which make use of phospho-enol pyruvate (PEP) as the first product of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ fixation is called as ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants as PEP is a 4-carbon containing compound. The ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathway is also called the Hatch-Slack pathway.
Let us take a look at this pathway step by step:
- First, phospho-enol pyruvate (PEP) which is present in the mesophyll cells accepts ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ under the influence of the enzyme PEP carboxylase. (Mesophyll cells of ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants lack RuBisCO enzyme and hence the normal pathway with OAA is not used).
- After accepting ${ CO }_{ 2 }$, Malic acid or aspartic acid form in the mesophyll cell itself which are then transported to bundle sheath cells. In bundle sheath cells these acids are broken down in order to release ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and a 3-carbon molecule.
- This 3-carbon containing molecule is then transported back to mesophyll cells where it again forms PEP and hence one turn of the cycle is completed.
- The ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ which was released in bundle sheath cells participates in the regular ${ C }_{ 3 }$ pathway since these cells are rich in RuBisCO enzyme but they lack PEPcarboxylase.
For better understanding, let us take a look at the diagram below –

Note:
Plants that show ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathways are called as ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants are showing a specific type of anatomy in the leaf called Kranz anatomy. They also respond to high light intensities and lack photorespiration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




