
Explain the heat of reaction.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The change in the enthalpy value of chemical reaction at constant pressure is known as the heat of reaction of enthalpy of reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
-The heat evolved in the surrounding or absorbed from the surrounding during the happening of a chemical reaction taking place at constant pressure and temperature is known as the heat of a chemical reaction.
-The heat of a chemical reaction is expressed as molar enthalpy in kJ/mol or as specific enthalpy in kJ/kg or kJ/L.
-According to the Law of Conservation of Energy, the amount of heat energy before and after the chemical reaction remains the same. Therefore, the amount of heat lost or gained in a reacting system is equal to the amount of heat lost or gained in the surrounding.
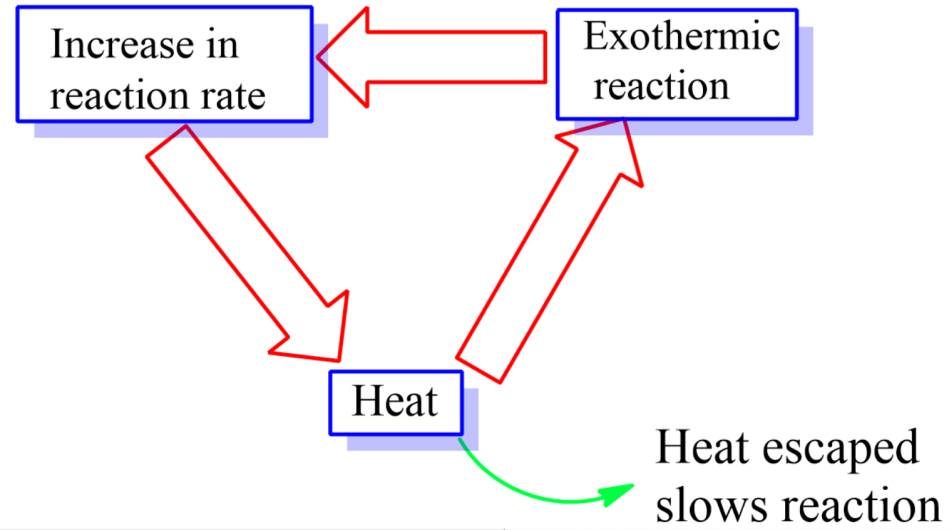
-An exothermic reaction liberates heat, due to which the temperature of the reaction mixture increases. An endothermic reaction absorbs heat, due to which the temperature of the reaction mixture decreases.
-The formula for the heat of reaction is given as-
$Q=m\times c\times \Delta T$
where ‘m’ is the mass of the medium.
‘c’ is the specific heat capacity of the medium of reaction.
‘Q’ is the heat of reaction
‘$\Delta T$’ is the difference in the temperature of the medium.
Note: The standard enthalpy of a chemical reaction is symbolized by $\Delta H{}^\circ \text{ or }\Delta H{{{}^\circ }_{rxn}}$ and can have both, positive as well as negative values. $'\Delta '$ here represents the change in enthalpy of the reactants and the products $(\Delta {{H}_{\text{products}}}-\Delta {{H}_{\text{reactants}}})$ . A positive value of standard enthalpy is taken where the products have greater enthalpy, i.e in endothermic reactions. A negative value of standard enthalpy is taken where the reactants have greater enthalpy, i.e in exothermic reactions. ${}^\circ$ signifies that the quantity taken into consideration occurs at standard temperature and pressure. ${{'}_{rxn}}'$ denotes that the change is in a chemical reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
-The heat evolved in the surrounding or absorbed from the surrounding during the happening of a chemical reaction taking place at constant pressure and temperature is known as the heat of a chemical reaction.
-The heat of a chemical reaction is expressed as molar enthalpy in kJ/mol or as specific enthalpy in kJ/kg or kJ/L.
-According to the Law of Conservation of Energy, the amount of heat energy before and after the chemical reaction remains the same. Therefore, the amount of heat lost or gained in a reacting system is equal to the amount of heat lost or gained in the surrounding.
-An exothermic reaction liberates heat, due to which the temperature of the reaction mixture increases. An endothermic reaction absorbs heat, due to which the temperature of the reaction mixture decreases.
-The formula for the heat of reaction is given as-

$Q=m\times c\times \Delta T$
where ‘m’ is the mass of the medium.
‘c’ is the specific heat capacity of the medium of reaction.
‘Q’ is the heat of reaction
‘$\Delta T$’ is the difference in the temperature of the medium.
Note: The standard enthalpy of a chemical reaction is symbolized by $\Delta H{}^\circ \text{ or }\Delta H{{{}^\circ }_{rxn}}$ and can have both, positive as well as negative values. $'\Delta '$ here represents the change in enthalpy of the reactants and the products $(\Delta {{H}_{\text{products}}}-\Delta {{H}_{\text{reactants}}})$ . A positive value of standard enthalpy is taken where the products have greater enthalpy, i.e in endothermic reactions. A negative value of standard enthalpy is taken where the reactants have greater enthalpy, i.e in exothermic reactions. ${}^\circ$ signifies that the quantity taken into consideration occurs at standard temperature and pressure. ${{'}_{rxn}}'$ denotes that the change is in a chemical reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




