
Explain the internal structure of the kidney?
Answer
526.2k+ views
Hint: The kidneys are bean-shaped paired organs located on each side of the back portion of the abdominal cavity. The fat or adipose surrounding the kidneys protects them from shock and acts as padding. The functional units of the kidney called nephrons lie inside the medulla of the kidney.
Complete answer: The bean-shaped kidneys have a reddish-brown shade. The outer side of the kidney is convex-shaped and the inner side is concave. The inner side consists of the renal artery, renal vein, and ureter. This inner side of the kidney is called the renal hilus. Each kidney is surrounded by a thin connective tissue layer called the renal capsule. The capsule functions to maintain the shape of the kidney and it also protects the inner kidney tissues.
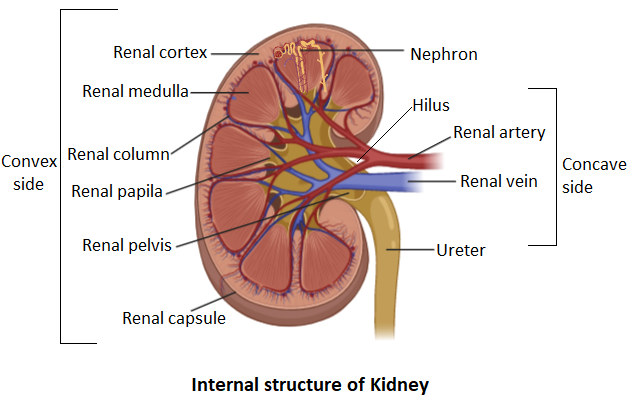
Inner to the renal capsule is the renal cortex. It is soft, dense, and vascular tissue. This layer encloses the inner renal medulla. The renal medulla consists of several raised compartments called renal pyramids. These are cone-shaped structures having apices that point towards the centre of the kidney. The apex of each renal pyramid is connected to a minor calyx which is a hollow tube that is responsible for collecting urine. The minor calyces merge to form three major calyces that merge further in the renal pelvis at the renal hilus. Urine drains to the ureter which is a larger duct that lies at the end of the renal hilus. The nephron which is the functional unit of the kidney and which is actually responsible for filtering of blood lies embedded in the renal medulla. More than a million nephrons lie in the renal cortex of the kidney. $85%$ nephrons are situated in the renal cortex and are called cortical nephrons. $15%$ of nephrons lie close to the medulla and are called juxtamedullary nephrons. The nephron is made up of a renal corpuscle, a renal tubule, and a network of capillaries that arises from the small cortical arteries. A network of capillaries called glomerulus and a cup-shaped chamber that surrounds glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule are the main functional units of a nephron. The glomerulus receives impure blood and filters it through its capillaries. The filtered blood is then passed on to a long, convoluted tubule which is further divided into three parts. The loop of Henle, the proximal convoluted tubule, and the distal convoluted tubule are three regions of the long convoluted tubule. These three empties the filtrate into collecting ducts. The collecting ducts together enter the papillae of the renal medulla. From the renal medulla, the urine passes as a fluid containing high sodium content and finally leaves from the kidney through renal papillae. From here it passes through renal calyces, then renal pelvis, and then into the bladder through the ureter.
Note: The kidney makes the body get rid of toxins including urea and excess salts. Urea is a nitrogenous waste product that is primarily produced in the liver. Kidneys also help to maintain the water and electrolyte balance of the body. Blood pressure is also regulated by the kidney by the production of angiotensin. Angiotensin constricts the blood vessels and helps retain sodium and water more in case of low blood pressure.
Complete answer: The bean-shaped kidneys have a reddish-brown shade. The outer side of the kidney is convex-shaped and the inner side is concave. The inner side consists of the renal artery, renal vein, and ureter. This inner side of the kidney is called the renal hilus. Each kidney is surrounded by a thin connective tissue layer called the renal capsule. The capsule functions to maintain the shape of the kidney and it also protects the inner kidney tissues.

Inner to the renal capsule is the renal cortex. It is soft, dense, and vascular tissue. This layer encloses the inner renal medulla. The renal medulla consists of several raised compartments called renal pyramids. These are cone-shaped structures having apices that point towards the centre of the kidney. The apex of each renal pyramid is connected to a minor calyx which is a hollow tube that is responsible for collecting urine. The minor calyces merge to form three major calyces that merge further in the renal pelvis at the renal hilus. Urine drains to the ureter which is a larger duct that lies at the end of the renal hilus. The nephron which is the functional unit of the kidney and which is actually responsible for filtering of blood lies embedded in the renal medulla. More than a million nephrons lie in the renal cortex of the kidney. $85%$ nephrons are situated in the renal cortex and are called cortical nephrons. $15%$ of nephrons lie close to the medulla and are called juxtamedullary nephrons. The nephron is made up of a renal corpuscle, a renal tubule, and a network of capillaries that arises from the small cortical arteries. A network of capillaries called glomerulus and a cup-shaped chamber that surrounds glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule are the main functional units of a nephron. The glomerulus receives impure blood and filters it through its capillaries. The filtered blood is then passed on to a long, convoluted tubule which is further divided into three parts. The loop of Henle, the proximal convoluted tubule, and the distal convoluted tubule are three regions of the long convoluted tubule. These three empties the filtrate into collecting ducts. The collecting ducts together enter the papillae of the renal medulla. From the renal medulla, the urine passes as a fluid containing high sodium content and finally leaves from the kidney through renal papillae. From here it passes through renal calyces, then renal pelvis, and then into the bladder through the ureter.
Note: The kidney makes the body get rid of toxins including urea and excess salts. Urea is a nitrogenous waste product that is primarily produced in the liver. Kidneys also help to maintain the water and electrolyte balance of the body. Blood pressure is also regulated by the kidney by the production of angiotensin. Angiotensin constricts the blood vessels and helps retain sodium and water more in case of low blood pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




