
Explain the internal structure of the leaf.
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: The green, flat structure in a plant body where photosynthesis occurs due to its distinct structure and contains chlorophyll.
Complete answer:
There are three distinct regions of leaf:
- Epidermis
- Mesophyll
- Vascular bundles
Epidermis: It is the outermost layer of the leaf and is present in the lower and upper surfaces. The upper epidermis contains parenchymatous cells, stomata, and chloroplast. The maximum amount of stomata are present at the lower epidermis. A waxy substance is released by the layer known as the cuticle.
Mesophyll cells: It is the middle layer that is made up of two types of cells: palisade and spongy parenchyma. The palisade cells contain chloroplasts and are active in photosynthesis while spongy cells are oval in shape and are arranged irregularly with air spaces.
Vascular Bundles: These are present in scatter form in spongy parenchyma and can be seen in veins and midribs of leaves.
Leaves are the structure that is responsible for photosynthesis, a process that helps in the production of food and to maintain the level of oxygen in the environment. They also maintain the water level as the presence of stomata keeps a check on the rate of transpiration. In many plants, they get a modification for different purposes like in desert plants they convert into thorns to prevent water loss.
Notes:
Difference between dicot and monocot leaves
- Bulliform cells are present in monocots that help in the reduction of the rate of transpiration and are absent in dicots.
- The mesophylls of monocots are not divided into two different layers while in dicot they are made up of palisade and spongy cells.
- The vascular bundles of monocots are conjoint and closed while dicots bundles are collateral and closed.
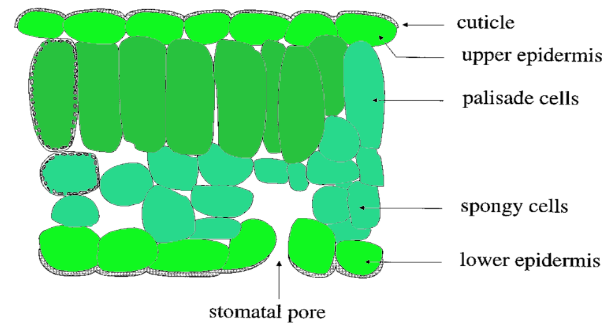
Fig.-Dicot leaf
Complete answer:
There are three distinct regions of leaf:
- Epidermis
- Mesophyll
- Vascular bundles
Epidermis: It is the outermost layer of the leaf and is present in the lower and upper surfaces. The upper epidermis contains parenchymatous cells, stomata, and chloroplast. The maximum amount of stomata are present at the lower epidermis. A waxy substance is released by the layer known as the cuticle.
Mesophyll cells: It is the middle layer that is made up of two types of cells: palisade and spongy parenchyma. The palisade cells contain chloroplasts and are active in photosynthesis while spongy cells are oval in shape and are arranged irregularly with air spaces.
Vascular Bundles: These are present in scatter form in spongy parenchyma and can be seen in veins and midribs of leaves.
Leaves are the structure that is responsible for photosynthesis, a process that helps in the production of food and to maintain the level of oxygen in the environment. They also maintain the water level as the presence of stomata keeps a check on the rate of transpiration. In many plants, they get a modification for different purposes like in desert plants they convert into thorns to prevent water loss.
Notes:
Difference between dicot and monocot leaves
- Bulliform cells are present in monocots that help in the reduction of the rate of transpiration and are absent in dicots.
- The mesophylls of monocots are not divided into two different layers while in dicot they are made up of palisade and spongy cells.
- The vascular bundles of monocots are conjoint and closed while dicots bundles are collateral and closed.

Fig.-Dicot leaf
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




