
Explain the magnetic elements of the earth’s magnetic field.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Earth revolves around sun as well as it rotates around its axis. Due to earth rotation friction between atmosphere and earth results in the origin of the magnetic field.
Complete step by step solution:
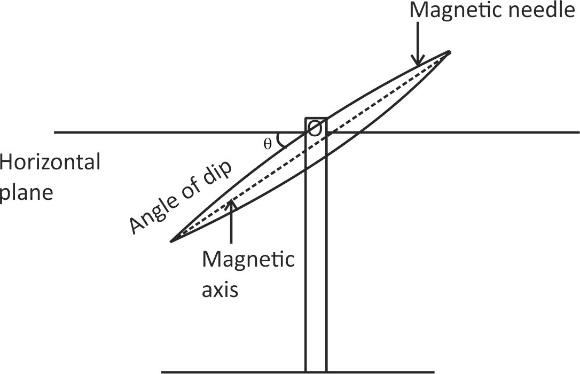
Following are the magnetic elements of earth’s magnetic field.
(i) Magnetic declination (\[{\text{q}}\])
(ii) Magnetic inclination (\[{\text{d}}\])
(iii) Horizontal component (\[{{\text{B}}_{\text{H}}}\])
(iv) Vertical component (\[{{\text{B}}_{\text{V}}}\])
(i) Magnetic declination: The small angle between magnetic axis and geographic axis at a place is defined as magnetic declination at that place it is represented by\[{\text{Q}}\].
(ii) Magnetic inclination: Magnetic dip, dip angle or magnetic inclination is the angle made with the horizontal by the compass needle of a vertically held compass. This angle varies at different locations on the earth surface. Positive values show that the magnetic field of earth is downward into the earth, at the point of measurement. At equator, the magnetic field is parallel to the horizon so there will be zero angle of dip and at the poles, the magnetic field is almost vertical, then dip will be maximum.
Horizontal and vertical component of the Earth’s magnetic field:
There are two components to explain the intensity of the earth’s magnetic field
(iii) Horizontal component: (\[{{\mathbf{B}}_{\mathbf{H}}}\])
\[{B_H}\, = B\,\cos \,\delta \]
(iv) Vertical component: (\[{{\mathbf{B}}_{\mathbf{V}}}\])
${B_V} = \,B\,\sin \,\delta $
Note: All elements help us to connect the all principle of earth’s magnetic field so that we can provide detailed study on earth magnetism. Earth is largely protected from the solar wind, a stream of energetic charged particles. The earth’s magnetic field can be closely approximated by the field of a magnetic dipole positioned near the center of the earth.
Complete step by step solution:

Following are the magnetic elements of earth’s magnetic field.
(i) Magnetic declination (\[{\text{q}}\])
(ii) Magnetic inclination (\[{\text{d}}\])
(iii) Horizontal component (\[{{\text{B}}_{\text{H}}}\])
(iv) Vertical component (\[{{\text{B}}_{\text{V}}}\])
(i) Magnetic declination: The small angle between magnetic axis and geographic axis at a place is defined as magnetic declination at that place it is represented by\[{\text{Q}}\].
(ii) Magnetic inclination: Magnetic dip, dip angle or magnetic inclination is the angle made with the horizontal by the compass needle of a vertically held compass. This angle varies at different locations on the earth surface. Positive values show that the magnetic field of earth is downward into the earth, at the point of measurement. At equator, the magnetic field is parallel to the horizon so there will be zero angle of dip and at the poles, the magnetic field is almost vertical, then dip will be maximum.
Horizontal and vertical component of the Earth’s magnetic field:
There are two components to explain the intensity of the earth’s magnetic field
(iii) Horizontal component: (\[{{\mathbf{B}}_{\mathbf{H}}}\])
\[{B_H}\, = B\,\cos \,\delta \]
(iv) Vertical component: (\[{{\mathbf{B}}_{\mathbf{V}}}\])
${B_V} = \,B\,\sin \,\delta $
Note: All elements help us to connect the all principle of earth’s magnetic field so that we can provide detailed study on earth magnetism. Earth is largely protected from the solar wind, a stream of energetic charged particles. The earth’s magnetic field can be closely approximated by the field of a magnetic dipole positioned near the center of the earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




