
Explain the mechanism of addition of HCN to a carbonyl group in presence of a base.
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: The addition of HCN to a carbonyl group in the presence of base is a nucleophilic addition reaction where the cyanide ion acts as a nucleophile which attacks at the double bond of carbon and oxygen and forms an addition product.
Complete answer:
In carbonyl compounds, the electron density is higher near the oxygen atom as it is more electronegative. This leads to the generation of a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the carbon atom.
Since the carbonyl carbon holds a partial positive charge, it behaves as an electrophile. And the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom is neutralized via the proton of an acidic group.
The reaction of HCN with carbonyl compounds is an example of the nucleophilic addition reaction. The mechanism involved is discussed below:
Step – 1: Attack of nucleophile from HCN to the slightly positive carbon atom.
The base is used as a catalyst and it deprotonates the HCN molecule to produce a stronger nucleophile – cyanide ion.
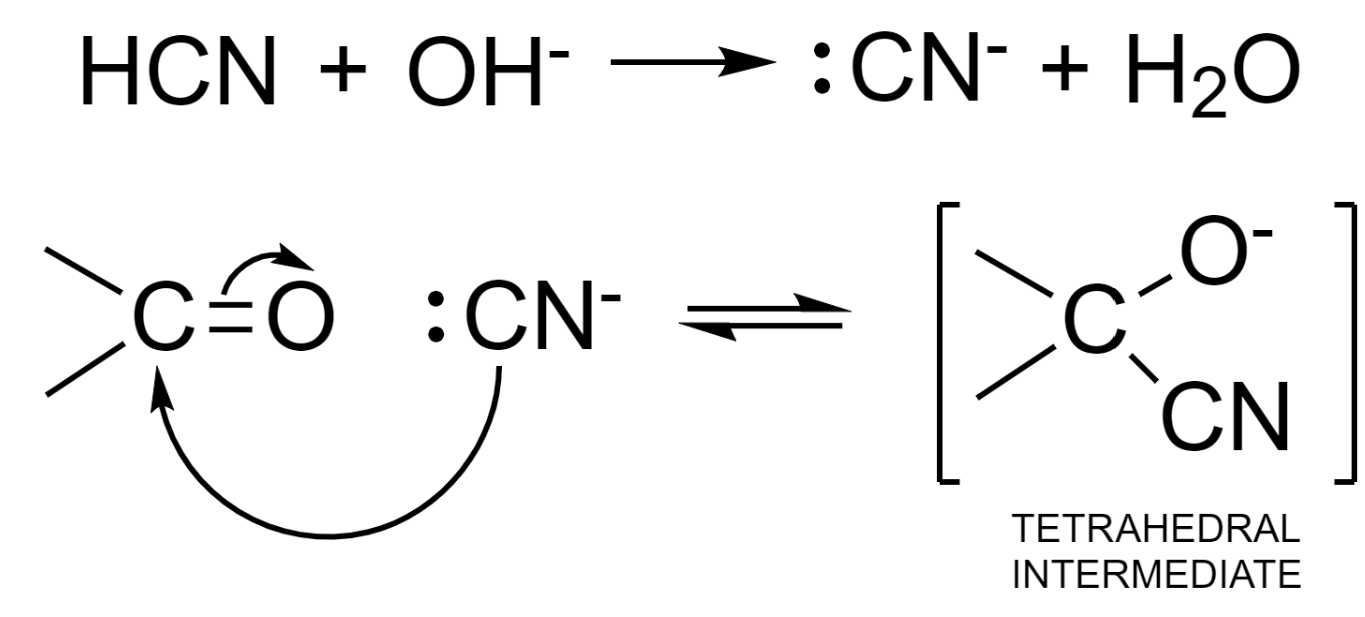
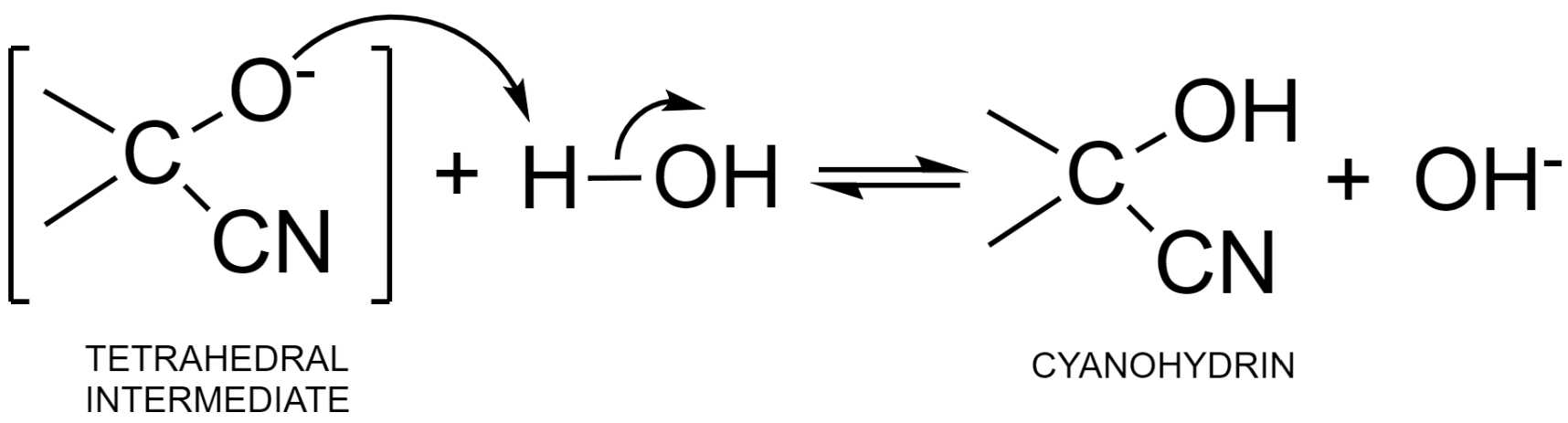
Step – 2: The negative charge in the tetrahedral intermediate is then neutralized by accepting a proton from a water molecule. This results in the formation of cyanohydrin – an additional product and hydroxyl ion. This hydroxyl ion can further be used up in the formation of the nucleophile.
Additional information:
HCN is not directly used in this reaction as it is highly poisonous. The reagent is prepared by adding dilute acid to sodium or potassium cyanide.
Note:
Aldehydes are relatively more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions than ketones. This is because the secondary carbocations formed by ketones are stabilized by the adjacent alkyl groups while the primary carbocations formed by aldehydes are less stable and are, therefore, more susceptible to nucleophilic attacks.
Complete answer:
In carbonyl compounds, the electron density is higher near the oxygen atom as it is more electronegative. This leads to the generation of a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the carbon atom.
Since the carbonyl carbon holds a partial positive charge, it behaves as an electrophile. And the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom is neutralized via the proton of an acidic group.
The reaction of HCN with carbonyl compounds is an example of the nucleophilic addition reaction. The mechanism involved is discussed below:
Step – 1: Attack of nucleophile from HCN to the slightly positive carbon atom.
The base is used as a catalyst and it deprotonates the HCN molecule to produce a stronger nucleophile – cyanide ion.

Step – 2: The negative charge in the tetrahedral intermediate is then neutralized by accepting a proton from a water molecule. This results in the formation of cyanohydrin – an additional product and hydroxyl ion. This hydroxyl ion can further be used up in the formation of the nucleophile.

Additional information:
HCN is not directly used in this reaction as it is highly poisonous. The reagent is prepared by adding dilute acid to sodium or potassium cyanide.
Note:
Aldehydes are relatively more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions than ketones. This is because the secondary carbocations formed by ketones are stabilized by the adjacent alkyl groups while the primary carbocations formed by aldehydes are less stable and are, therefore, more susceptible to nucleophilic attacks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




