
Explain the mechanism of muscle contraction with a diagram?
Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: Muscle contraction takes place when the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide past each other. It is assumed that this process is driven by cross-bridges that extend from the myosin filaments. They cyclically interact with the actin filaments like ATP is hydrolyzed.
Complete answer:
Mechanisms of muscle contraction:
Over time, many different concepts are used to explain the process of muscle contraction. There is a contractile unit of the muscle known as the sarcomere. It is composed of two types of filaments- myosin and actin. These filaments slide over one another during contraction. Also, the length of the A-band remains constant and the length of the I-band changes during muscle contraction. This results in pulling together the Z discs which leads to the contraction of the muscle. ATP is a source of energy for contraction. The ATP molecules help in contraction by binding to the myosin head and getting attached to the actin filament.
Initiation of muscle contraction: The generation of the action potential in the muscle fibers is responsible for the Initiation of contraction of skeletal muscles. These elicit electrical currents leading to the release of calcium ions. These ions then initiate the chemical events of the contractile process. This overall process that controls muscle contraction is called excitation.
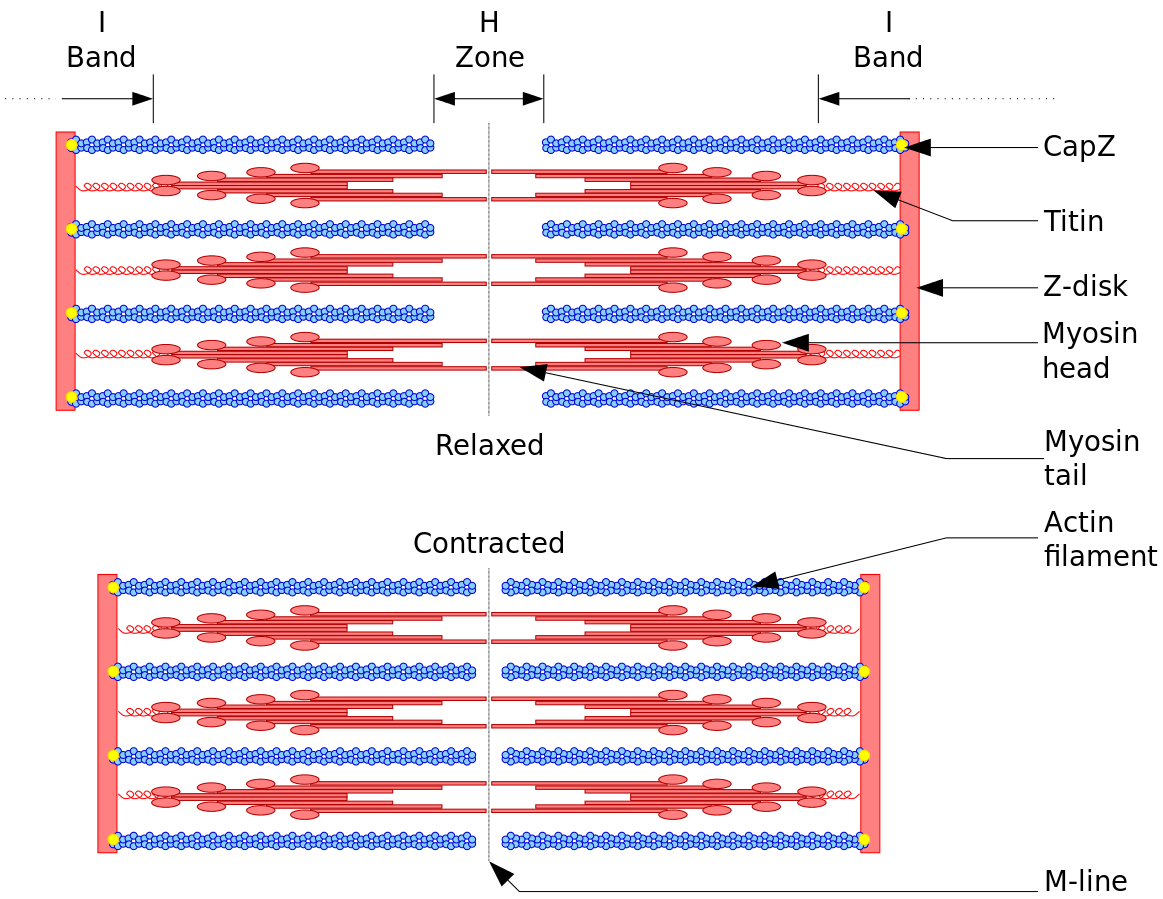
Note: The most widely accepted explanation for contraction of muscle is the sliding filament theory. According to this theory, muscle contraction is a cycle of molecular events. The actin filaments are attached to Z discs (end of a sarcomere). The sliding of the filaments pulls the Z discs closer together resulting in shortening of sarcomere and muscle contraction.
Complete answer:
Mechanisms of muscle contraction:
Over time, many different concepts are used to explain the process of muscle contraction. There is a contractile unit of the muscle known as the sarcomere. It is composed of two types of filaments- myosin and actin. These filaments slide over one another during contraction. Also, the length of the A-band remains constant and the length of the I-band changes during muscle contraction. This results in pulling together the Z discs which leads to the contraction of the muscle. ATP is a source of energy for contraction. The ATP molecules help in contraction by binding to the myosin head and getting attached to the actin filament.
Initiation of muscle contraction: The generation of the action potential in the muscle fibers is responsible for the Initiation of contraction of skeletal muscles. These elicit electrical currents leading to the release of calcium ions. These ions then initiate the chemical events of the contractile process. This overall process that controls muscle contraction is called excitation.

Note: The most widely accepted explanation for contraction of muscle is the sliding filament theory. According to this theory, muscle contraction is a cycle of molecular events. The actin filaments are attached to Z discs (end of a sarcomere). The sliding of the filaments pulls the Z discs closer together resulting in shortening of sarcomere and muscle contraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




