
Explain the mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomata. Sunlight is the main agent to induce the opening and closing of stomata.
Complete answer:
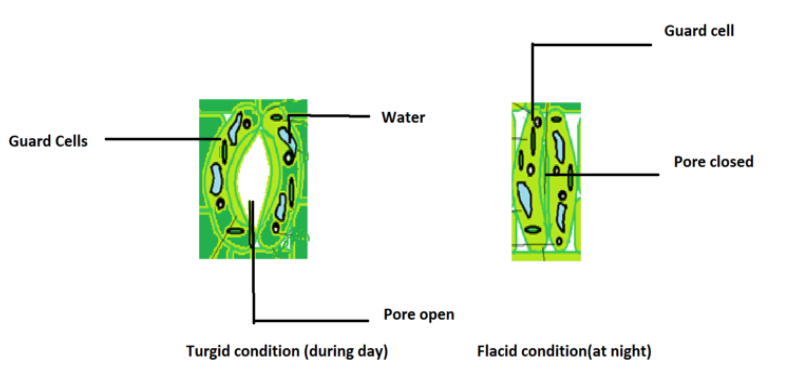
Stomata are the pores present in abundance at the lower epidermis of the leaf. They are also present in the stem. The gaseous exchange and transpiration occur through stomata. The stomata are surrounded by two guard cells which regulate its opening and closing. Stomata open during the day time for gaseous exchange and also release water vapour through transpiration. The opening and closing of stomata is due to the change in turgor pressure of the guard cell.
During the day the roots absorb water due to greater transpiration pull and it is transported to different parts of the plant through xylem. The guard cell on receiving this water swells and becomes turgid. As a result of which the stomatal pore is open.
At night, the roots absorb less water, thus the guard cell becomes flaccid and shrinks. As a result of which stomatal pores closes.
Additional information During the day time plant takes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere for photosynthesis and releases oxygen which we breathe. This gaseous exchange occurs through stomatal pore. At night photosynthesis doesn’t take place. Plants take in oxygen for respiration and release carbon dioxide.
Note: The rate of transpiration is regulated by the guard cells. When the guard cells are turgid, stomata open and when it is flaccid, the stomata closes.
Complete answer:
Stomata are the pores present in abundance at the lower epidermis of the leaf. They are also present in the stem. The gaseous exchange and transpiration occur through stomata. The stomata are surrounded by two guard cells which regulate its opening and closing. Stomata open during the day time for gaseous exchange and also release water vapour through transpiration. The opening and closing of stomata is due to the change in turgor pressure of the guard cell.
During the day the roots absorb water due to greater transpiration pull and it is transported to different parts of the plant through xylem. The guard cell on receiving this water swells and becomes turgid. As a result of which the stomatal pore is open.
At night, the roots absorb less water, thus the guard cell becomes flaccid and shrinks. As a result of which stomatal pores closes.

Additional information During the day time plant takes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere for photosynthesis and releases oxygen which we breathe. This gaseous exchange occurs through stomatal pore. At night photosynthesis doesn’t take place. Plants take in oxygen for respiration and release carbon dioxide.
Note: The rate of transpiration is regulated by the guard cells. When the guard cells are turgid, stomata open and when it is flaccid, the stomata closes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




