
Explain the oxygen cycle in detail.
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: There are few biogeochemical cycles that are essential for the cycling of nutrients in an ecosystem. Some examples of these cycles are the carbon cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, etc. This oxygen cycle involves the movement of oxygen and all the processes are evaluated as either source or sink.
Complete Answer:
The oxygen cycle helps move oxygen through the Atmosphere, the Biosphere, and the Lithosphere.
The Atmosphere is the region of gases that lies just above the Earth’s surface and is one of the largest reservoirs of free oxygen. The Biosphere consists of the sum of all the Earth’s ecosystems and it too has some free oxygen produced from photosynthesis and other life processes carried out by the organisms. The largest reservoir of oxygen is the lithosphere in the bound form present as a part of chemical compounds such as silicates and oxides.
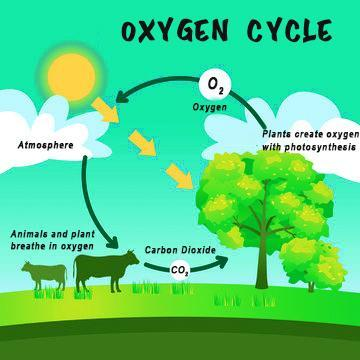
In the atmosphere, oxygen is freed by a process known as photolysis in which high-energy sunlight breaks apart the oxygen-bearing molecules to produce free oxygen. The ozone cycle is also an example of this process. The oxygen molecule is broken down to atomic oxygen by the ultraviolet rays. This free oxygen then recombines with the existing oxygen to form ozone. This part of the oxygen cycle is important as it shields the Earth from most of the harmful UV radiation turning it into harmless heat.
In the biosphere, the main cycles include respiration and photosynthesis which are essential for sustaining life. Respiration is when organisms consume oxygen by breathing in and use it in metabolic processes and then exhale carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis is the process of conversion of light energy from sunlight to chemical energy in the form of food. It is the reverse of respiration and is mainly done by the plants.
The lithosphere fixes oxygen in minerals such as silicates and oxides and the process is mostly automatic. All it takes is for a pure element to come in contact with free oxygen. A portion of the oxygen from the bound minerals is freed by chemical weathering thus releasing free oxygen to the sink.
Note:
- A source is the process that acts as the cause for the production of oxygen. For example, the process of photosynthesis and thus plants act as a source for oxygen.
- A sink is a process that acts as the site of consumption of oxygen. For example, in respiration free oxygen is utilized by the organism and thus the process of respiration is a sink.
- Source and sink vary according to the process involved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




