
Explain the process of receptor mediated endocytosis.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Endocytosis is used to describe various types of active transport that moves particles into a cell by enclosing them in a vesicle which is made out of plasma membrane. Endocytosis is further classified into: pinocytosis, phagocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. There are variations of endocytosis, but all have the same basic process. Firstly, the plasma membrane of the cell invaginates, forming a pocket around the targeted particle or particles. With the help of specialized proteins, the pocket then pinches off, leaving the particle trapped in a newly created vacuole or vesicle inside the cell.
Complete answer:
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a type of endocytosis, where the receptor proteins present on the cell surface are used to capture a specific target molecule. The receptors are transmembrane proteins, clustered in regions of the plasma membrane called coated pits. This name comes from a layer of proteins, called coat proteins, which are found on the cytoplasmic side of the pit.
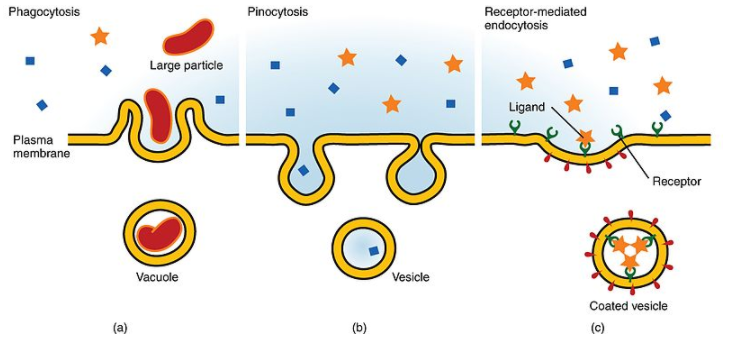
Endocytosis is triggered, when the receptors bind with a specific target molecule, and the receptors and the attached molecules are taken into the cell in a vesicle. By giving the vesicle its rounded shape and helping it bud off from the membrane, the coat proteins participate in this process. Large amounts of molecules that are relatively rare or present in low concentrations in the extracellular fluid are taken up by the receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Although this process is intended to bring useful substances into the cell, other, less friendly particles also may gain entry by the same route. Diphtheria, cholera toxin and flu viruses all use receptor-mediated endocytosis pathways to get entry into cells.
Note: Cells take in certain molecules, like nutrients. But they also need to release other molecules, such as waste products and signaling proteins, to the outside environment. Exocytosis is a type of bulk transport in which materials are transported from inside to the outside of the cell in membrane-bound vesicles which fuse with the plasma membrane.
Complete answer:
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a type of endocytosis, where the receptor proteins present on the cell surface are used to capture a specific target molecule. The receptors are transmembrane proteins, clustered in regions of the plasma membrane called coated pits. This name comes from a layer of proteins, called coat proteins, which are found on the cytoplasmic side of the pit.

Endocytosis is triggered, when the receptors bind with a specific target molecule, and the receptors and the attached molecules are taken into the cell in a vesicle. By giving the vesicle its rounded shape and helping it bud off from the membrane, the coat proteins participate in this process. Large amounts of molecules that are relatively rare or present in low concentrations in the extracellular fluid are taken up by the receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Although this process is intended to bring useful substances into the cell, other, less friendly particles also may gain entry by the same route. Diphtheria, cholera toxin and flu viruses all use receptor-mediated endocytosis pathways to get entry into cells.
Note: Cells take in certain molecules, like nutrients. But they also need to release other molecules, such as waste products and signaling proteins, to the outside environment. Exocytosis is a type of bulk transport in which materials are transported from inside to the outside of the cell in membrane-bound vesicles which fuse with the plasma membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




