
Explain the stages of germination with the help of diagrams.
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Germination is defined as a process by which a plant develops from the seed and develops of its parents kind.
The five steps mainly occur in seed germination. It is a very crucial event for the production of future generations.
Complete answer:
Imbibition:-
It is the process by which seed absorbs water. It is the first process in seed germination. It is a type of diffusion. The seed volume increased. The water uptake is by the dry seed. The non dormant seed takes up water. When seeds take water it starts to develop its radical.
Respiration:- when oxygen is supplied to the seed it starts to grow. So the seeds respire for the exchange of gases and start to grow. Seed coat ruptures now.
Light:- seeds take up light for their further growth. The radicle that is root grows away from light and the plumule that is shot starts growing towards light. The two conditions are called negative phototropism and positive phototropism respectively.
Growth regulators:- when seeds are being provided with growth regulators such as auxin and cytokinin and further grows. The seed expands and becomes a rich source of food.
Embryo development:- the seed now converts into embryo. Embryo is the future generation of the plant. Now the germination of seed gets completed.
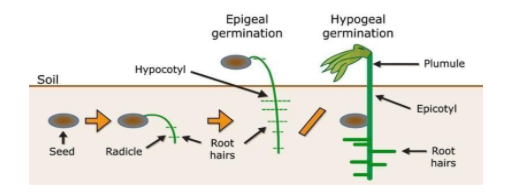
Note:
> When germination takes place above the ground it is termed as epigeal germination.
> When germination takes place below the ground it is termed as hypogeal germination.
> The region of embryo above the cotyledon is called epicotyl.
> The region of embryo below cotyledon is called hypocotyl.
The five steps mainly occur in seed germination. It is a very crucial event for the production of future generations.
Complete answer:
Imbibition:-
It is the process by which seed absorbs water. It is the first process in seed germination. It is a type of diffusion. The seed volume increased. The water uptake is by the dry seed. The non dormant seed takes up water. When seeds take water it starts to develop its radical.
Respiration:- when oxygen is supplied to the seed it starts to grow. So the seeds respire for the exchange of gases and start to grow. Seed coat ruptures now.
Light:- seeds take up light for their further growth. The radicle that is root grows away from light and the plumule that is shot starts growing towards light. The two conditions are called negative phototropism and positive phototropism respectively.
Growth regulators:- when seeds are being provided with growth regulators such as auxin and cytokinin and further grows. The seed expands and becomes a rich source of food.
Embryo development:- the seed now converts into embryo. Embryo is the future generation of the plant. Now the germination of seed gets completed.

Note:
> When germination takes place above the ground it is termed as epigeal germination.
> When germination takes place below the ground it is termed as hypogeal germination.
> The region of embryo above the cotyledon is called epicotyl.
> The region of embryo below cotyledon is called hypocotyl.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




