
Explain the structure and function of neurons.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Neurons are the basic units of the brain and nervous system, the cells responsible for processing sensory feedback from the outside world, for transmitting motor instructions to our muscles, and for converting and relaying electrical signals at any phase in between. Neurons are also called neurons or nerve cells.
Complete answer:
The building blocks of the nervous system are neurons. To various parts of the body, they receive and transmit signals. In both physical and electrical types, this is carried out. There are several distinct types of neurons that promote information transmission.
Sensory neurons bring data to the brain from the sensory receptor cells that are found in the body. Motor neurons, on the other hand, relay information from the brain to the muscles. Information between various neurons in the body is transmitted by the interneurons.
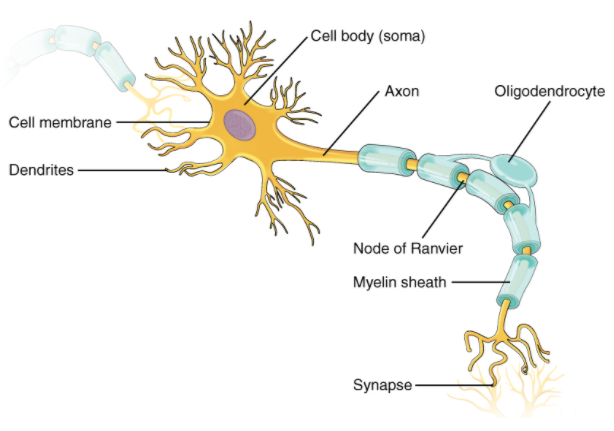
Structure of Neuron
Depending on its function and position, a neuron varies in type and duration. There are three common components of all neurons: dendrites, cell body and axon.
Neuron parts
The various components of a neuron are below:
Dendrites:These are branch-like systems that receive signals from other neurons and allow messages to be transmitted to the body of the cell.
Cell Body : With a nucleus, Golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and other components, each neuron has a cell body.
Axon:Axon is a structure similar to a tube that brings electrical impulse to the axon terminals from the cell body that transfers the impulse to another neuron.
Synapse: It is the chemical junction of one neuron's terminal with the dendrites of another neuron.
Types Of Neuron
Three different types of neurons exist:
Sensory Neurons:The sensory neurons translate signals into corresponding internal stimuli from the external environment. The sensory inputs activate the sensory neurons and bring to the brain and spinal cord sensory information. In structure, they are pseudo unipolar.
Motor Neuron:sThese are multipolar and are located outside the central nervous system in the central nervous system that expands their axons. This is the most prevalent type of neuron and transmits information to the muscles of the body from the brain.
Interneurons: In form, they are multipolar. Their axons only bind to the sensory and motor neurons nearby. Assistance in the passage of signals between two neurons.
The Functions of Neurons
A neuron's major roles are:
Chemical Synapse:In chemical synapses, through a distance present between two neurons known as the synapse, the action potential affects other neurons. The potential for action is carried along the axon to a postsynaptic ending that initiates the release of neurotransmitters known as chemical messengers. The postsynaptic neurons that contain an action potential of their own are excited by these neurotransmitters.
Electrical Synapse :It results in an electrical synapse when two neurons are connected by a gap junction. These differences include ion channels that assist in a positive electrical signal being directly transmitted. These are much quicker than synapses of chemicals.
Note:A single neuron can not do very much on its own and the role of the nervous system relies on groups of neurons working together. To stimulate or inhibit their behaviour, individual neurons connect to other neurons, forming circuits that can process incoming information and perform a response. Neuronal circuits, consisting of just a few neurons, can be very simple, or they can include more complex neuronal networks.
Complete answer:
The building blocks of the nervous system are neurons. To various parts of the body, they receive and transmit signals. In both physical and electrical types, this is carried out. There are several distinct types of neurons that promote information transmission.
Sensory neurons bring data to the brain from the sensory receptor cells that are found in the body. Motor neurons, on the other hand, relay information from the brain to the muscles. Information between various neurons in the body is transmitted by the interneurons.
Structure of Neuron
Depending on its function and position, a neuron varies in type and duration. There are three common components of all neurons: dendrites, cell body and axon.
Neuron parts
The various components of a neuron are below:
Dendrites:These are branch-like systems that receive signals from other neurons and allow messages to be transmitted to the body of the cell.
Cell Body : With a nucleus, Golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and other components, each neuron has a cell body.
Axon:Axon is a structure similar to a tube that brings electrical impulse to the axon terminals from the cell body that transfers the impulse to another neuron.
Synapse: It is the chemical junction of one neuron's terminal with the dendrites of another neuron.
Types Of Neuron
Three different types of neurons exist:
Sensory Neurons:The sensory neurons translate signals into corresponding internal stimuli from the external environment. The sensory inputs activate the sensory neurons and bring to the brain and spinal cord sensory information. In structure, they are pseudo unipolar.
Motor Neuron:sThese are multipolar and are located outside the central nervous system in the central nervous system that expands their axons. This is the most prevalent type of neuron and transmits information to the muscles of the body from the brain.
Interneurons: In form, they are multipolar. Their axons only bind to the sensory and motor neurons nearby. Assistance in the passage of signals between two neurons.
The Functions of Neurons
A neuron's major roles are:
Chemical Synapse:In chemical synapses, through a distance present between two neurons known as the synapse, the action potential affects other neurons. The potential for action is carried along the axon to a postsynaptic ending that initiates the release of neurotransmitters known as chemical messengers. The postsynaptic neurons that contain an action potential of their own are excited by these neurotransmitters.
Electrical Synapse :It results in an electrical synapse when two neurons are connected by a gap junction. These differences include ion channels that assist in a positive electrical signal being directly transmitted. These are much quicker than synapses of chemicals.

Note:A single neuron can not do very much on its own and the role of the nervous system relies on groups of neurons working together. To stimulate or inhibit their behaviour, individual neurons connect to other neurons, forming circuits that can process incoming information and perform a response. Neuronal circuits, consisting of just a few neurons, can be very simple, or they can include more complex neuronal networks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




