
Explain the structure of T- even bacteriophages.
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: Bacteriophages are a type of viruses which complete their life cycle in a bacterial host. Viruses are microscopic parasites and contagious sellers with residing and non-living characteristics. These viruses can infect plants, animals, and different microorganisms.
Complete answer:
Viruses are non-cellular, microscopic, and infectious marketers that stay by way of relying upon the host cell They incorporate genetic material as RNA or DNA and proteins; they invade and reproduce through using organisms, plants, and animal cell organelles as they lack the required cell material. Certain viruses that infect microorganisms are known as Bacteriophage or phage i.e. microorganism eater.
Bacteriophages are the viruses that parasitize them and reproduce inside them. Some of their traits are:
a) These Bacteriophages like other viruses additionally consist of a core of genetic cloth that is surrounded by a capsid.
b) Genetic fabric of bacteriophage can either be DNA or RNA in accordance to their common composition.
c)After infecting bacterial host cells they hijack the cellular manager of the host cell and stop them from producing bacterial factors and force them to produce viral components.
d) They typically carry about the lysis of bacterial host cells.
Structural composition of Bacteriophage:
Typical bacteriophage composed of a polyhedral head, a quick collar, and a helical tail. The Head is hexagonal and consists of 2000 capsomeres with genetic cloth double-stranded DNA or single-stranded RNA present in the head.
Collar and whiskers of phage assist to attach the six lengthy tail fibres to the phage particle all through virus assembly.
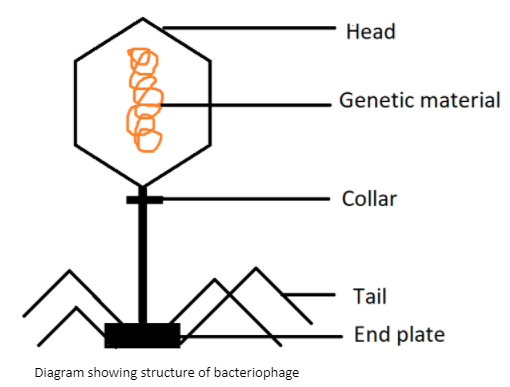
The tail is cylindrical and is composed of a central hole tube which is surrounded by a contractile sheath (protein) with annular rings and the distal quit of the tail consists of a basal plate that has tail fibres.
Note: Bacteriophage replicates and also multiplies inside the bacterial cell with the help of either a lytic or lysogenic cycle. These Bacteriophages are highly specific for their target bacteria, and it is essential against multi-resistant pathogens.
Complete answer:
Viruses are non-cellular, microscopic, and infectious marketers that stay by way of relying upon the host cell They incorporate genetic material as RNA or DNA and proteins; they invade and reproduce through using organisms, plants, and animal cell organelles as they lack the required cell material. Certain viruses that infect microorganisms are known as Bacteriophage or phage i.e. microorganism eater.
Bacteriophages are the viruses that parasitize them and reproduce inside them. Some of their traits are:
a) These Bacteriophages like other viruses additionally consist of a core of genetic cloth that is surrounded by a capsid.
b) Genetic fabric of bacteriophage can either be DNA or RNA in accordance to their common composition.
c)After infecting bacterial host cells they hijack the cellular manager of the host cell and stop them from producing bacterial factors and force them to produce viral components.
d) They typically carry about the lysis of bacterial host cells.
Structural composition of Bacteriophage:
Typical bacteriophage composed of a polyhedral head, a quick collar, and a helical tail. The Head is hexagonal and consists of 2000 capsomeres with genetic cloth double-stranded DNA or single-stranded RNA present in the head.
Collar and whiskers of phage assist to attach the six lengthy tail fibres to the phage particle all through virus assembly.

The tail is cylindrical and is composed of a central hole tube which is surrounded by a contractile sheath (protein) with annular rings and the distal quit of the tail consists of a basal plate that has tail fibres.
Note: Bacteriophage replicates and also multiplies inside the bacterial cell with the help of either a lytic or lysogenic cycle. These Bacteriophages are highly specific for their target bacteria, and it is essential against multi-resistant pathogens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




