
Explain with a well labelled diagram different regions of root and also explain the structure of root hair?
Answer
522.5k+ views
Hint: The regions of roots are divided into three parts on the basis of activities of cells in different regions: Zone of cell division, zone of elongation and zone of maturation.
Complete answer:
As we know, the regions of roots are divided into: Zone of cell division, zone of elongation and zone of maturation. In most vascular plants two types of roots are found: primary roots and secondary roots.Primary root grows downwards without giving branches. Secondary roots grow horizontally and downwards branches to the side.
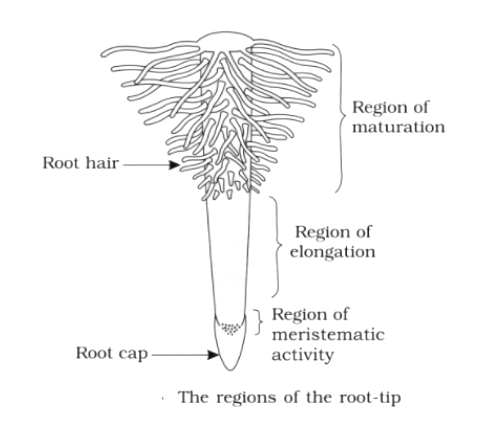
In the diagram we can easily see there are three regions and each has different activities. It starts from the tip and moving in upward direction
- Zone of active cell division (meristematic area) where cells divide and increase in numbers
- Zone of cell elongation, where size of cell increased and converted into mature cells
- Zone of maturation, where matured cells are stored and in this zone there are also root hairs which absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Structure of root hair: Root hairs are thin and long extensions of the epidermal cells on the surface of the root in the zone of maturation. The tiny root hairs have a very large absorptive surface area, which allows absorption of large quantities of water.
Note: The apical part of the root is covered by the root cap which protects the apex of the root. The root cap secretes mucilage for lubrication for the root to make way through the soil. As the root grows into the soil, the root cap degrades and renews.
Complete answer:
As we know, the regions of roots are divided into: Zone of cell division, zone of elongation and zone of maturation. In most vascular plants two types of roots are found: primary roots and secondary roots.Primary root grows downwards without giving branches. Secondary roots grow horizontally and downwards branches to the side.

In the diagram we can easily see there are three regions and each has different activities. It starts from the tip and moving in upward direction
- Zone of active cell division (meristematic area) where cells divide and increase in numbers
- Zone of cell elongation, where size of cell increased and converted into mature cells
- Zone of maturation, where matured cells are stored and in this zone there are also root hairs which absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Structure of root hair: Root hairs are thin and long extensions of the epidermal cells on the surface of the root in the zone of maturation. The tiny root hairs have a very large absorptive surface area, which allows absorption of large quantities of water.
Note: The apical part of the root is covered by the root cap which protects the apex of the root. The root cap secretes mucilage for lubrication for the root to make way through the soil. As the root grows into the soil, the root cap degrades and renews.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




